Common questions of blood pressure measurement
3. Why measure Blood Pressure at home?
Blood pressure measured at a clinic or doctor's office may cause
apprehension and can produce an elevated reading, 25~30 mmHg higher
than that measured at home. Home measurement reduces the effects of
outside influences on blood pressure readings, supplements the doctor's
readings and provides a more accurate, complete blood pressure history.
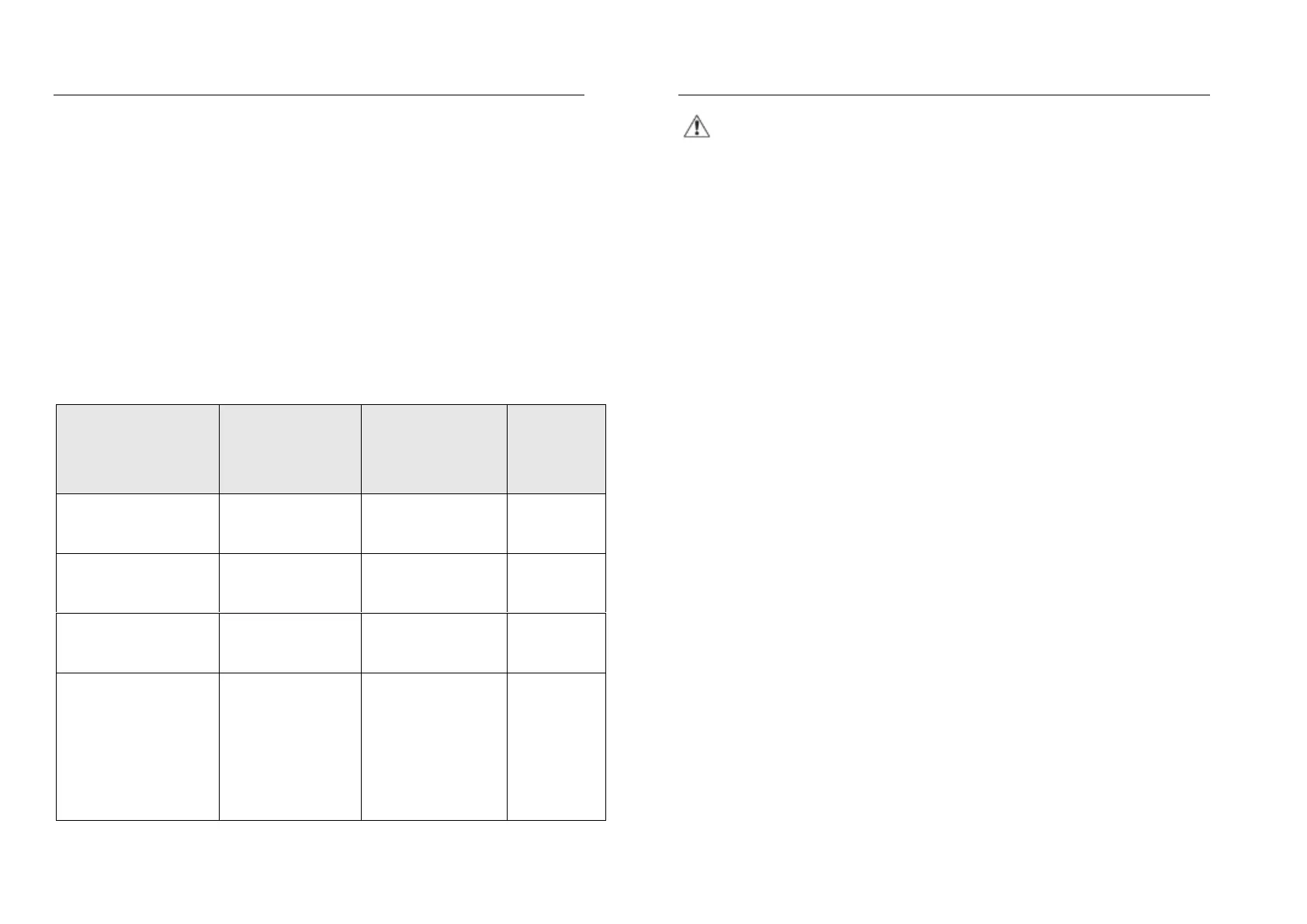
4. WHO Blood Pressure Classification?
Standards to assess high blood pressure, without regard to age, have been
established by the world Health Organization (WHO), as shown below:
Common questions of blood pressure measurement
Note: There is no definition about hypopiesia, and generally SYS
(systolic pressure) less than 90mmHg or DIA (diastolic pressure) less than
60mmHg is called hypotension.
5. Blood pressure variations?
An individual's blood pressure varies greatly on a daily and seasonal basis.
It may vary by 30 to 50 mmHg due to various conditions during the day. In
hypertensive individuals variations are even more pronounced. Normally, the
blood pressure rises while at work or play and falls to its lowest levels during
sleep. So do not be overly concerned by the results of one measurement.
Take measurements at the same time every day using the procedure
described in this manual to get to know your normal blood pressure. Regular
readings give a more comprehensive blood pressure history. Be sure to note
date and time when recording your blood pressure. Consult doctor to
interpret the blood pressure data.

 Loading...
Loading...