Chapter 3: Linear Functions Section 1: Slope with Grid
Topics in Algebra 1 © 2001 Texas Instruments Teacher Notes 3-6
Linear Functions: Slope with Grid Teacher Notes
Objectives
•
To impose a grid on a line to quantify the steepness of a line.
•
To introduce slope as the ratio of the vertical change divided by the horizontal change.
•
To illustrate the slope characteristics of lines as positive, zero, negative, or undefined (no
slope).
•
To associate the terms with the appropriate graph of a line: increasing, horizontal,
decreasing, or vertical.
•
To observe that the slope of a straight line is a constant.
Math Highlights
This section defines slope as the steepness of a line. It begins with a bike riding along a
piecewise linear path. Students see the definition of slope as a ratio:
Slope =
m
=
vertical change
horizontal change
=
rise
run
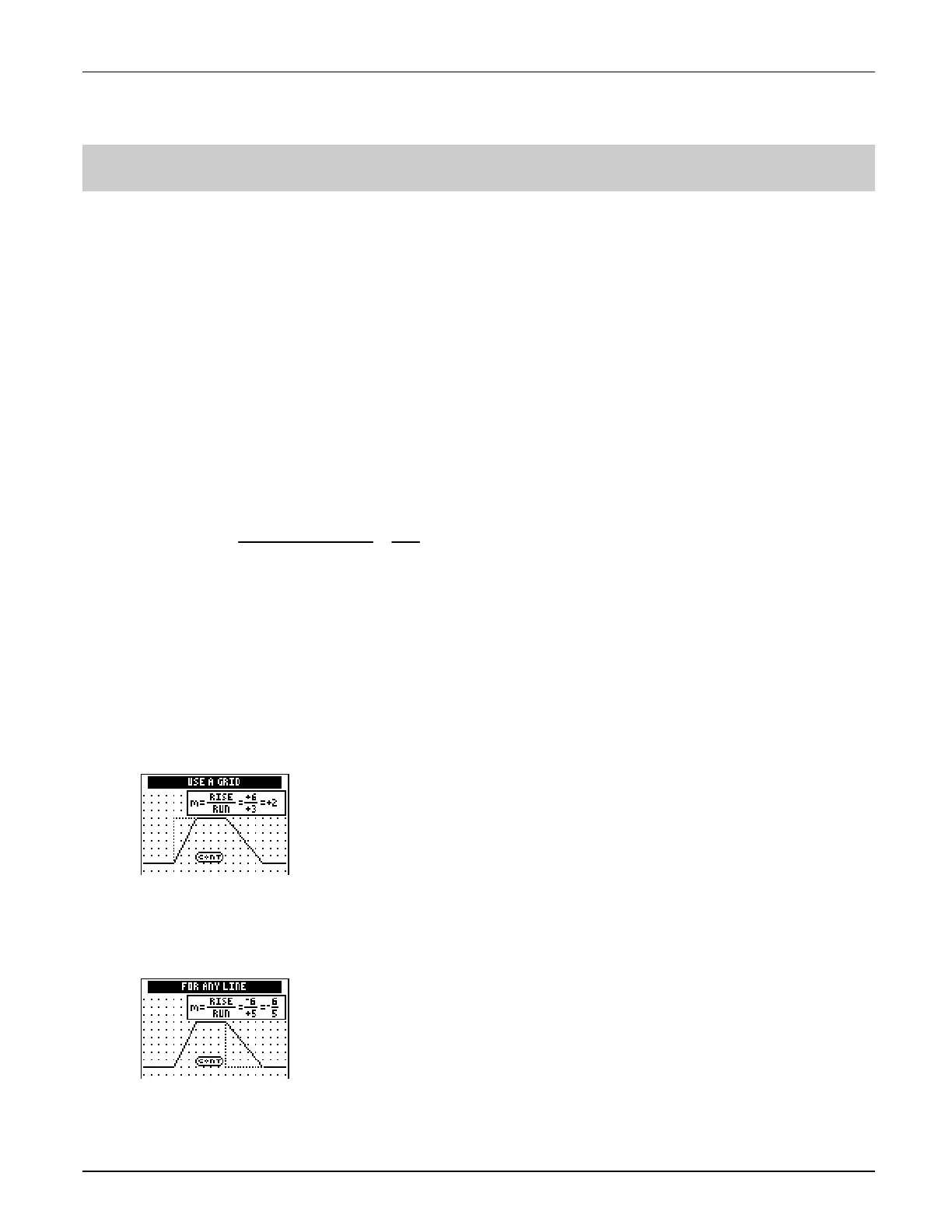
A grid is imposed on the bike path to help illustrate how students can quantify the slope of each
line segment. Next, lines with positive, zero, negative, and no slope are illustrated.
Common Student Errors
•
Students may have difficulties counting the
spaces
between grid points; therefore, they may
count the grid points instead of the spaces. For example, students who count grid points may
think that the slope shown on the screen below is 7
à
4 instead of 6
à
3. Using a Geoboard or
grid paper, redraw the line segment to help these students count the distance between the
grid points rather than the points themselves.
•
In the screen below, the rise/run of the fourth segment is calculated as
M
6
à
5. For some
students, associating “down 6 units, or
M
6” with the word
rise
can be confusing. The use of
the terms
vertical change
or
horizontal change
helps students understand that
change
could
be up or down, right or left.

 Loading...
Loading...











