XC4000 Series Field Programmable Gate Arrays
4-30 September 18, 1996 (Version 1.04)
The buffer enable is an active-High 3-state (i.e. an active-
Low enable), as shown in Table 15.
Another 3-state buffer with similar access is located near
each I/O block along the right and left edges of the array.
(See Figure 33 on page 39.)
The horizontal longlines driven by the 3-state buffers have a
weak keeper at each end. This circuit prevents undefined
floating levels. However, it is overridden by any driver, even
a pull-up resistor.
Special longlines running along the perimeter of the array
can be used to wire-AND signals coming from nearby IOBs
or from internal longlines. These longlines form the wide
edge decoders discussed in “Wide Edge Decoders” on
page 31.
Three-State Buffer Modes
The 3-state buffers can be configured in three modes:
• Standard 3-state buffer
• Wired-AND with input on the I pin
• Wired OR-AND
Standard 3-State Buffer
All three pins are used. Place the library element BUFT.
Connect the input to the I pin and the output to the O pin.
The T pin is an active-High 3-state (i.e. an active-Low
enable). Tie the T pin to Ground to implement a standard
buffer.
Wired-AND with Input on the I Pin
The buffer can be used as a Wired-AND. Use the WAND1
library symbol, which is essentially an open-drain buffer.
WAND4, WAND8, and WAND16 are also available. See
the
XACT Libraries Guide
for further information.
The T pin is internally tied to the I pin. Connect the input to
the I pin and the output to the O pin. Connect the outputs of
all the WAND1s together and attach a PULLUP symbol.
Wired OR-AND
The buffer can be configured as a Wired OR-AND. A High
level on either input turns off the output. Use the
WOR2AND library symbol, which is essentially an open-
drain 2-input OR gate. The two input pins are functionally
equivalent. Attach the two inputs to the I0 and I1 pins and
tie the output to the O pin. Tie the outputs of all the
WOR2ANDs together and attach a PULLUP symbol.
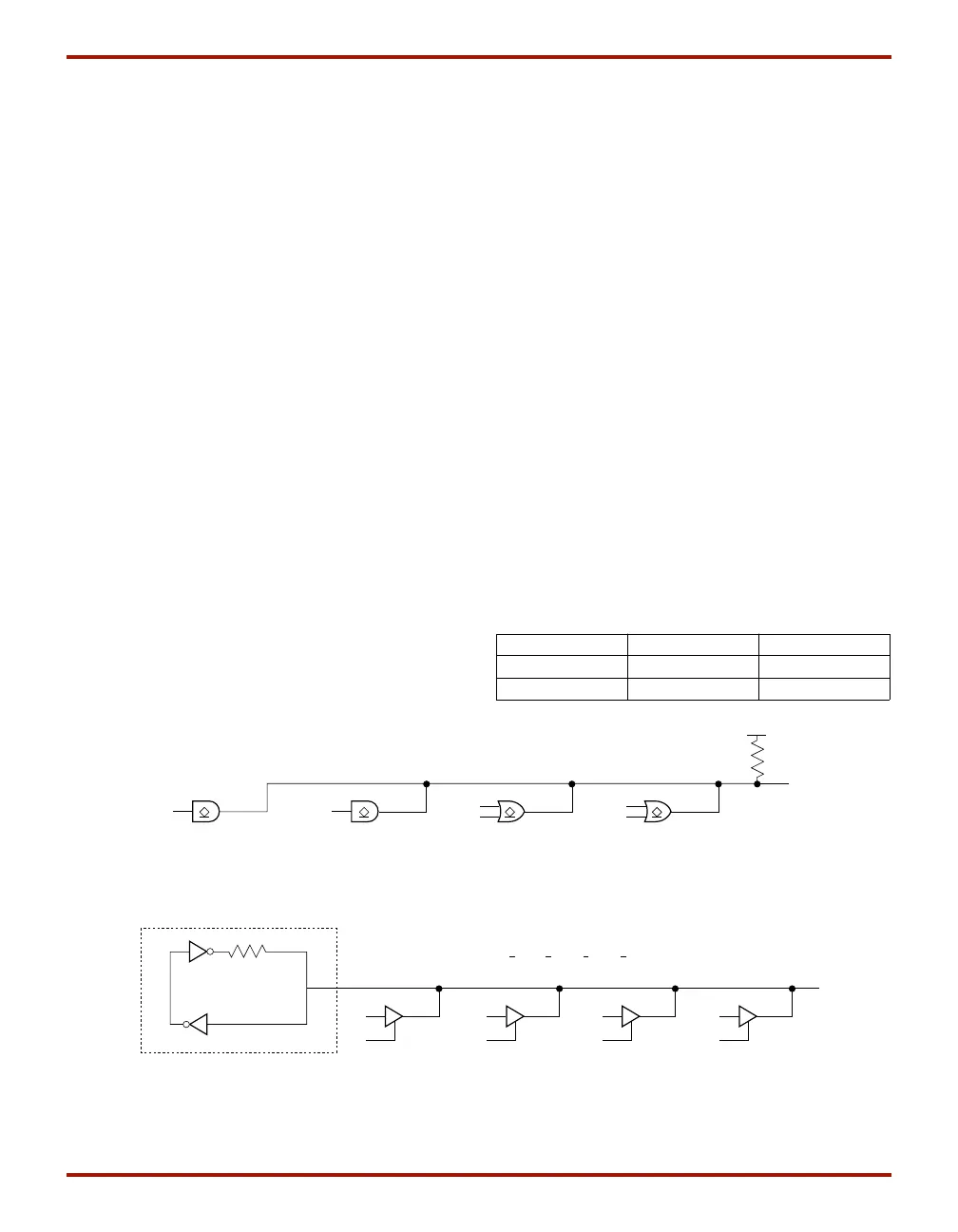
Three-State Buffer Examples
Figure 22 shows how to use the 3-state buffers to imple-
ment a wired-AND function. When all the buffer inputs are
High, the pull-up resistor(s) provide the High output.
Figure 23 shows how to use the 3-state buffers to imple-
ment a multiplexer. The selection is accomplished by the
buffer 3-state signal.
Pay particular attention to the polarity of the T pin when
using these buffers in a design. Active-High 3-state (T) is
identical to an active-Low output enable, as shown in
Table 15.
Table 15: Three-State Buffer Functionality
IN T OUT
X1Z
IN0IN
P
U
L
L
U
P
Z = D
A
● D
B
● (D
C
+D
D
) ● (D
E
+D
F
)
D
E
D
F
D
C
D
D
D
B
D
A
WAND1 WAND1
W0R2AND W0R2AND
X6465
Figure 22: Open-Drain Buffers Implement a Wired-AND Function
D
N
D
C
D
B
D
A
ABCN
Z = D
A
• A + D
B
• B + D
C
• C + D
N
• N
~100 kΩ
"Weak Keeper"
X6466
BUFT BUFT BUFT BUFT
Figure 23: 3-State Buffers Implement a Multiplexer

 Loading...
Loading...