Model 35 Viscometer Instruction Manual
208878 Revision N, February 2013 32
η =
Equation 7-7
where
is the shear stress, dynes/cm
2
is also calculated as k
1
k
2
θ
γ is the shear rate, sec
-1
γ is also calculated as k
3
N
η is the viscosity, Poise
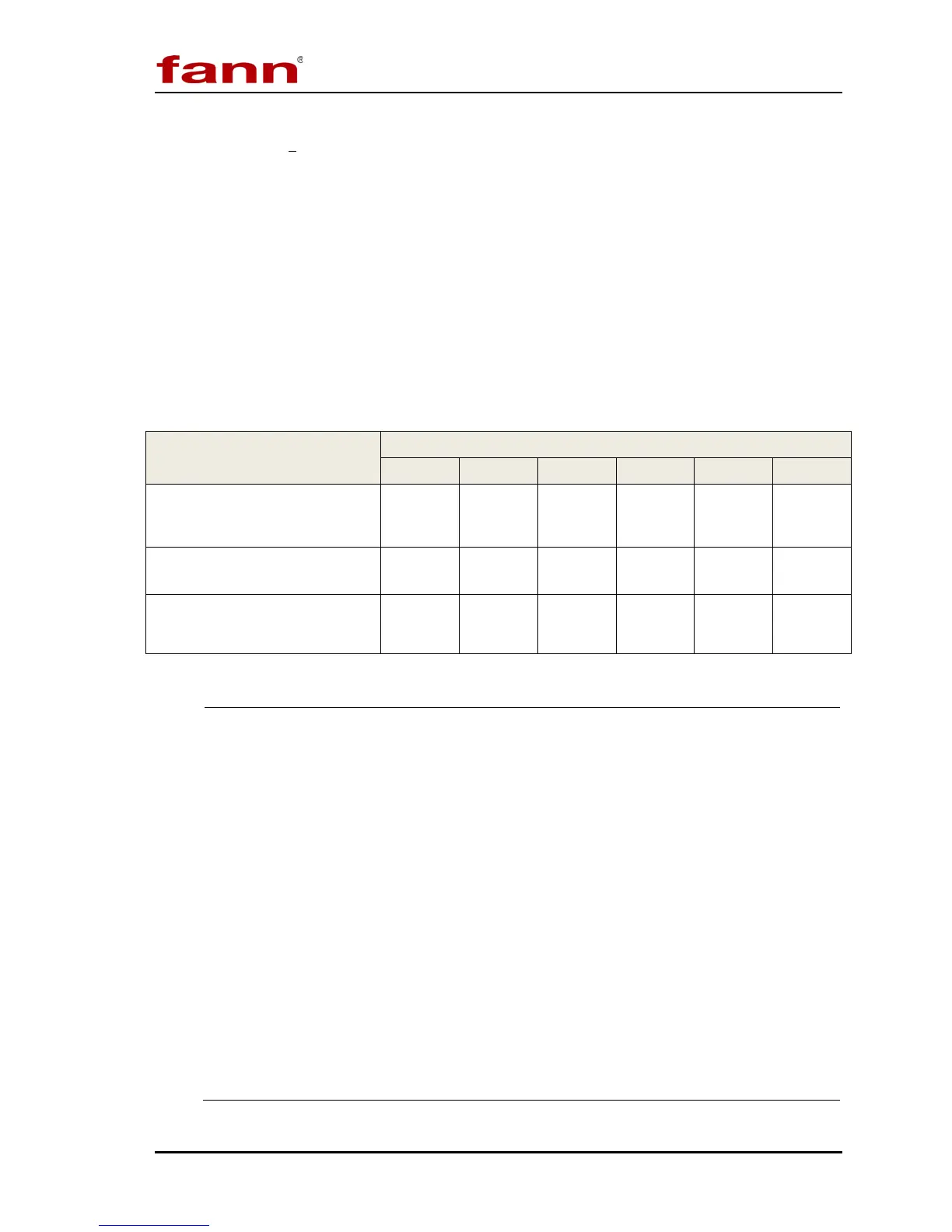
Table 7-4 Constants for Viscosity Calculations
Constant
Rotor-Bob Combinations
R1 B1 R2 B1 R3 B1 R1 B2 R1 B3 R1 B4
Overall Instrument Constant, K
Standard F1 Torsion Spring
η = Kfθ/N
300 94.18 1355 2672 7620 15,200
Shear Rate Constant k
3
,
(sec
-1
per rpm)
1.7023 5.4225 0.377 0.377 0.268 0.268
Shear Stress Constant for
Effective Bob Surface k
2
,
-3
0.01323 0.01323 0.01323 0.0261 0.0529 0.106
Table 7-5 Conversion Factors
Symbol Unit Conversion Factor
SI Units
Shear Stress
τ
Pa
(Newton/m
2
)
1 Pa = 10 dynes/cm
2
Shear Rate
γ
s
-1
1 s
-1
(no change)
Viscosity ƞ
Pa ⋅ s
mPa⋅ s
1 Pa ⋅ s = 10 poise
1 mPa⋅ s = 1 cP
Oilfield Units (R1-B1-F1)
Shear Stress
τ
dynes/cm
2
1
•
Fann = 5.11 dynes/cm
2
Shear Stress
τ
lb/100 ft
2
1
•
Fann = 1.065 lb/100 ft
2
Shear Stress
τ
lb/100 ft
2
1
•
Fann = 1 lb/100 ft
2
Shear Rate
γ
1/sec 1/sec = 1.7023 N
Viscosity
µ cP
µ = (5.11θ / 1.70N) x 100= 300 x (θ / N)
Effective Viscosity
µ
e
cP
µ
e
= 300 x (θ / N)

 Loading...
Loading...