25
3.4 How to Use the Standard I/O Library
3.4 How to Use the Standard I/O Library
In general, the programs contained in the standard I/O library are written using the C
interface. Accordingly, you must use the function execution interface for the C
language when using the library from an assembly language program.
When 0ng a function written in C, the calling program pushes the parameters being
passed onto the stack. After the function completes, the calling program must restore
the stack to its previous level.
■ Program interface
In general, the programs contained in the standard I/O library are written using the C interface.
Accordingly, you must use the function execution interface for the C language when using the
library from an assembly language program.
When using the standard I/O library from a C program, use the functions in the same way as
standard C functions.
■ Function call interface
When executing a function written in C, the calling program pushes the parameters being
passed onto the stack. After the function completes, the calling program must restore the stack
to its previous level. When there is more than one argument, push the arguments onto the stack
in order from the right. For value arguments, push the 2-byte or 4-byte value onto the stack. The
number of bytes is determined by the type (two bytes for the char and short (int) types and four
bytes for the long type). For address arguments, push the 4-byte address for the large model or
2-byte address for the small model.
The function return value is returned in the AL register.
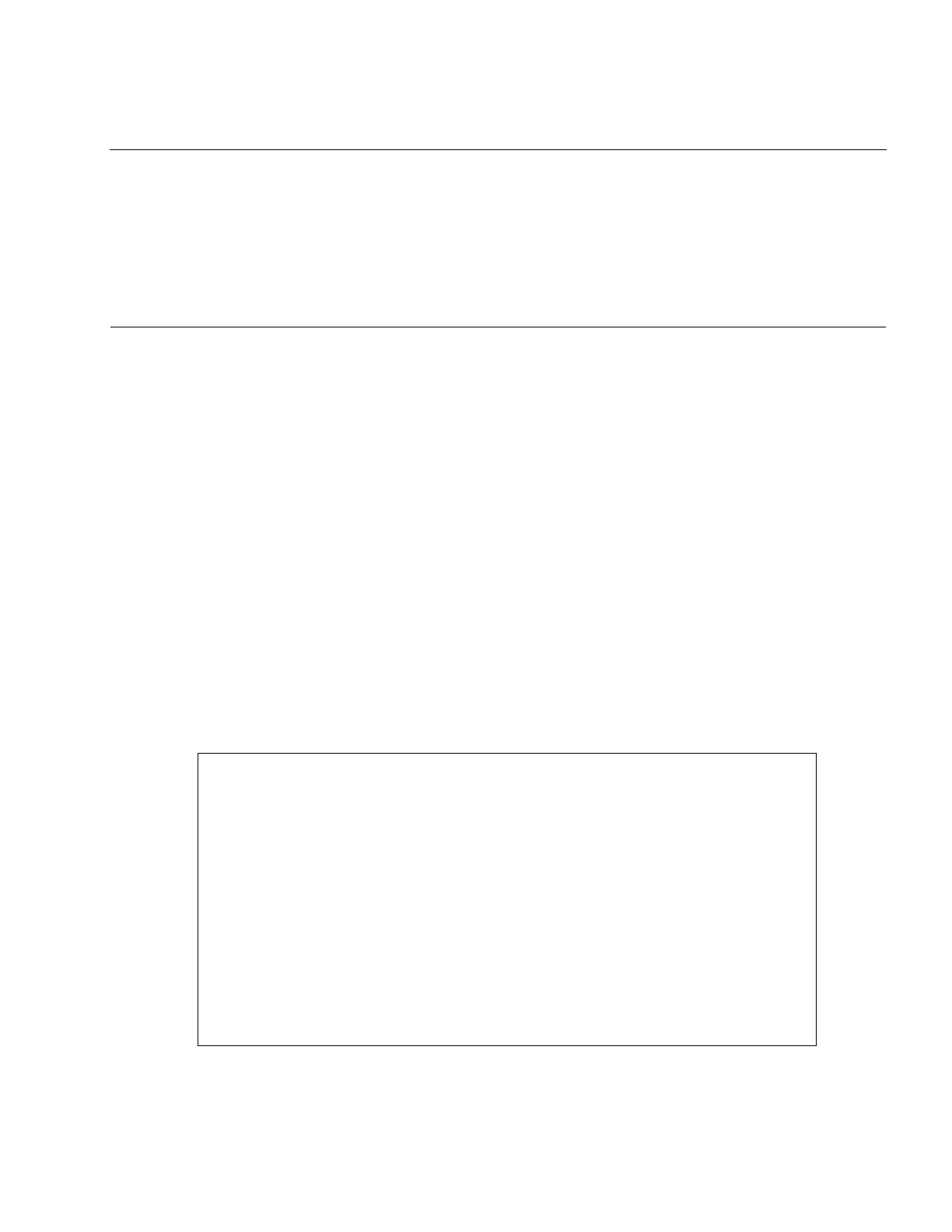
Figure 4.4a shows an example of calling the "chrcnt = printf("%d %ld \n", 100, 5000L);" function
from assembly language. The example is for the large model library.
.import _printf
.section CSEG,CODE,ALIGH=2
format .data.b"%d %|d", 10, 0 ; \n = 10, string terminator = 0
: :
movl a,#5000 ; Push long data (5000) onto stack
pushw ah ;
pushw a ;
mov a,#100 ; Push int data (100) onto stack
pushw a :
movl a,#format ; Push address of format string onto stack
pushw ah :
pushw a :
callp _printf ; Execute printf. Add _ in front of the entry label
addsp #10 ; Release stack
; AL=chrcnt
Figure 3.4a Example of Calling the printf Function
 Loading...
Loading...