Application, Charts, Tips
Cooking and frying utensils
Thebetterthepotorthepan,thebettertheboiling
or frying result.
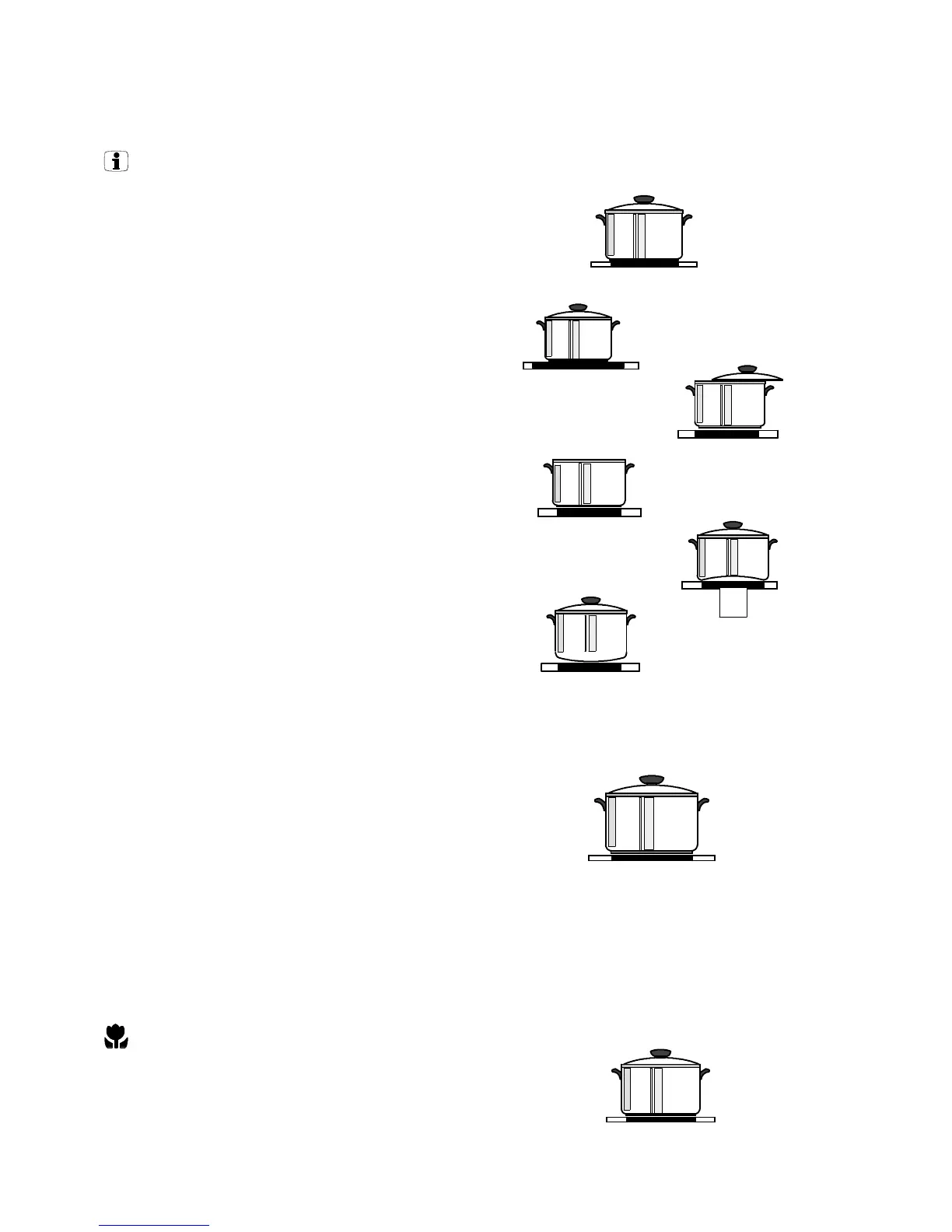
D You can recognise good quality pans by their
base.Thebaseshouldbethickandasflataspos-
sible.
D Rough bases (i.e. burrs and sharp edges) will
scratch the ceramic glass surface.
D Utensils with aluminium and copper bases can
leave behind metallic discolorations which can
only be removed with difficulty or sometimes not
at all.
D Saucepansandfryingpans shouldnot besmaller
than the cooking zone, and preferably not more
than 10--15 mm larger than the diameter of the
cooking zone.
D When cold, pan bases normally curve slightly
inwards (are concave). In no case should they
curve outwards (be convex).
D When buying new pots or pans pay attention to
the base diameter. Manufacturers often state the
upper diameter of the edge of a dish.
D If youareusingspecialcookingutensils likepres-
surecookersoraWOK,followthemanufacturer’s
instructions.
D Follow any guidelines provided by the saucepan
manufacturer. Ensure theyarerecommendedfor
use on ceramic hobs.
General hints
D The bases should always be clean and dry.
D To avoid scratching or damaging the ceramic
glasssurface,potsandpansshouldbe movedon
the hob by lifting them, and not by sliding.
D Scratches can also be caused by grains of sand
(e.g. originating from the previous washing of
vegetables), drawnover thecookingsurfacewith
the pan, or by burrs and the rims of pan bases.
D Use highsidedpansfor disheswith alot of liquid,
so that nothing boils over.
Energy consumption
To save energy, you should:
D place pots and pans in position before switching
on the cooking zone.
D useonlycookingandfryingutensils withsmooth,
flat bases.
8
8
8
8
8
8
8

 Loading...
Loading...