As a starting point, make sure your car has equal lengths on shocks, camber links and steering rods on both sides (left and right).
As a starting point, make sure your car has equal lengths on shocks, camber links and steering rods on both sides (left and right).
Front and rear do not need to be equal.
Front and rear do not need to be equal.
ACKERMAN
The difference in turning angle between the inside wheel and outside wheel in a turn.
Rear Hole: Less initial steering into a corner. Smoother steering
response. Better for large fl owing tracks.
Forward Hole: More initial steering into corner. Steering is
more aggressive. Better for tight technical tracks.
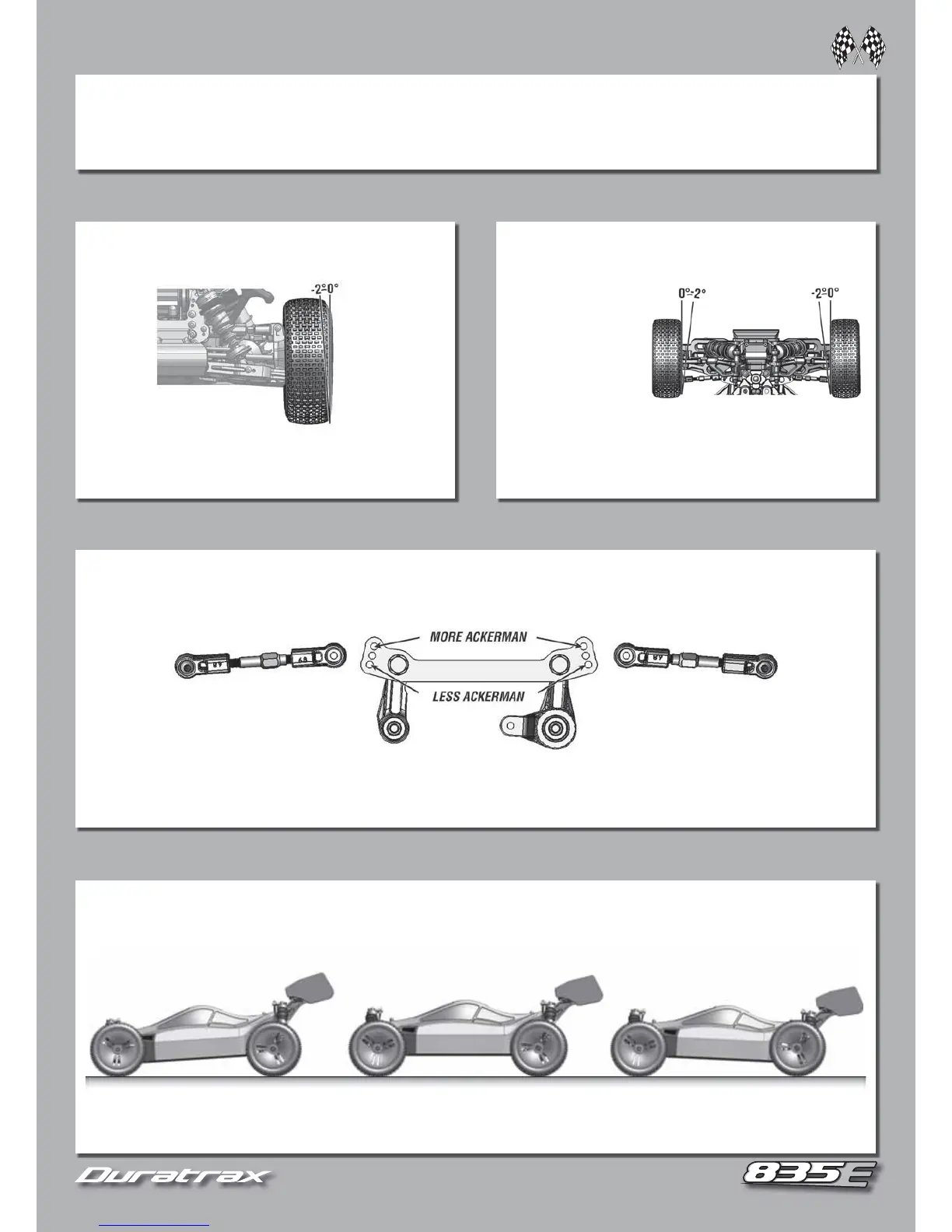
CAMBER
Angle of the tire and wheel in relation to the ground when
viewed from the front.
Negative Camber =
Top of the tire and wheel lean inward (Typically 0° to -2°)
• Improved traction while corning.
• Adds overall stability.
Positive Camber = Tire and wheel lean outward (NOT recommended).
FRONT TOE-IN AND TOE-OUT
Direction the wheels point in relationship with each other,
when viewed from the front.
Toe-Out: Fronts of the wheels point away from each other.
• Decreased stability when accelerating and increased steering
when entering a corner.
Toe-In: Front of the
wheels point toward each
other. (Typically 0 to -2°)
• Increased stability when
accelerating. Decreased
steering when entering
a corner.
8
Rotate the collar on the shock to change ride height. Adjust left and right equally.
RIDE HEIGHT
Distance the chassis sits from the ground and how much weight is transferred when the vehicle changes speed and direction.
More rear traction but reduces steering.
More rear traction but reduces steering.
Increases steering but can
Increases steering but can
cause rear end to lose traction.
cause rear end to lose traction.
 Loading...
Loading...