WESTLOCK CONTROLS CORPORATION
280 MIDLAND AVENUE, SADDLE BROOK, NJ 07663 TEL: 201-794-7650 FAX: 201-794-0913
www.westlockcontrols.com
5/05/12 TECH-461/D.W.O. 19909 Page 9 of 24
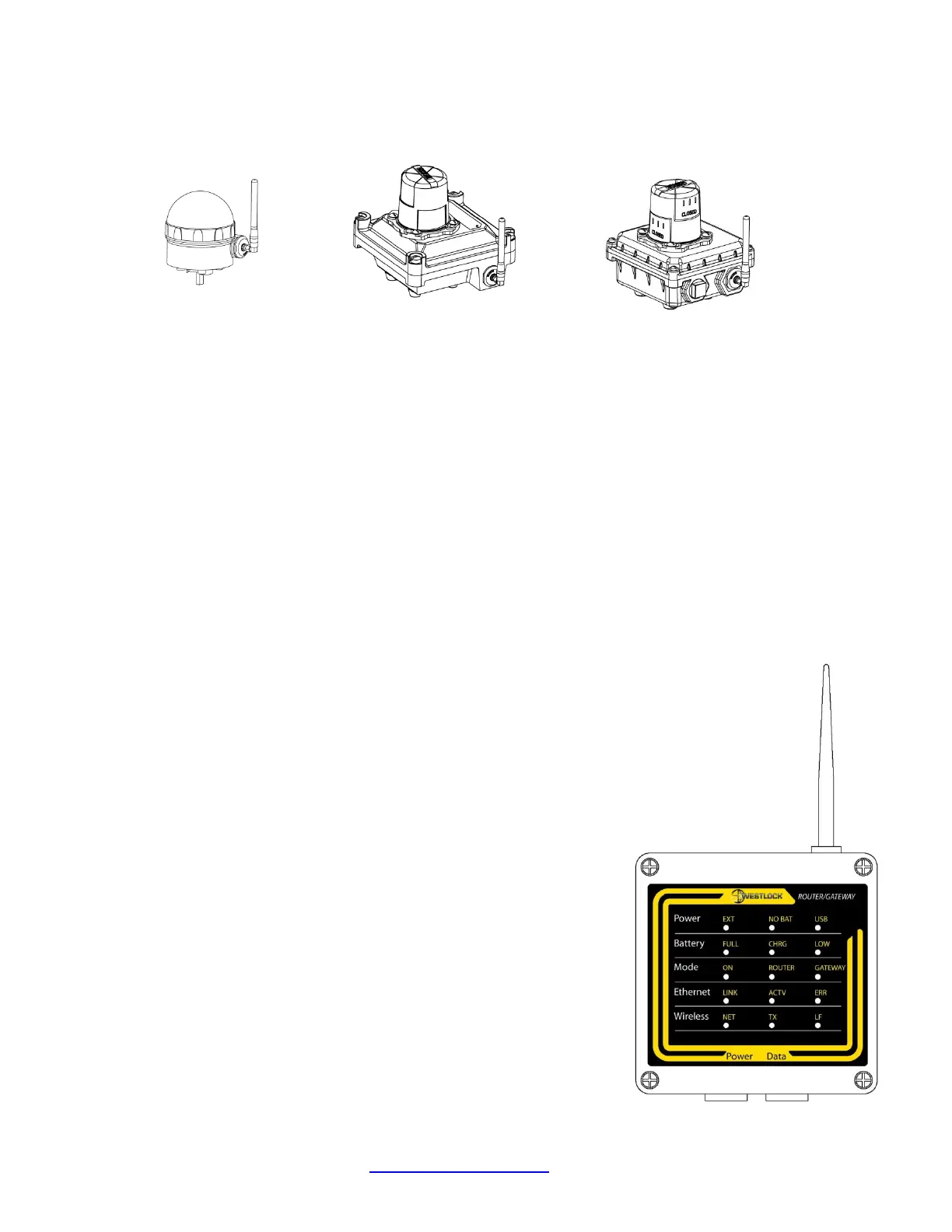
1.7.2 Wireless Device (WD)
A Westlock Wireless Device (WD) is bracket-mounted to any type of valve or actuator and –
using the standard wireless IEEE802.15.4/ZigBee Pro, 2.4 GHz protocol – wirelessly transmits
and receives messages relevant to the position status of the valve in real time. The WD is
powered by 4 half AA Lithium batteries. In nominal operation, the battery life of the WD is
above 10 years. A battery pack can be replaced in the field if allowed by local regulations.
The WD includes a shaft that is fastened to the valve’s stem through a special adapter. It
transfers the angle position of the stem to the WD. An internal WD sensor measures the
position of the WD shaft thus providing information about the angular position of the stem in
degrees relative to the valve. The WD reports the valve position (angle) immediately when
motion of the valve lever is sensed or every 15 minutes (configurable). The WD temperature,
WD battery status, and other WD housekeeping information are broadcast with every WD
message. Each WD message is transmitted with a real time stamp. In between transmissions the
WD is in sleep status to save battery power. The WD also includes a Low Frequency (LF)
receiver for receiving setting commands from the Wireless
Handheld and to commission, decommission, calibrate, and
setup the unit and to perform diagnostic procedures.
1.7.3 Wireless Router (WR)
Each WR collects and routes data from nearby WRs and up to
32 associated WDs, and transmits the information towards the
control center by hops from WR to WR.
The WR acts as a relay that retransmits the messages received
from a remote WR, through the ZigBee wireless network, until
they reach a WG (see below for details). Data transfer
redundancy and self-healing is assured by automatic routing of
the wireless devices through a mesh topology and providing
multiple WGs for each wireless network.
1.7.4 Wireless Gateway (WG)
The Wireless Gateway (WG) is the last-hop that transfers
collected data from WRs and WDs to the Wireless Management
System. Several WGs can be connected, via TCP/IP, to the
Wireless Management System (thus ensuring full redundancy
and avoiding a single point of failure).
 Loading...
Loading...