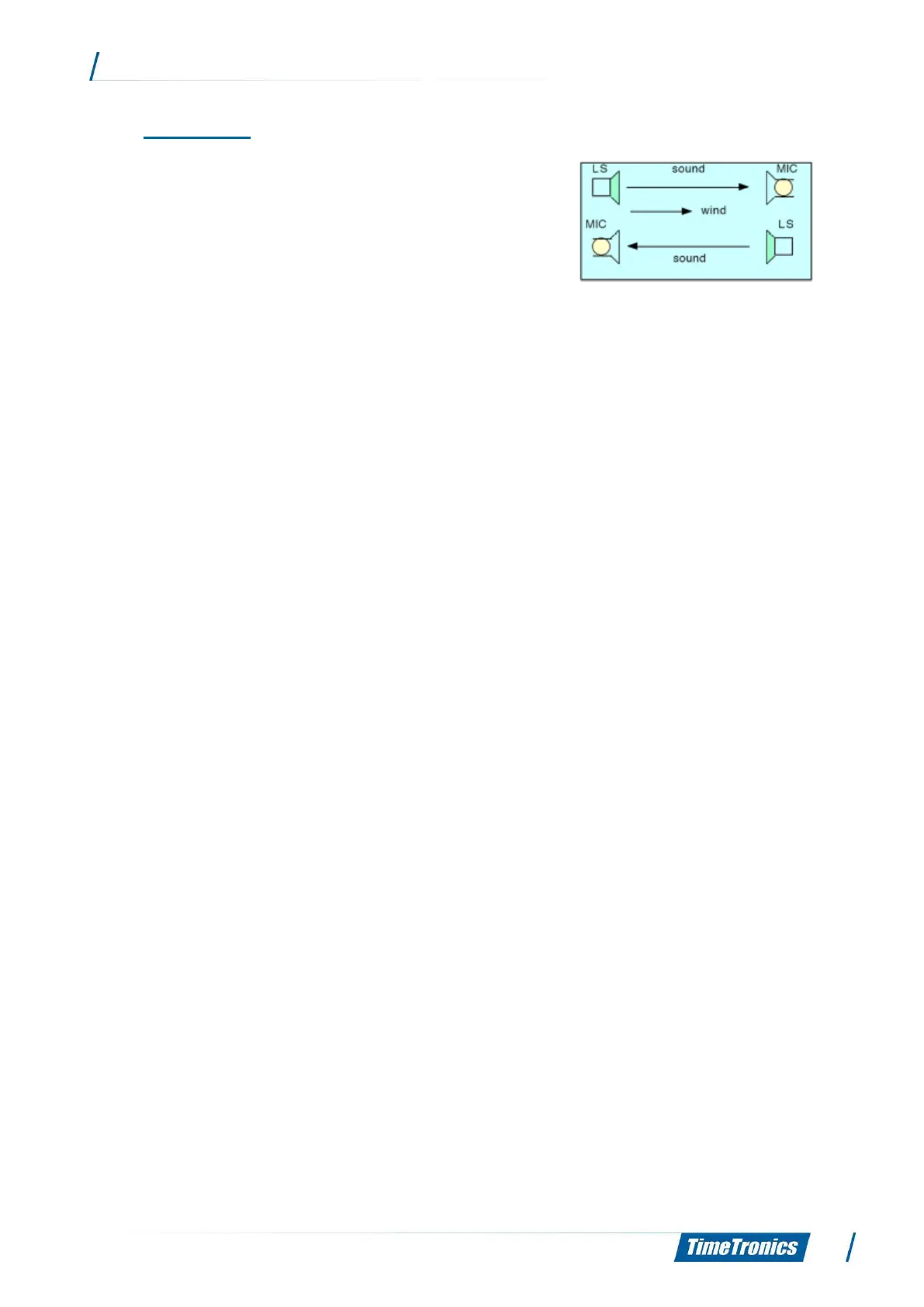
2. Principle
A sonic wave is sent via from a minuscule loudspeaker to a
tiny microphone. As is generally known, the speed of sound
approximately measures 341 m/s., which is directly related
to the medium of surrounding air.
In case this medium would start moving, the sound, which “drifts“ with the wind, will arrive at
the MIC a little sooner than the sound, which has to travel against the wind.
By measuring and registering the difference in speed between the sonic waves, which are
travelling along with the wind, and the ones, which are travelling against it, we can very
accurately determine the wind velocity.
Do bear in mind that any material whatsoever does not impede the free space between the LS
and the MIC.
 Loading...
Loading...