15
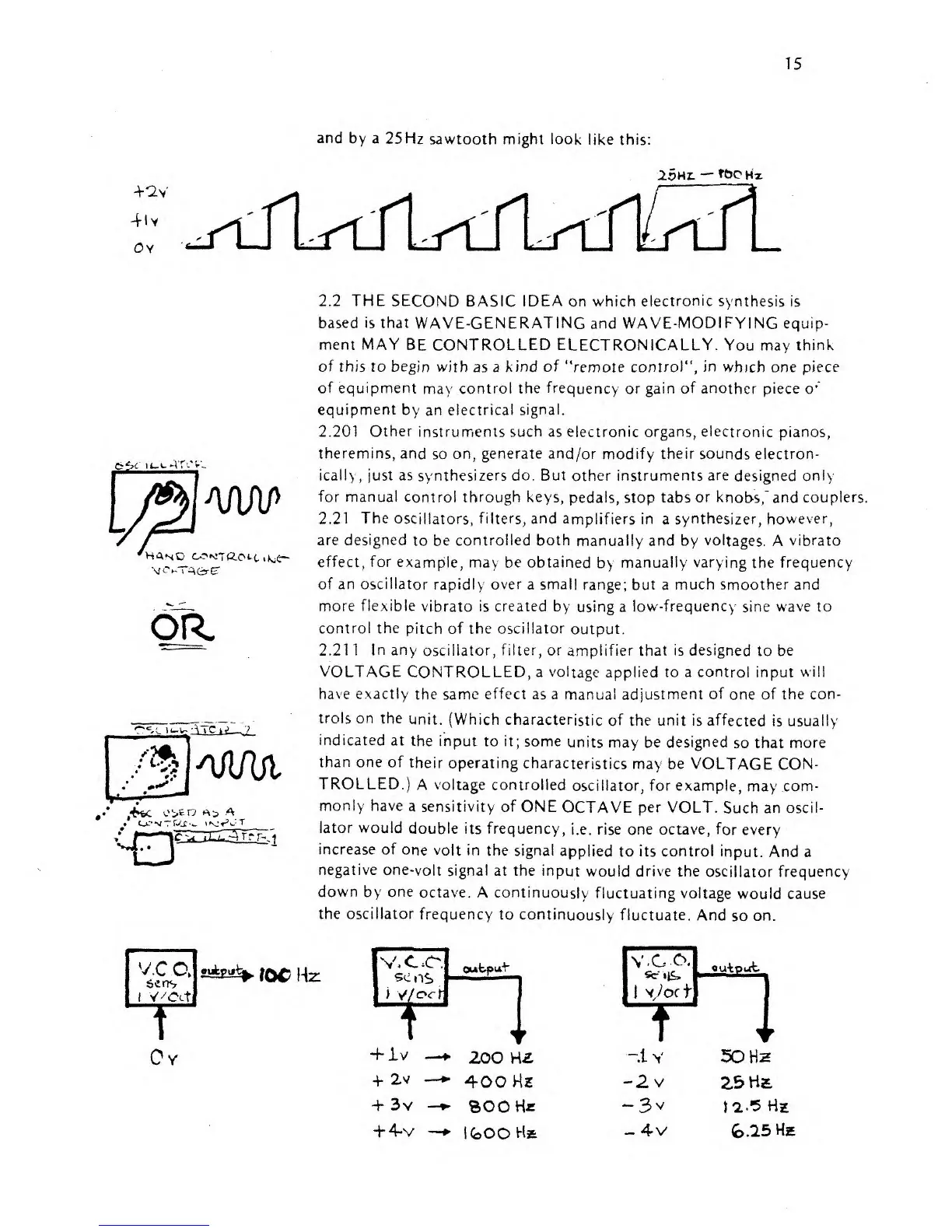
and
by a
25Hz
sawtooth might look
like this:
20HX.
—
ttsetfx
C-^'li-w^E
A/W
lu-u
'\
|g
;
A/lAil
1
2.2
THE
SECOND BASIC IDEA on
which
electronic synthesis
is
based
is
that
WAVE-GENERATING and WAVE-MODIFYING equip-
ment
MAY
BE CONTROLLED ELECTRONICALLY.
You may
think
of
this to begin with as a kind
of
"remote
control",
in
which
one piece
of equipment
may
control
the frequency or gain of
another piece o*~
equipment
by an electrical
signal.
2.201
Other
instruments such as electronic
organs,
electronic pianos,
theremins,
and
so
on, generate
and/or modify
their
sounds electron-
ically,
just
as
synthesizers
do. But
other
instruments
are
designed
only
for
manual
control through keys,
pedals, stop
tabs
or
knobs,"
and couplers.
2.21 The oscillators, filters,
and
amplifiers
in a synthesizer,
however,
are designed
to be
controlled
both
manually
and by voltages.
A
vibrato
effect,
for
example,
may be obtained
by
manually
varying
the
frequency
of
an
oscillator rapidly over a small
range; but
a
much
smoother and
more
flexible
vibrato
is
created by
using
a
low-frequency sine wave to
control the
pitch
of
the oscillator
output.
2.21 1
In
any
oscillator,
filter, or
amplifier that
is
designed
to
be
VOLTAGE
CONTROLLED,
a voltage
applied to a control input
will
have exactly
the
same
effect
as a manual adjustment
of
one
of the con-
trols on
the
unit. (Which
characteristic
of
the
unit
is affected
is usually
indicated at
the
input to
it;
some
units may
be designed
so
that
more
than
one
of
their
operating
characteristics
may be VOLTAGE CON-
TROLLED.)
A
voltage
controlled
oscillator, for example,
may com-
monly have
a
sensitivity of ONE
OCTAVE per VOLT.
Such
an oscil-
lator would
double
its
frequency,
i.e.
rise one octave, for
every
increase
of
one volt
in the
signal
applied
to
its
control
input.
And
a
negative
one-volt signal at the
input would drive the
oscillator frequency
down by
one
octave.
A continuously
fluctuating
voltage
would
cause
the oscillator
frequency to
continuously
fluctuate. And
so
on.
•h**^
IOC
Hz
Or
+ iv
+
3v
+
4-v
200 HZ
400 Hh
SOOH*
1
fcOO
Ha
-I
V
-2v
-4v
50Hh
23
Hz.
i>
.25
Hz

 Loading...
Loading...