32
CONTOUR
®
TS meter CONTOUR
®
TS test strips
Technical,
Service & Care
Principles of the Procedure: The CONTOUR
®
TS blood
glucose test is based on measurement of electrical current
caused by the reaction of the glucose with the reagent on
the electrode of the strip. The blood sample is drawn into
the tip of the test strip through capillary action. Glucose in
the sample reacts with FAD glucose dehydrogenase
(FAD-GDH) and potassium ferricyanide. Electrons are
generated, producing a current that is proportional to the
glucose in the sample. After the reaction time, the glucose
concentration in the sample is displayed. No calculation is
required.
Comparison Options: The C
ONTOUR
®
TS system is
designed for use with venous and capillary whole blood.
Comparison to a laboratory method must be done
simultaneously with aliquots of the same sample. Note:
Glucose concentrations drop rapidly due to glycolysis
(approximately 5% – 7% per hour).
4
Specifi cations
5718657_CntrTS_Karajishi_UG_EN_FpBp_v0.indd 32 3/24/17 4:13 AM
33
Technical,
Service & Care
Specifi cations
The following symbols are used throughout the product
labeling for the CONTOUR
®
TS blood glucose monitoring
system (meter packaging and labeling, and test strip and
control solution packaging and labeling).
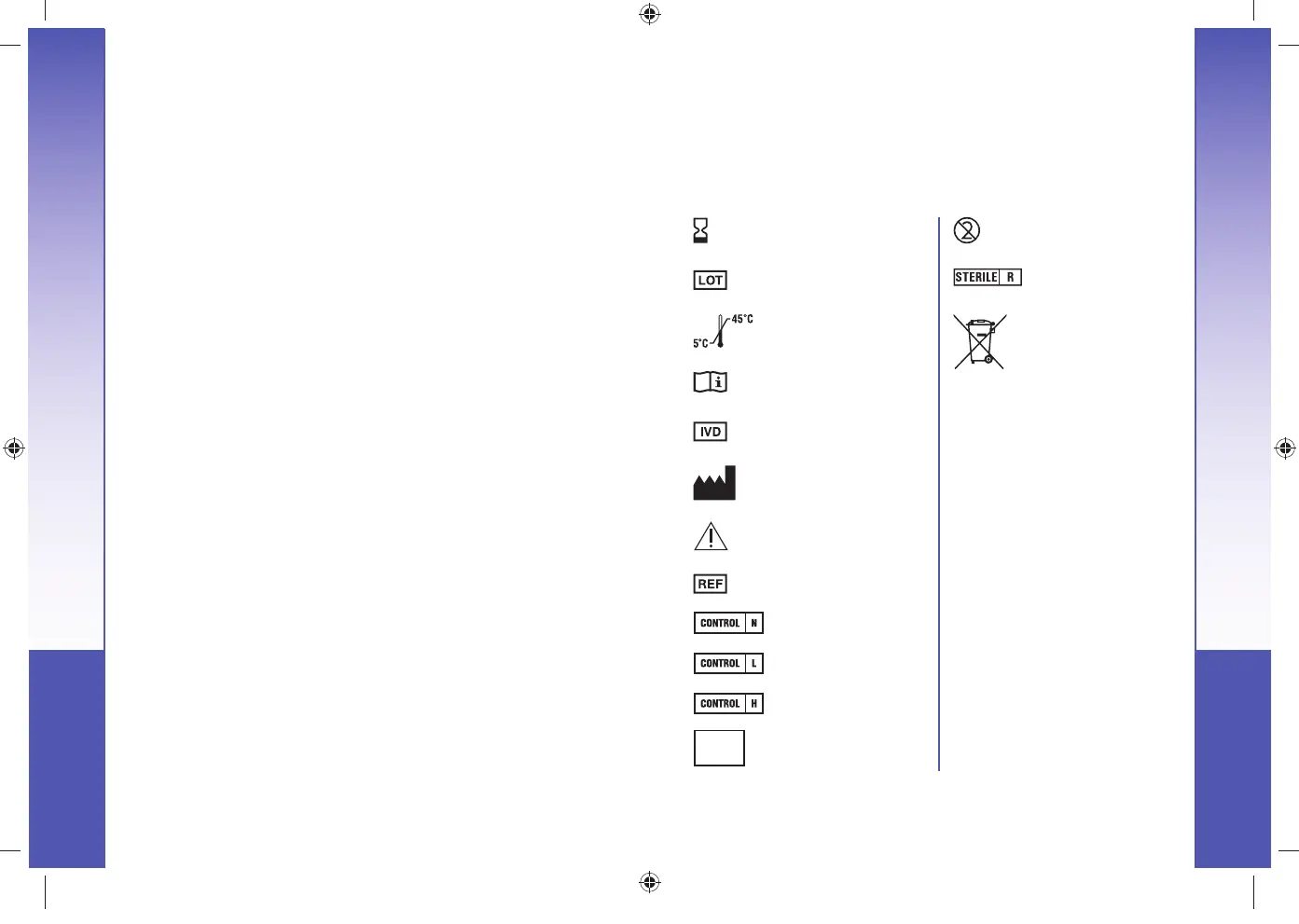
Symbols Used
Use by date
(last day of month)
Do not reuse
Batch code
Sterilized using
irradiation
Temperature
limitations
Batteries must be
disposed of in
accordance with
laws in your country. Contact
your competent local
authority for information on
the relevant laws regarding
disposal and recycling in
yourarea.
The meter should be treated
as contaminated and
disposed of according to
local safety rules. It should
not be disposed of with
waste electronic equipment.
Contact your health care
professional or local waste
disposal authority for medical
waste disposal guidelines.
Consult instructions
for use
In Vitro Diagnostic
Medical Device
Manufacturer
Caution
Catalogue number
Control Range Normal
Control Range Low
Control Range High
Discard
Date:
Control Discard Date
5718657_CntrTS_Karajishi_UG_EN_FpBp_v0.indd 33 3/24/17 11:30 AM
33
Technical,
