Routing
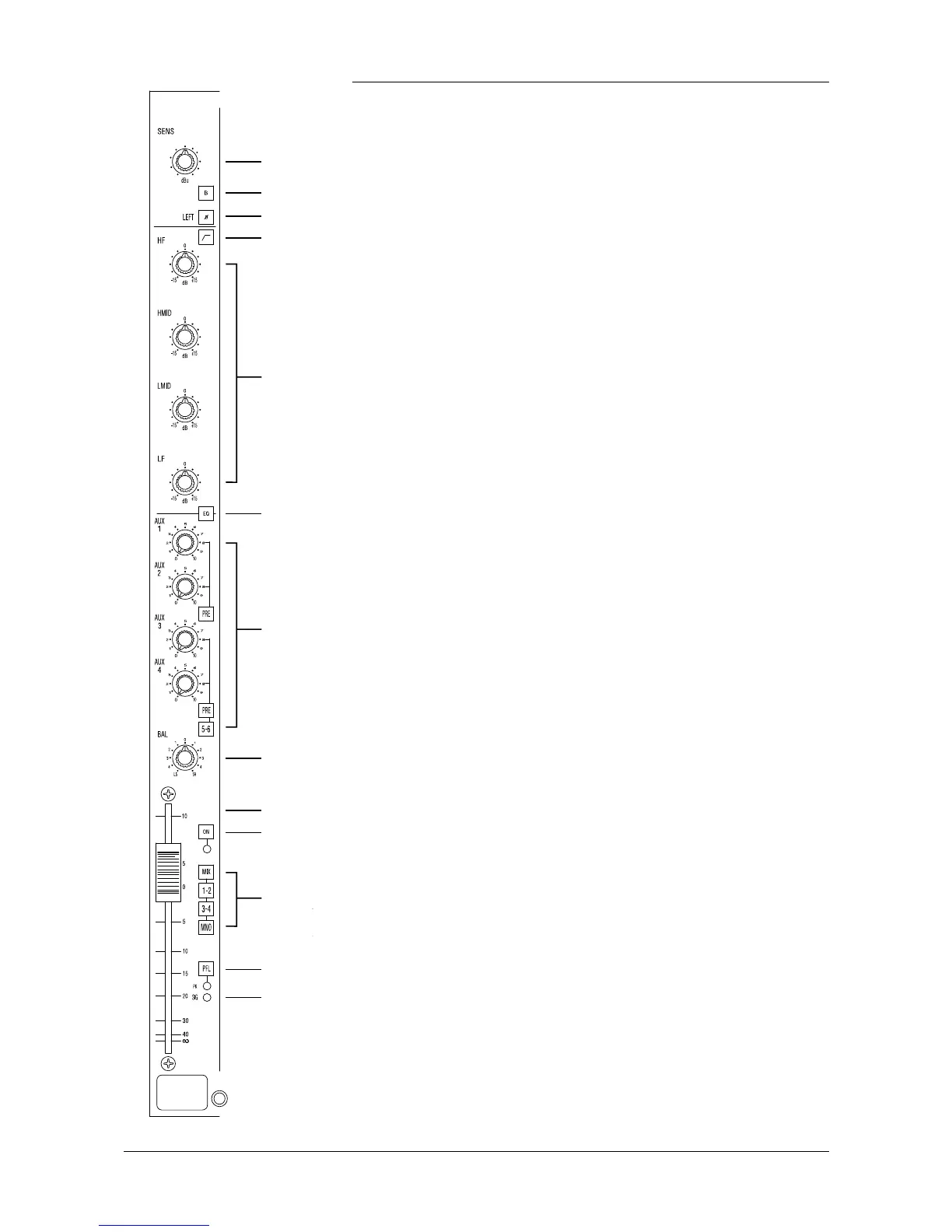
8 The BAL (Balance) control determines the relative levels of the L and R signals.
In the centre position its gain is unity. Turning it fully clockwise increases the right
signal by 4.5dB, and reduces the left signal to zero. Full anticlockwise rotation has
the opposite effect. Balance left biases the signal to odd numbered busses, balance
right to even busses.
9 The long-travel FADER has 10dB of gain and is the main level control for the
channel, enabling rapid and accurate control of the channel output level. When
mixing, you will get optimum headroom and signal-to-noise ratios by keeping the
fader at about the unity gain (0) mark. Avoid running the input sensitivity too high,
and the fader resultingly low, since this gives very little headroom. Similarly,
running the input sensitivity very low, and the fader fully up (10dB of gain) will
increase noise levels, and does not allow any increase in gain on the fader should
the source signal drop unexpectedly.
10 The ON switch enables the post EQ, post-Insert channel signal path: when
released, all post-fade Auxiliary Sends and all routing outputs are muted. We
recommend that you switch all unused channels OFF to prevent unwanted noise
being added to any parts of the mix.
11 The signal is sent to the stereo mix bus, mono bus and 4 group busses using
the MIX, MNO, 1-2 & 3-4 switches respectively, subject to the position of the
BAL control (see above).
The mono bus is fed directly from the post-fader signal.
12 The PFL switch feeds a mono sum of the stereo source pre-fade signal into
the monitor/phones system where it replaces the selected monitor source.
The red LED illuminates when the PFL switch is pressed, and also serves as a PEAK
(PK) indicator, monitoring the left and right signals post-EQ, pre-fader and
illuminates when either channel reaches 4dB before clipping.
13 The green SIG LED monitors the left and right signals at the input amp and
illuminates when the signal at either point exceeds -30dBu.
-5
+5
+10
-10
-15
-20
0
1
2
3
4
6
8
9
10
11
12
13
5
7
4.6 December 1994 Functional Descriptions

 Loading...
Loading...











