Analyze Waveform Data
The FF T feature provides fou r windows. Each is a trade-off between frequency resolution and magnitude accuracy. W hat you
want to measure and your source signal characteristics help determine which window to use. Use the following guidelines
to select the best window.
Description Window
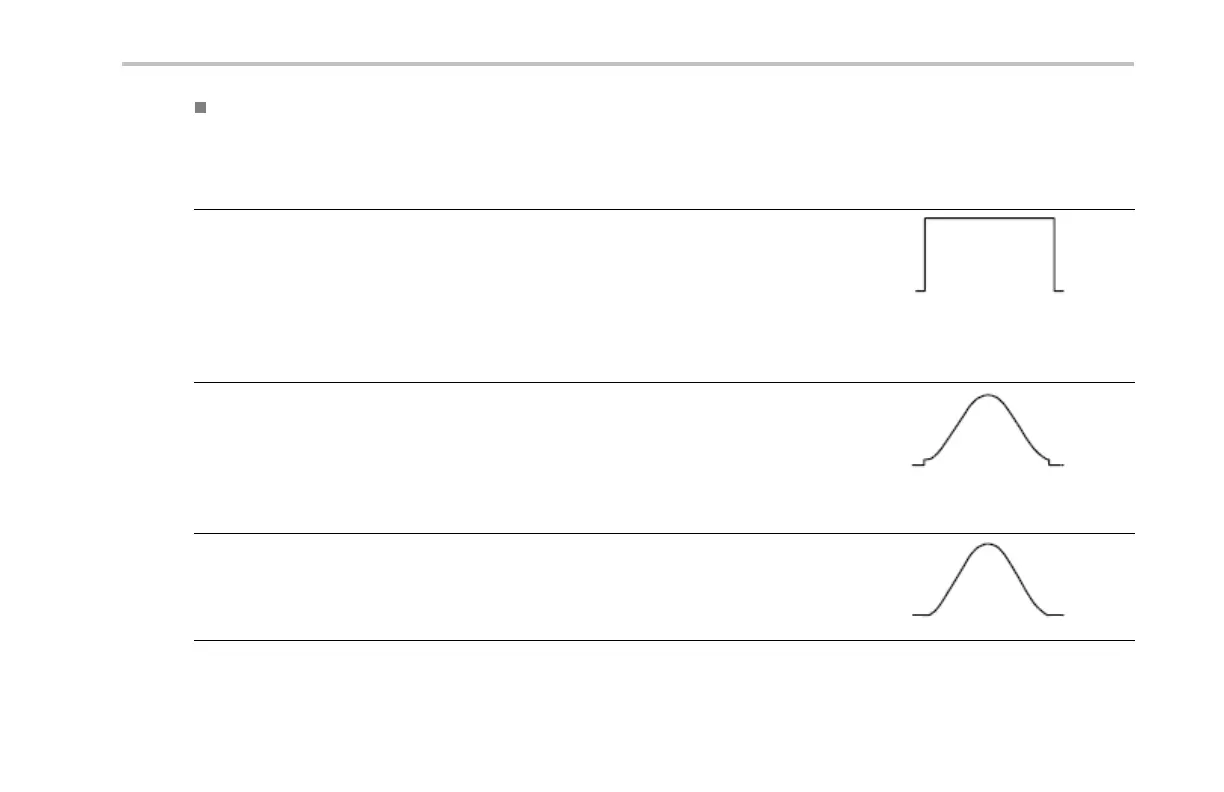
Rectangular
This is the best type of window for resolving fre quencies that are very close to the same va lue but
worst for accu rately measuring the amplitude of those frequencies. It is the best type for measuring
the frequency spectrum of nonrepetitive signals and measuring frequency components near DC.
Use Rectangular for measuring transients or bursts where the signal level before and after the
event are nearly equal. Also, use this window for equal-amplitude sine waves with frequencies that
are very close and for broadband random noise with a relatively slow varying spectrum.
Hamming
This is a very good window for resolving frequencies that are very close to the sam e value with
somewhat improved am plitude accuracy over the rectangular wind ow. It has a slightly better
frequency resolution than the Hanning.
Use H amming for measuring sine, periodic, and narrow band random noise. This window works
on transients or bursts where the signal levels before and after the event are significantly different.
Hanning
This is a very good window for measuring amp litude accuracy but less so for resolving frequencies.
Use Hanning for measuring sine, periodic, and narrow band random noise. This window works o n
transients or bursts w here the signal levels before and after the event are significantly different.
MSO4000 and DPO4000 Series Oscilloscopes User Manual 219

 Loading...
Loading...