EVGA Z370 MICRO (121-KS-E375)
- 61 -
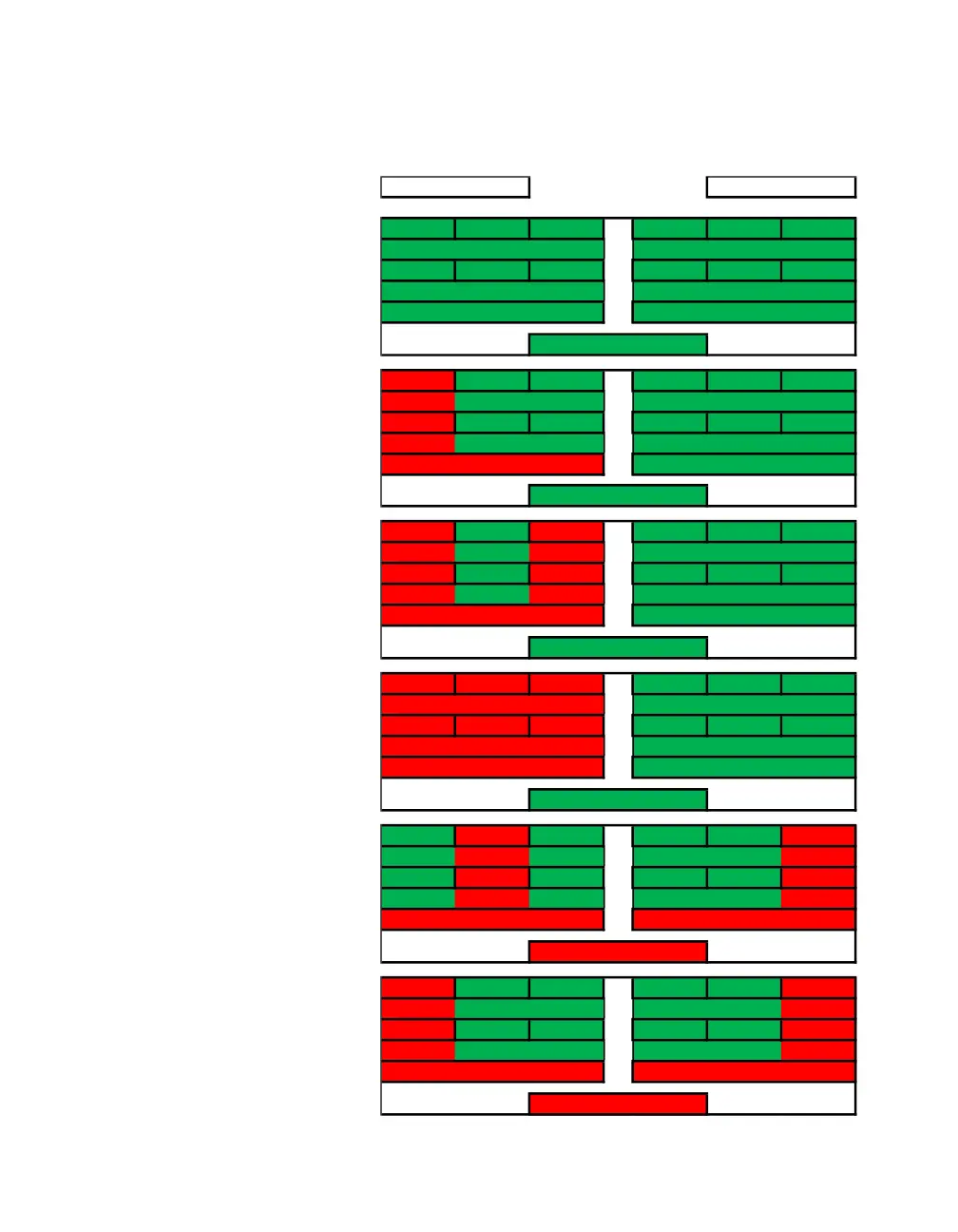
As you can see, the
difference between
RAID0+1 and RAID10 is
significant when looking at
how data is stored.
Although the drive volume
scaling and the level of fault
tolerance is the same,
internalizing the
redundancy can make a
significant difference
overall to the array.
In the examples to the
right, you can see that when
one drive fails the entire
stripe set fails; for a
RAID0+1, you would need
to rewrite 3TB worth of
data back onto the failed
node when rebuilding,
rather than 1TB for the
same drive count on a
RAID10.
RAID10 is the current
standard on Intel
®
PCH
based RAID controllers,
largely because the fault
tolerance for it is a bit more
forgiving and the rebuild
speed is overall significantly
faster than its RAID0+1
predecessor.
P-DRIVE1 P-DRIVE2 P-DRIVE3 P-DRIVE4 P-DRIVE5 P-DRIVE6
DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C
P-DRIVE1 P-DRIVE2 P-DRIVE3 P-DRIVE4 P-DRIVE5 P-DRIVE6
DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C
P-DRIVE1 P-DRIVE2 P-DRIVE3 P-DRIVE4 P-DRIVE5 P-DRIVE6
DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C
P-DRIVE1 P-DRIVE2 P-DRIVE3 P-DRIVE4 P-DRIVE5 P-DRIVE6
DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C
P-DRIVE1 P-DRIVE2 P-DRIVE3 P-DRIVE4 P-DRIVE5 P-DRIVE6
DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C
P-DRIVE1 P-DRIVE2 P-DRIVE3 P-DRIVE4 P-DRIVE5 P-DRIVE6
DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C DATA-A DATA-B DATA-C
 Loading...
Loading...