1-4
Cisco PNNI Network Planning Guide for MGX and SES Products, Release 5
Part Number OL-3847-01 Rev. D0, April, 2004
Chapter 1 Introduction to PNNI
The Hierarchical PNNI Network Topology
Note Hierarchical PNNI networks are not supported on Cisco MGX 8850 switches before Release 2.1.60, and
they are not supported on the SES PNNI Controller before Release 1.1.60.
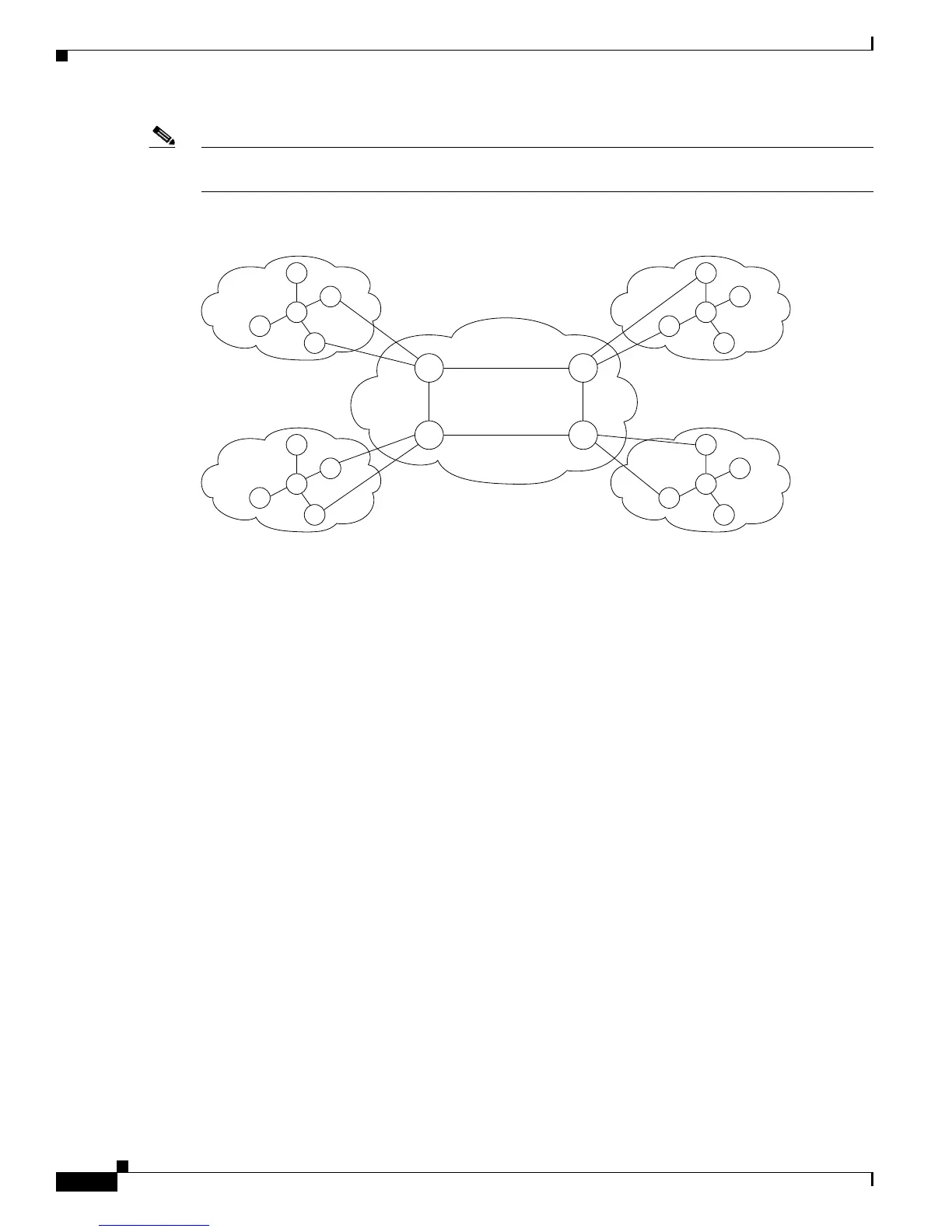
Figure 1-2 Example Hierarchical PNNI Network Topology Showing Multiple Peer Groups
Notice that the only difference between the single peer group in Figure 1-1 and the hierarchical PNNI
network in Figure 1-2 is the grouping of the nodes. This grouping of the nodes creates smaller PNNI
databases within the nodes in each peer group and reduces the PNNI processing requirements in each
node. This grouping also provides room to add more nodes in each of the groups.
In a hierarchical network, the database for each peer group is smaller because the peer group collects,
stores and processes PTSEs for only those nodes in the same peer group. The nodes within a peer group
do receive information on other peer groups, but the information is summarized. From the perspective
of an individual peer group, other peer groups appear to be single nodes. Nodes within one peer group
do not receive PTSEs from other peer groups and therefore do not collect, store, and process information
about all the individual nodes and links in other peer groups.
The Cisco switches described in this guide support up to 32 visible peer groups in one network. (The
specifications for Cisco switches are described in Table 2-1 in Chapter 2, “Interoperability and
Performance Planning.”) A visible peer group is a peer group with which the local peer group can
communicate. Because each visible peer group appears as a logical group node (LGN), each visible peer
group reduces the available node count for a peer group. For example, if the local peer group discovers
32 visible peer groups, the node count for the local peer group is reduced to 128 (160 - 32 = 128).
Figure 1-3 demonstrates why a multiple peer group PNNI network is called a hierarchical PNNI
network.
66058
PNNI networks
Peer group 1
Peer
group 2
Peer
group 3
Peer
group 4
Peer
group 5
 Loading...
Loading...











