SAMPLE ANALYSIS
2-26 Sysmex KX-21 Operator’s Manual -- Revised October 1998
6. LIMITATIONS
6.1 Cell Count Parameters
Some abnormal samples may give incorrect results by automated cell counting methods. The
following table shows examples of specific specimens that could cause errors.
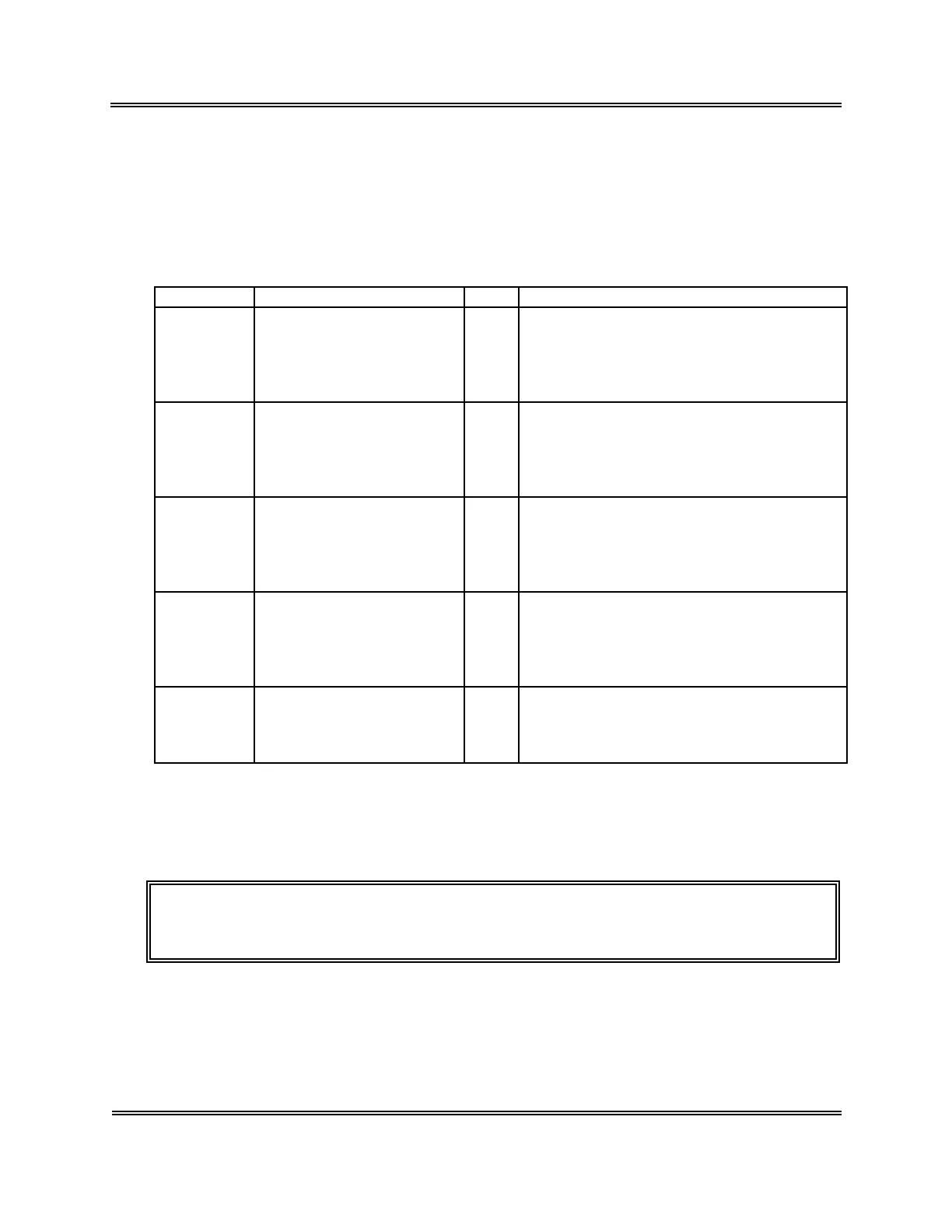
Parameter Specimen Error Possible Indication of Error
WBC Cold Agglutinin
Platelet aggregation
Erythroblastosis
Nucleated RBC
Cryoglobulins
(+)
(+)
(+)
(+)
(+)
↑MCV, ↓HCT, red cell clumping on smear
Platelet aggregates on smear
Erythroblasts on smear
NRBC on smear
RBC Cold Agglutinin
Severe Microcytosis
Fragmented RBC
Leukocytosis
(>100,000/µL)
(-)
(-)
(-)
(+)
↑MCV, ↓HCT, red cell clumping on smear
Elevation of WBC
HGB Leukocytosis
(>100,000/µL)
Lipemia
Abnormal Protein
(+)
(+)
(+)
Elevation of WBC
↑MCHC, “milky” appearance of plasma
↑MCHC, Lysed Hgb/WBC sample turns
cloudy
HCT Cold Agglutinin
Leukocytosis
(>100,000/µL)
Abnormal Red Cell Fragility
Spherocytosis
(-)
(+)
(?)
(?)
↑MCV, ↓HCT, red cell clumping on smear
Elevation of WBC
↓MCV, spherocytes on smear
PLT Pseudothrombocytopenia
Platelet Aggregation
Increased Microcytosis
Megalocytic Platelets
(-)
(-)
(+)
(-)
Platelet Satellitism on smear
Platelet Aggregation on smear
↓MCV
(+): Instrument count is affected by an increase in the result.
(-): Instrument count is affected by a decrease in the result.
(?): Instrument count is affected by either an increase or decrease in the result which is
sample dependent.
CAUTION: • WBC results may be elevated erroneously due to unlysed red cells in
patients with hemoglobinopathies, severe liver disease or in neonates.
 Loading...
Loading...