AX
Series
48
Selection guide (2)
For "MC2 curve " selection guide
What is MC2 curve?
The MC2 curve has a constant velocity in movement the same
as the MC (modified constant velocity) curve, but by setting an
acceleration/deceleration time, the constant velocity is set freely.
With the MC (general name: MCV50) curve, the constant velocity
section is 50%
Note: Accelleration/decelleration time is set to one-half or less
of movement time. If accelleration/decelleration time
setting exceeds one-half of movement time, the cam curve
is automatically changed to an MS (modified sine wave)
curve.
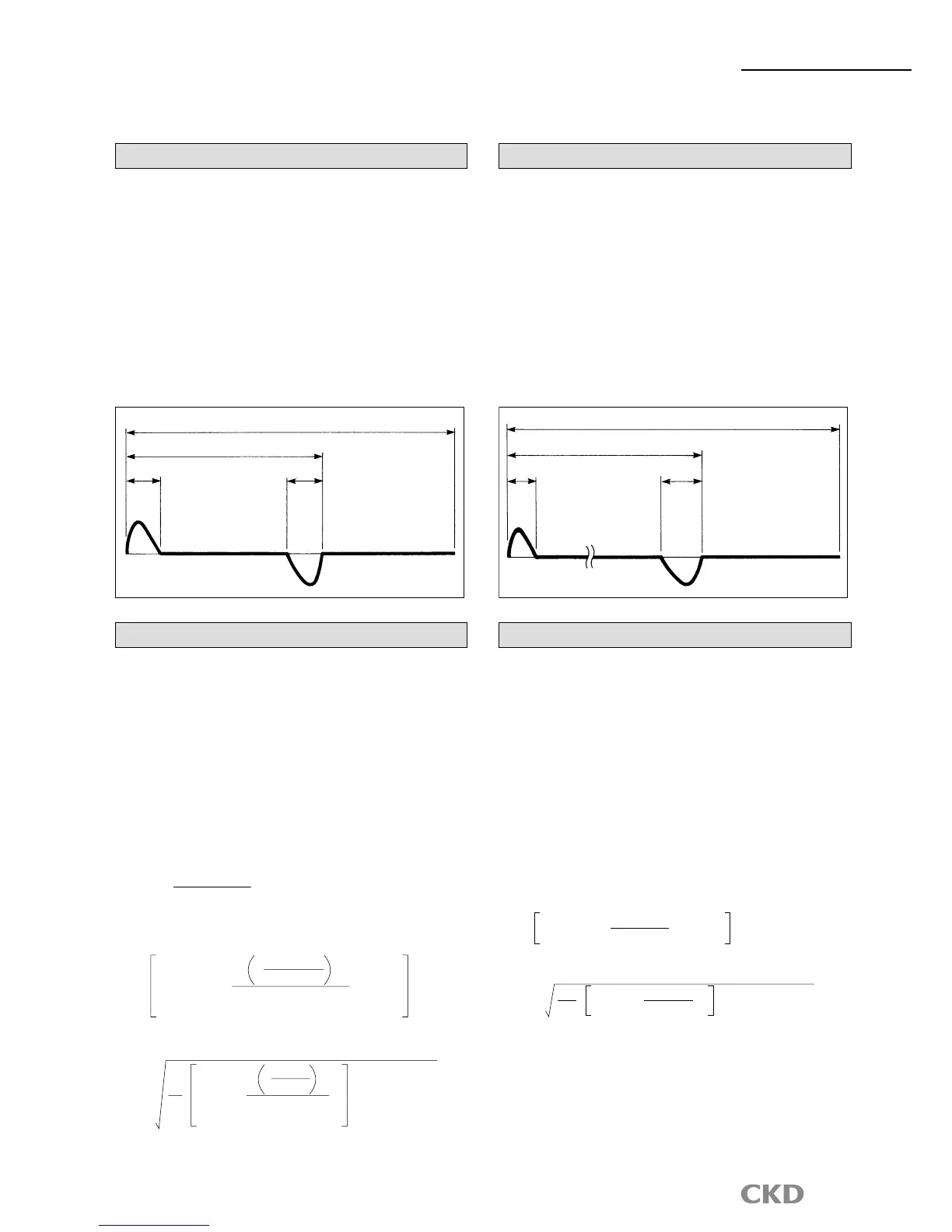
In the example, accelleration/decelleration time (ta) is set to 0.5
sec. for movement time (t
1
): 4 sec., a speed pattern that sets the
constant velocity to 75% is created.
4(t1)
0.5(ta) 0.5(ta)
(t0)
Constant velocity section (75%)
MC2
Selection guide
With the MC2 curve, the model is selected using the
following formula:
Moving angle : ψ(°)
Cycle time : t
0
(s)
Moving time : t
1
(s)
Acceleration or deceleration time
: ta(s)
Load moment of inertia
: J(kg•m
2
)
Output shaft moment of inertia
: J
M
(kg•m
2
)
Friction torque : Tf (N•m)
Working torque : T
w
(N•m)
Output shaft friction torque
: T
MF
(N•m)
When " continuous rotation " is selected
Continuous rotation.
Continuous rotation has with or less.
1. Continuous
rotation
:
Continuously rotates at a set speed until
the continuous rotation stop signal is input.
2. Equal index
position stop
:
If used with equal division designation,
stops at an equal division when the
continuous rotation stop signal is input.
3. Timing output :
If used with equal division designation, the
timing output pulse is output at the equal
division during rotation.
In the example, the shaft accelerates at acceleration
time: ta to set speed: N, and when a continuous rotation
stop is input, stops with deceleration time: td.
Selection guide
For continuous rotation, select the model with the following formula.
Rotation speed : N(rpm)
Cycle time : t
0
(s)
Acceleration hour : ta(s)
Deceleration hour : td(s)
Load moment of inertia
: J(kg•m
2
)
Output shaft moment of inertia
: J
M
(kg•m
2
)
Friction torque : Tf (N•m)
Working torque : Tw (N•m)
Output shaft friction torque
: T
MF
(N•m)
Max. rotation speed: N•max. (rpm)
Load torque (max.): T
m
(N•m)
Tm =
5.53 (J + JM)/ • fc + TMF+ Tf + TW
720, ta2
ψ• • π1-
t1-0.863ta
t1-2ta
Load torque (effective): Trms (N•m)
Trms =
•
3.91 (J + JM)/ + ( (Tf + Tw)/fc + TMF)
2
•
fc
720, ta2
ψ
• •
π1-
t1-0.863ta
t0
2ta
t1-2ta
2
Max. rotation speed :Nmax(rpm) (Note 1)
N
•max. = N
Load torque (max.): Tm (N•m)
Tm =
5.53 (J + JM)/ • fc + TMF
+ Tf + Tw
720, ta2
6.82N/ta/π
Load torque (effective): Trms (N•m)
Trms =
• • fc3.91 (J + JM)/ + ( (Tf + Tw)/fc + TMF)
2
720, ta2
6.82N/ta/π
t0
2ta
2
The above formula applies for ta≤td. If ta>TD, then
replace ta with td, and select.
Note 1) The maximum rotation speed will be limited
during continuous rotation. Use accordingly to actuator
specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...