149
The T-1 Notebook : Reference & Guide
148
The T-1 Notebook : Reference & Guide
NOTESNOTES
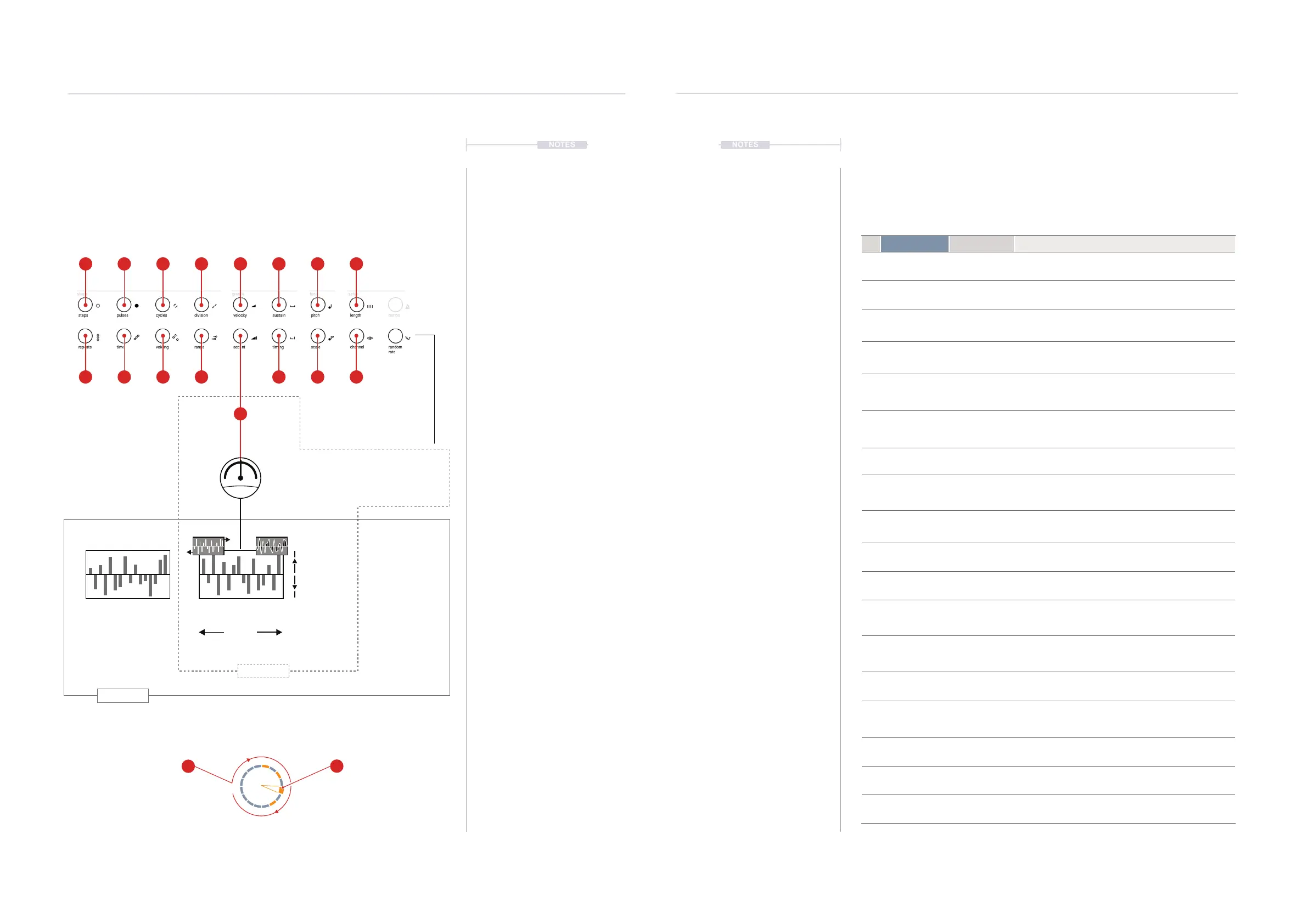
7.7 Randomisation Overview
Random is a function that operates globally as a 16 step sequence in
parallel to all of the primary T-1 parameters. It allows random and
unpredictable variations to be applied to parameter values over the period
of the random sequence. The sequence can be slewed. Think of this as a
generative random modulation sequence lane per parameter.
(RANDOM)
0% - 100%
Global
Local
RATE
Parameter Lane
Phase Shift Slew
Parameter Lane
(PARAMETER)
+
(RANDOM)
[CTRL]
+
(RATE)
Modulation applied
to the parameter.
Sets Amount
Random operates as a global function affecting all randomised parameter sequences. Specic
parameters have the amount of modulation set individually.
Modulation Range
Sets Variance
Rate of Random
Sequence.
Sets Division.
Cycle Controlled
Governed by Cycle iterations. Length
determined by steps & division.
Rate Controlled
Governed by Step iterations.
Time division set by rate.
7.8 Random Selectable Parameters
The primary parameters labelled with the white text font are typically the
ones that can be randomised plus also the secondary function probability.
Tempo is an exception and cannot be randomised. The random modulation
amount setting is bi-polar.
Cycles & Random
7
Cycles & Random
7
R
C
R
R
CC
R
C
R
C
R
C
R
R
C
C
R
R
Parameter Control Affects
1 Steps Cycle Changes the number of steps after each cycle.
2 Pulses Cycle Changes the number of pulses after each cycle.
3 Cycles Cycle Probability of skipping or repeating a cycle
4 Division Cycle Probability of the division macro being applied.
5 Velocity Cycle Velocity of Individual pitch menu notes. Changes all
the notes differently - polyphonic random or equally
monophonic random
6 Pitch Cycle Transposes inserted notes each cycle. Changes all the
notes differently - polyphonic random or equally
monophonic random
7 Scale Cycle Applies a new Scale algorithm adjustment for major /
minor changes after each cycle
8 Sustain Rate
Amount of random subtraction applied to reduce the
sustain value. Changes all the notes differently -
polyphonic random or equally monophonic random
9 Repeats Rate Number of repeats after each pulse
10 Time Rate Note value of the repeats
11 Voicing Rate Adds randomness to voicing or style
12 Range Rate Amount of melodic note movement. Changes all the
notes differently - polyphonic random or equally
monophonic random
13 Accent Rate Velocity of each note Individually. Changes all the
notes differently - polyphonic random or equally
monophonic random
14 Timing Rate Adjusts micro-timing. Changes all the notes differently -
polyphonic random or equally monophonic random
15 Channel Rate The change of notes transmitted. Changes all the
notes differently - polyphonic random or equally
monophonic random
16 Probability - Probability.
17 Length - Length of current track.
18 CC Tracks - Applied the random 16 step bi-polar sequence to the
CC value of a CC track parameter.

 Loading...
Loading...