TURBO CHARGER SYSTEM 5–3
INTRODUCTION
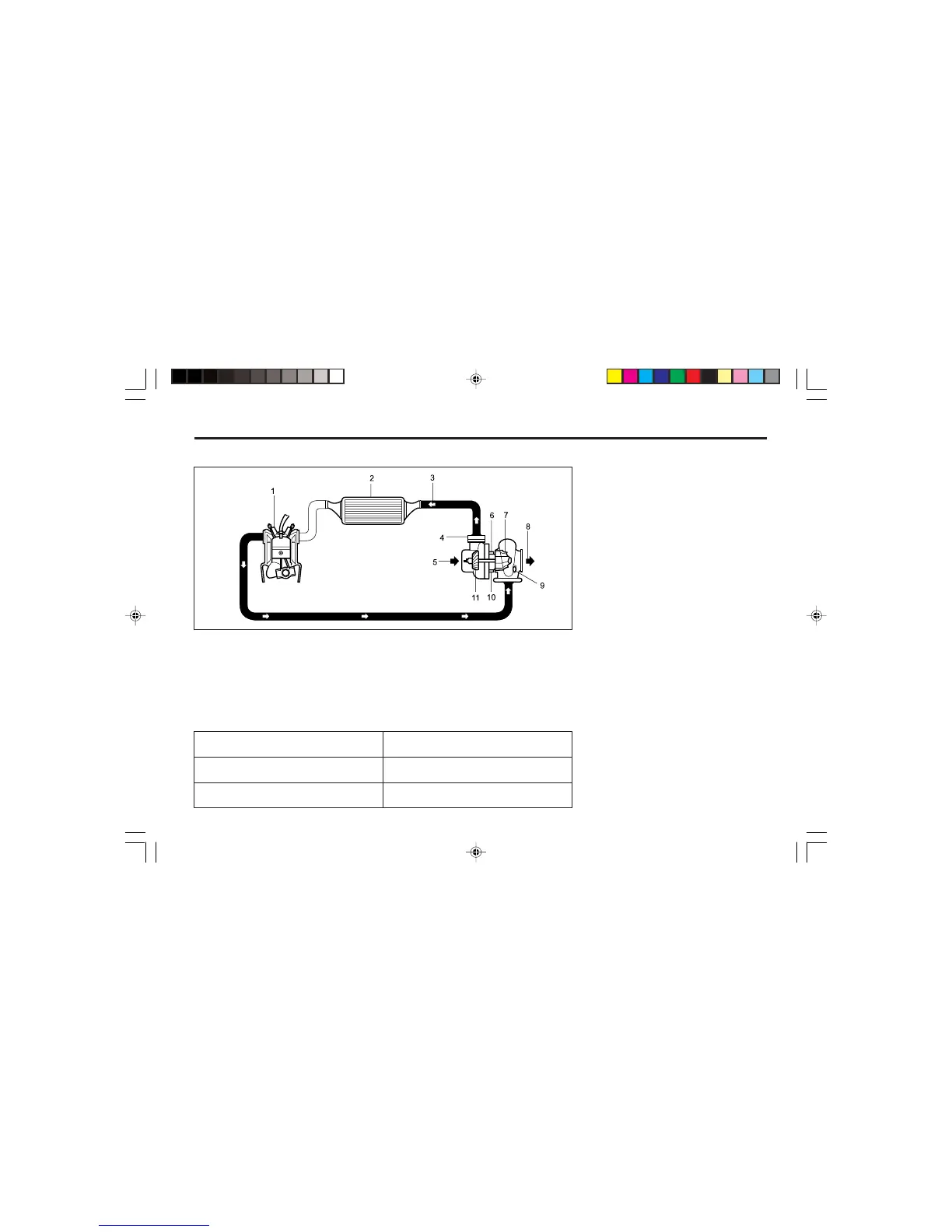
1. Cylinder
2. Intercooler
3. Compressed air flow
4. Compressor
5. Air inlet
6. Turbocharger oil inlet
7. Turbine wheel
8. Exhaust gas outlet
9. Bypass valve
10. Turbocharger oil outlet
11. Compressor wheel
What is the Turbocharger?
Turbochargers are based on gas turbine
engine technology, but operate under con-
siderably greater pressure.
The turbocharger consists of two turbo el-
ements, a turbine and a compressor, both
of which are driven from the main center
shaft. The turbine rotates between
50,000~160,000 spins per minute and uses
the energy of the exhaust gas to drive the
compressor. The compressor, in turn, draws
in fresh air which it supplies to the cylinders
in compressed from.
As more fuel is drawn into the engine, out-
put performance is boosted between 15-
30% in comparison to a non-turbocharged
engine.
Advantages of a Turbocharger
Turbocharger helps the engine operate more
smoothly and with greater efficiency.
• Increase specific power
• Compensate for power loss at altitude
• Reduce emissions and noise
Specification
Model
Max. torque (N
.
m/rpm)
Max. output (ps/rpm)
D29ST (Diesel)
256 / 2100
120 / 4000
K140_RHD_EN_05.p65 2004-11-11, ¿ÀÈÄ 4:083

 Loading...
Loading...