Service & Care
Specifi cations
The following symbols are used throughout the product
labeling for the CONTOUR
®
TS blood glucose monitoring
system (meter packaging and labeling, and test strip and
control solution packaging and labeling).
Symbols Used
Use by date
(last day of month)
Do not reuse
Batch code
Sterilized using
irradiation
Temperature
limitations
Batteries must be
disposed of in
accordance with
laws in your country. Contact
your competent local
authority for information on
the relevant laws regarding
disposal and recycling in
yourarea.
The meter should be treated
as contaminated and
disposed of according to
local safety rules. It should
not be disposed of with
waste electronic equipment.
Contact your health care
professional or local waste
disposal authority for medical
waste disposal guidelines.
Consult instructions
for use
In Vitro Diagnostic
Medical Device
Manufacturer
Caution
Catalogue number
Control Range Normal
Control Range Low
Control Range High
Discard
Date:
Control Discard Date
5718657_CntrTS_Karajishi_UG_EN_FpBp_v0.indd 33 3/24/17 11:30 AM
32
CONTOUR
®
TS meter CONTOUR
®
TS test strips
Technical,
Service & Care
Principles of the Procedure: The CONTOUR
®
TS blood
glucose test is based on measurement of electrical current
caused by the reaction of the glucose with the reagent on
the electrode of the strip. The blood sample is drawn into
the tip of the test strip through capillary action. Glucose in
the sample reacts with FAD glucose dehydrogenase
(FAD-GDH) and potassium ferricyanide. Electrons are
generated, producing a current that is proportional to the
glucose in the sample. After the reaction time, the glucose
concentration in the sample is displayed. No calculation is
required.
Comparison Options: The C
ONTOUR
®
TS system is
designed for use with venous and capillary whole blood.
Comparison to a laboratory method must be done
simultaneously with aliquots of the same sample. Note:
Glucose concentrations drop rapidly due to glycolysis
(approximately 5% – 7% per hour).
4
Specifi cations
5718657_CntrTS_Karajishi_UG_EN_FpBp_v0.indd 32 3/24/17 4:13 AM
85718657_CntrTS_Karajishi_UG_EN_FpBp_v4_placed.pdf:34
 Loading...
Loading...