Updating our TPDU example, and assuming we are sending the first message, i.e.
message reference is 00, our updated table is now:
PDU
Type
Message
Reference
Destination
Address
Protocol
Identifier
Data
Coding
Scheme
Validity
Period
User
Data
Length
User
Data
01 00
0B91515521
4365F7
1 Octet 1 Octet
0,1, or 7
Octets
1 Octet
0-140
Octets
The Protocol Identifier or PID indicates whether the message is being sent to another
SMS device or to an email account. Use 00 for a regular SMS message, or 12 for an
email message
The Data Coding scheme handles a multitude of settings including,
• The character set or message coding of the user data,
• The message class, which determines where on the receiving device the SMS
message is delivered (SIM, NV, or Terminal Equipment),
• Request whether or not the message is automatically deleted after it’s read.
Automatic Deletion is often used with notification messages.
• Message type indication to alert the user to a waiting voicemail, fax or email.
The settings of bits 7-4 determine the meaning of bits 3-0.
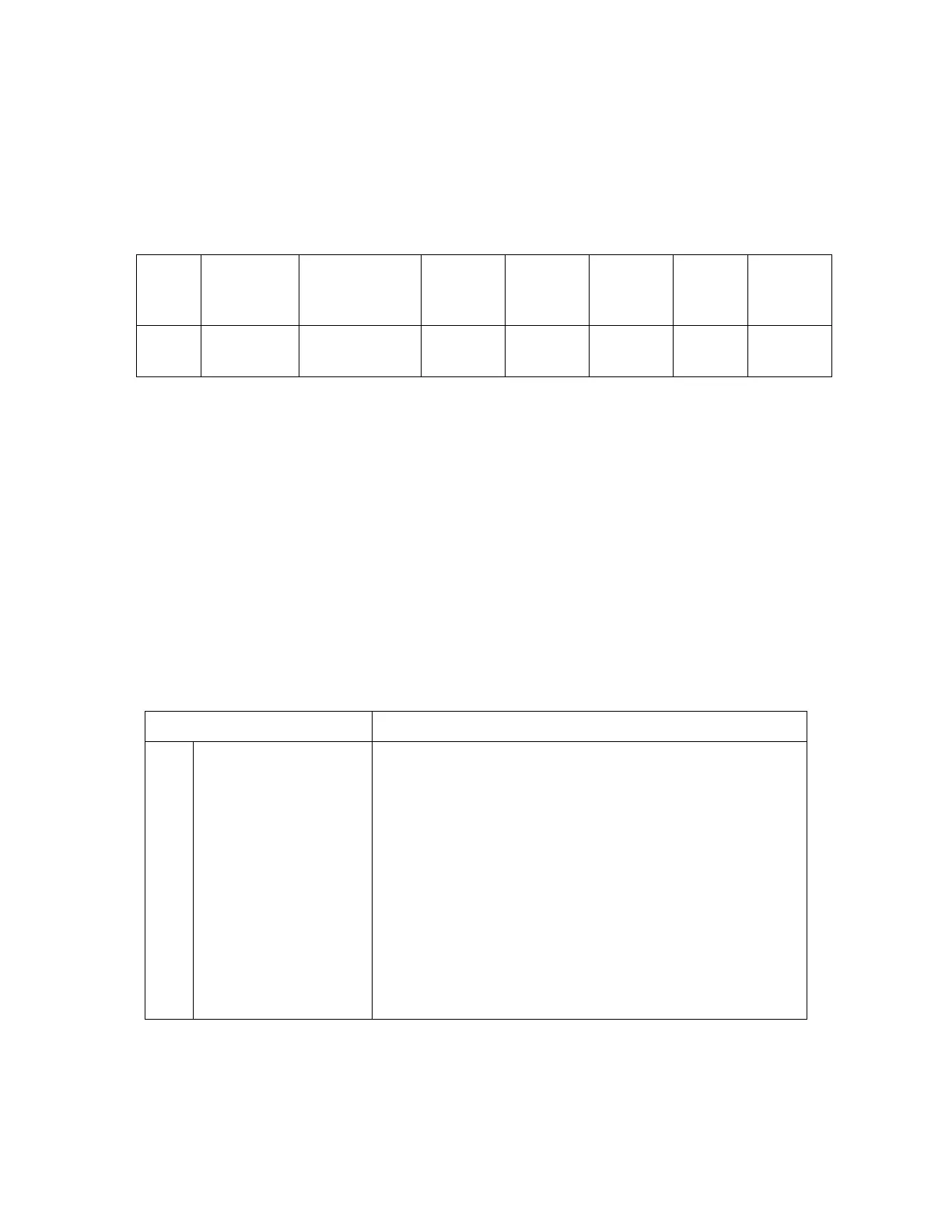
Bits 7-4 Bits 3-0
000 Bit 4 set to 0 indicates
that bits 1 and 0 are
ignored.
Bit 4 set to 1 indicates
that bits 1 and 0 serve
as the message type
indication.
Bit 1 Bit 0 Message type indication
0 0 Class 0 - message is displayed on the
user interface but not stored.
0 1 Class 1 – message is stored in NV (or SIM
card if NV full)
1 0 Class 2 – message are stored to the SIM
card only
1 1 Class 3 – stored to the TE, message is
automatically displayed on the Terminal
Equipment
Bit 3 Bit 2 Message Encoding
30
 Loading...
Loading...