when they are full. These three tables are returned to the GET request done by a supervisor.
The historic event and hardware anomaly tables allow reading the recent problems that have
occurred. Some of these problems correspond to the traps sent by OmniPCX Office, but most
of them only describe less important troubles that the system has encountered.
When an alarm reports the occurrence of a problem, and another one reports the end of the
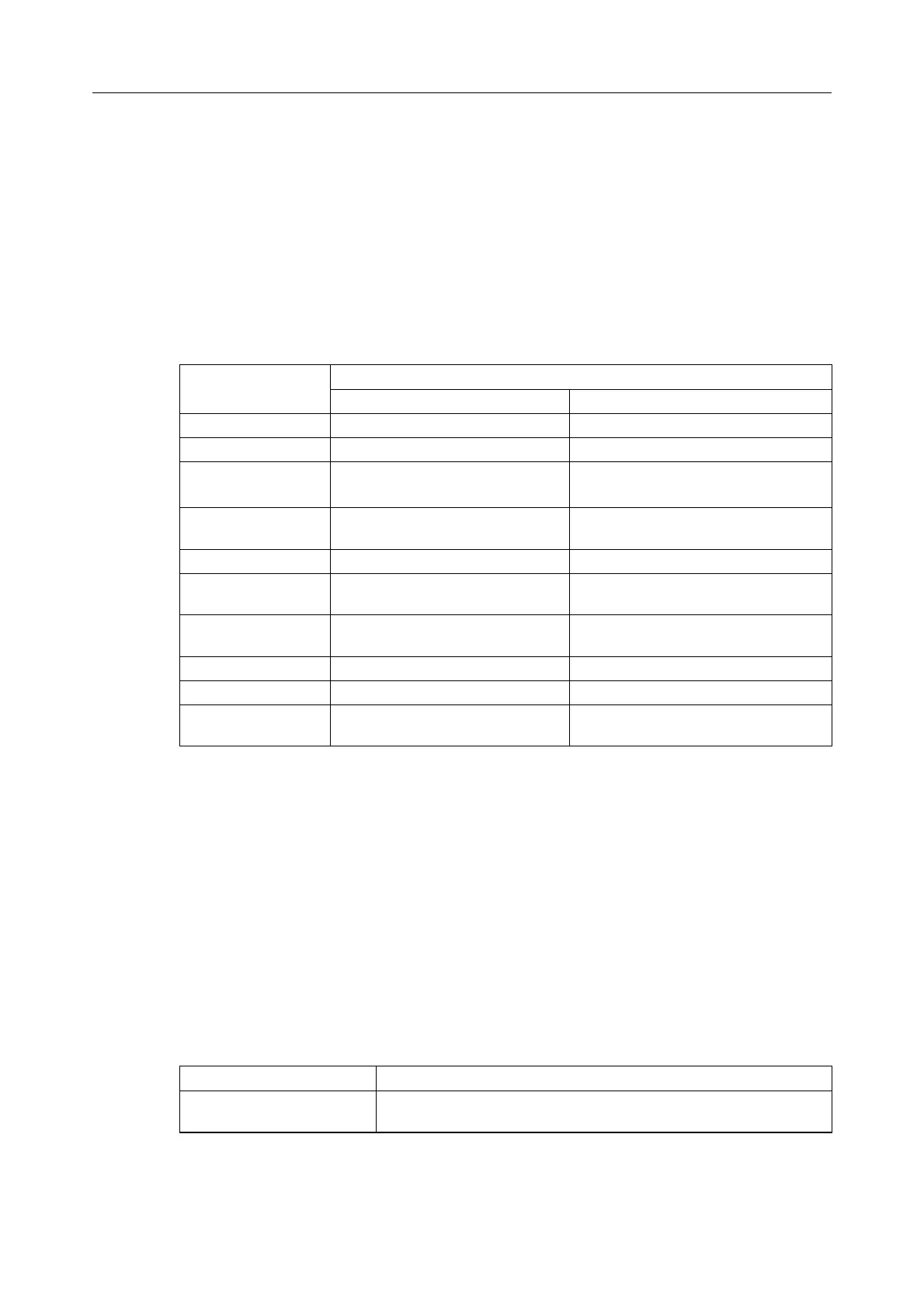
same problem, then they are correlated. The following table is a synthetic view of correlated
alarms of the call handling MIB.
table 10.2: Call handling MIB
Alarm description
Alarm
Start End
System reset ochmSystemRestart ochmSystemRestarted
Cabinet alarm ochmCabinetUnplugged ochmCabinetOperational
Board alarm ochmBoardUnplugged
ochmBoardPermanentReset
ochmBoardOperational
Main power supply
failure
ochmPowerSupplyFailure ochmPowerSupplyOperational
Fan alarm ochmFanFailure ochmFanOperational
ISDN T2 access
problem
ochmIsdnFailure ochmIsdnOperational
VoIP board Ethernet
interface problem
ochmVoipLinkDown ochmVoipLinkUp
IBS alarm ochmIbsSynchroDown ochmIbsSynchroUp
Access Mbx ochmRemoteAccessMbxLocked ochmRemoteAccessMbxUnlocked
Access Wsapi ochmRemoteAccessWsapi-
Locked
ochmRemoteAccessWsapiUnlocked
10.3 Configuration
10.3.1 Configuring the SNMP Service
The SNMP configuration is performed using the OMC tool. The SNMP service can be
activated or deactivated via the OMC tool (deactivated by default).
Note:
In case of default, the access to the SNMP service is not enabled for the supervisor and all parameter
fields are empty.
To declare the SNMP Service to Supervisors:
1. From the OMC tool, navigate to the menu
2. Review/modify the following global parameters:
Enable Flag Select the check box to activate the SNMP service
System Contact Enter contact information of the person responsible for this man-
aged system
/'
! "#$ ! % $& !
61/62

 Loading...
Loading...











