Sampling time (T) : is the time to sample the feedback value. In eachs ampl ing period thecontroller
runs one time.The l onger the sam plingt ime, the sl ower the r esponding.
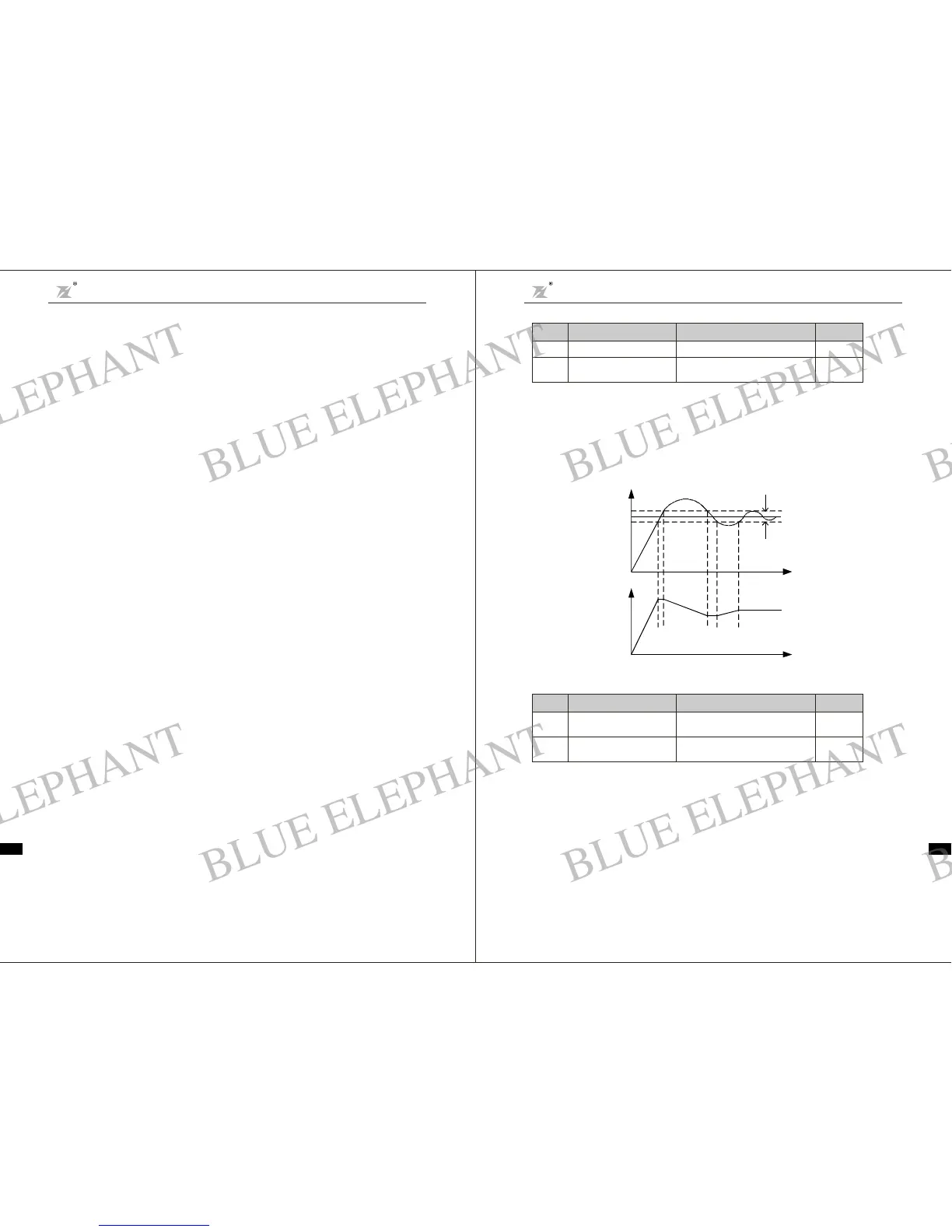
PID c ontroldiscr epancy limit:t he allowable maximum discrepancy o f PID sys tem outputvalue re lative
t othe cl osed-loop as sign ed value.Asshown in following diagram, w ithin the discrepancylimit, PID
controller stops adjustment. Properlysetting t his function code can improve t he accuracy and stabilit y of
PIDsystem.
Feedback disconnected detecting value:this detecting valueis relative to the full range (100%) .
