1.2D Calibration
Digital blood pressure monitors do not require recalibration. If the unit turns on and does not display an
error code, the product is working properly. In extremely rare cases, the cuff may have developed a pin-hole
leak, or the gasket where the cuff connector enters the monitor may not have a proper seal; both of these
leaking air issues will potentially cause errors in accuracy, but otherwise the product will work accurately
without drifting out of calibration.
1.3 What do your Numbers Mean?
Blood pressures is the pressure in your blood vessels while blood circulates throughout your body. High
blood pressure or “Hypertension” is the pressure at which ones normal average blood pressure is considered
too high and other health risks including: heart attack, stroke, dementia, kidney failure, heart disease and
erectile dysfunction may occur. It is expressed as two numbers: systolic/diastolic 120 mmHg/ 80 mmHg
(mmHg= millimeters of mercury). “Systolic” numbers refer to the pressure on the walls of your arteries
while the heart is contracting and pushing blood. “Diastolic” pressure is the lower number when the
heart is at rest and relaxed. A simple way to understand this is to picture a garden hose. When the tap is
turned on, the immediate pressure on the walls of the hose is the “systolic” value, and when the tap is
turned off it is the “diastolic” number.
There are many different causes of high blood pressure. We differentiate between common primary
(essential) hypertension, and secondary hypertension. The latter group can be ascribed to specific organic
malfunctions. Please consult your doctor for information about the possible origins of your own increased
blood pressure values.
1.4 Normal Blood Pressure Values
Blood pressure is too high when measuring at home and you have rested, the diastolic pressure is above
85 mmHg or the systolic blood pressure is over 135 mmHg. If you obtain readings in this range, consult
your doctor immediately. High blood pressure values over time can damage blood vessels, vital organs
such as the kidney, and your heart.
With blood pressure values that are too low (i.e., systolic values under 105 mmHg or diastolic values
under 60 mmHg), consult with your doctor.
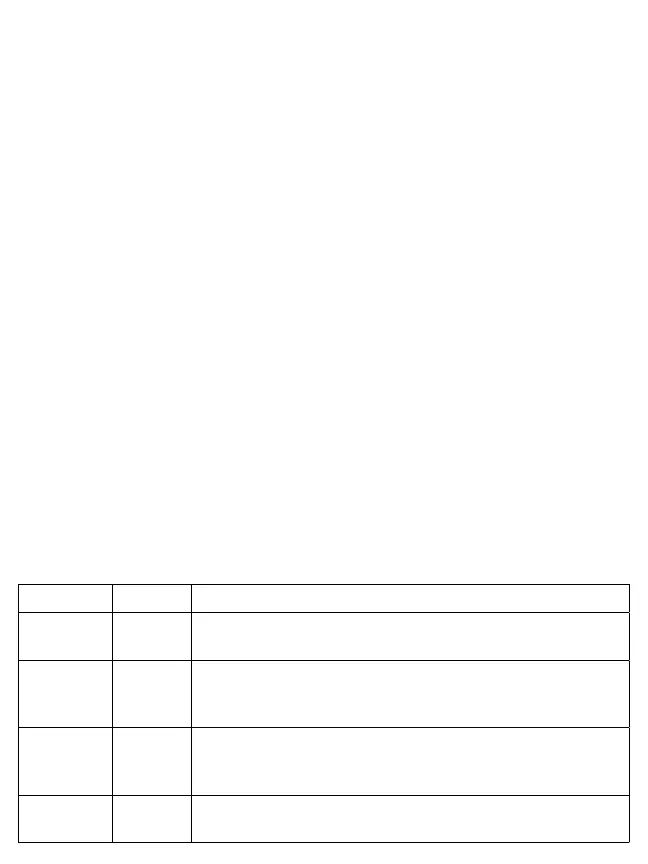
Systolic Diastolic Comment
Below 120
Less than
80
This range is considered “Normal” and ideal
120 - 139 80 – 89
This range is considered “Pre-hypertension”: Discuss with your health
care professional. Lifestyle modifications maybe required to avoid
advancing into hypertension.
140 – 159 90 - 99
This is in the hypertension range. Discuss with your health care
professional. Medication(s) and lifestyle modifications are typical
treatments.
160 and
higher
100 +
Discuss with your medical professional, medication(s) and lifestyle
modifications are necessary to control your hypertension

 Loading...
Loading...