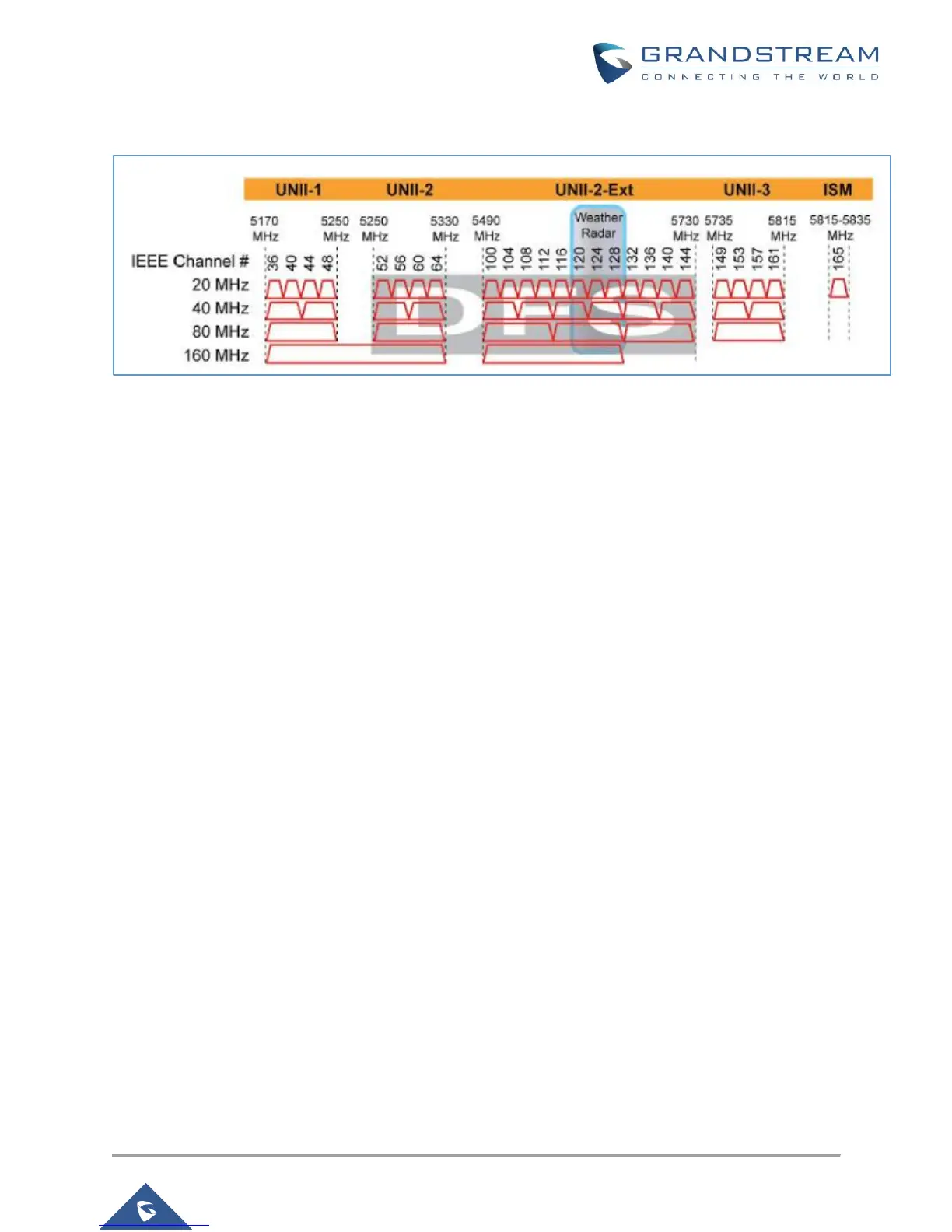
Below is an example for US GWN model, 5GHz channel numbers and distribution maps (Figure 11):
Figure 11: 5GHz channel numbers and distribution maps (GWN US model)
• 20MHz channel width: 9 available (CH36~48, CH149~CH165)
• 40MHz channel width: 4 available (CH38, CH46, CH151, CH159)
• 80MHz channel width: 2 available (CH 42, CH155)
c) More spatial streams (NSS)
By 802.11ac standard, it can achieve up to 8SS (compared to the 4SS of the 802.11n standard,
theoretically this is 100% growth). However, considering the production cost, and the size of Access
Point, 2~3SS are commonly used. From the client device, 1 (smartphone) to 2 (tablet, notebook) space
streams are common accepted.
d) Introducing multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO)
MU-MIMO introduced by the second-generation 802.11ac product (ie 802.11ac Wave2) is not used to
improve the connection speed, but to improve the transmission efficiency. To directly take advantage of
MU-MIMO, it requires client to support 802.11ac Wave2 too.
Figure 12 is a diagram of downlink transmission of SU-MIMO and MU-MIMO, where SU-MIMO represents
the first generation 802.11ac standard and MU-MIMO represents the second generation 802.11 standard.

 Loading...
Loading...