The systemdetects the P ID feedback valueall the time.When thefeedback value is less orequal to the
feedbackdisconnected detecting value,the syst em s tarts to time the detection.When the detecting time
exceeds thef eedbac kdi sconnected detect ing time, the system will s end an a lert offeedba ck disconnecting
failure .(E02E)
Fig. 6-19Coi ncidenc e relation of discrepa ncy limit and output frequency
Feedback
Assigned
Value
Discrepancy Li mit
Output f
Time t
Time t
F4.25
Samplingcycletime(T)
0.01 99.99 s
~
0.10s
F4.2 6
P ID c ontrol
di sc repanc y li m it
0.0 100.0%
~
0.0 %
Fu nction
Code
Name
Setting Rang e
Default
Value
F4.27
Feedb a ck di sconn ection
de t e cting value
0.0 100.0%
~
0.0 %
F4.28
Feedb a ck di sconn ection
detecting t ime
0.0 360.0s
~
1.0 s
Fu nction
Code
Name
Setting Rang e
Default
Value
Chapter 6 Parameter D escripti on
DZB Series
-62-
Proportional gain (K p): det ermi nesthe adjusting strength of PI D adjustor. T hebigger the P, the bigger
the a djus ti ng st reng th is. This para m e te r be ing 100 means tha t wh en th e d iffer e n ce betw ee n the PID
fee dback value a nd the assi gnedvalue i s 100%, the adjustingrange of PID a djus torto the output freque ncy
command isthe m axi mum frequency ( ignore i ntegralaction a nd derivativeaction).
Integrating ti me (Ti): determi nesthe speed at which PID adju stor performs integral regu lat ion to the
discre pancy betweenthe PIDfeedbackvalue and t he assigned value.The Tiis indicati ng the per iod of time
tha t integral contr oll er (ignore proporti onala ction and derivative action),when the discrepancy between
the PID feedba ck value and the assigned va lue i s 100%, continuously re gulates to make the regulating
amou ntto reach the m axi mum frequency ( F0. 047).The shorter the i ntegra tingtime,the st ronger the
ad justing strength i s .
Differenti al time (T d): determi nes the contr ollingstrengtha t whichPID adjustor pe rforms adjustment
to the va r ia nce r atio of d i scre pa n cy be tw een th e PI D feedback value an d the a ssi g ned va lue. TheTd is
indi catingt he period of time w ithin whi ch if the fee dback value is chang ed 100%, t he regulating amount
of integral controlleris the maximum frequency (F 0. 04)(i gnor e proporti onalaction and integral action).
The longe rthe Td ,the bigger the c ontrolling s trengthis.PID is the most popularl y used cont rolmode in
process control,with ea ch part pl aying different role.Following simplyintroducesthe operational
principle and the controlling method:
Proportion cont rol (P): when thereis dis crepa ncy betweenfeedbackand the assignment,output t he
regul ating amount in proporti onto the discrepancy.If t he discrepancy is c onstant, the regulating amount
kee ps constant. Pr opo rt ion c ontrol can res ponsequickl yto the feedback va ria tion,butonly u sing
proportion control is unabl e to perf ormnoncorrespondi ngcontrol .The b iggerthe proportional gain, the
fast er the s ystem regulating speed, but being too bigma ycause os cillation. The control methodis first to
seta long int egratingtime and a zero differ entialtime, and then run the s ystem only byusing proportion
cont rol. Change the assigned value,and wa tch the stablediscrepancy(steady-stat e error)of feedback
signal andassigned value. If the s te ad y-stateerror isat the varying directi on ofassigne d value(for
instance, i ncrease the assigned value, the feed back value after the system is st eady is always less than the
as signed value),continue to increase theproportional gain, otherwise decrease it.Repeat t he above until
the ste ady- st a te e rror is relativ e ly s m all (i t is v ery d iffic ult t o do n o steady-s ta te er r or).
Integral t ime(I): when there is a discrepa ncy between the feedbac k and assignment, continuously
acc um ulate t he o ut pu t regu l a tion a m ou nt. I f th e discr e p ancy s ti ll e xists, co ntinu e to increase the reg ula ti o n
amou ntuntil ther e is nodi screpancy. I nte gralcontrollercan e ffectively eliminatet hesteady-stateerror.
Integral controller being too strong can cause repeated overs hooti ng, system unstable a ndup tilloscillati ng.
The characteri sti c ofoscillation c aused b ytoo strong integral actionis t hatt he feedba ck signal i s swinging
up and downaround the assigned value,and the amplitude ofswing inc reases graduallytill theoscillation
happens. Normally th e integral timeis adjusted frombigt osmall, gradually regulate the integral time, and
wa tch the effec t, until the system stable speed meet sre quirements.
Differentialtime (D): whenthediscrepancy betweenfeedback and assignment varies,output a regulation
amount i n pro portion to the v arianc e r atio of di scr epancy. The regul ation a mount is r e lated t o t h e dire ct ion
and magnitude of discrepa ncyvariation, but irrel evant to the direction and value of the d iscrepancy itsel f.
The differential contr olactioni st o per formthe c ontrol according to the va ryingtrend whe n the feedback
signal variationhappens, and ther ebyto restra in the feedback signal va riation. It should be c aution to use
dif fere nti alcontrolle r a s the di ffer ential controlhave a trend tomagnify the system i nterference , especiall y
the high varyingf requencyinterference.
Chapter 6 Parameter Descr iption
DZB S eri es
-61-
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
BLUE ELEPHANT
 Loading...
Loading...