17
Figure 8 Identifying whether the devices are commonly grounded well
Troubleshooting through looping
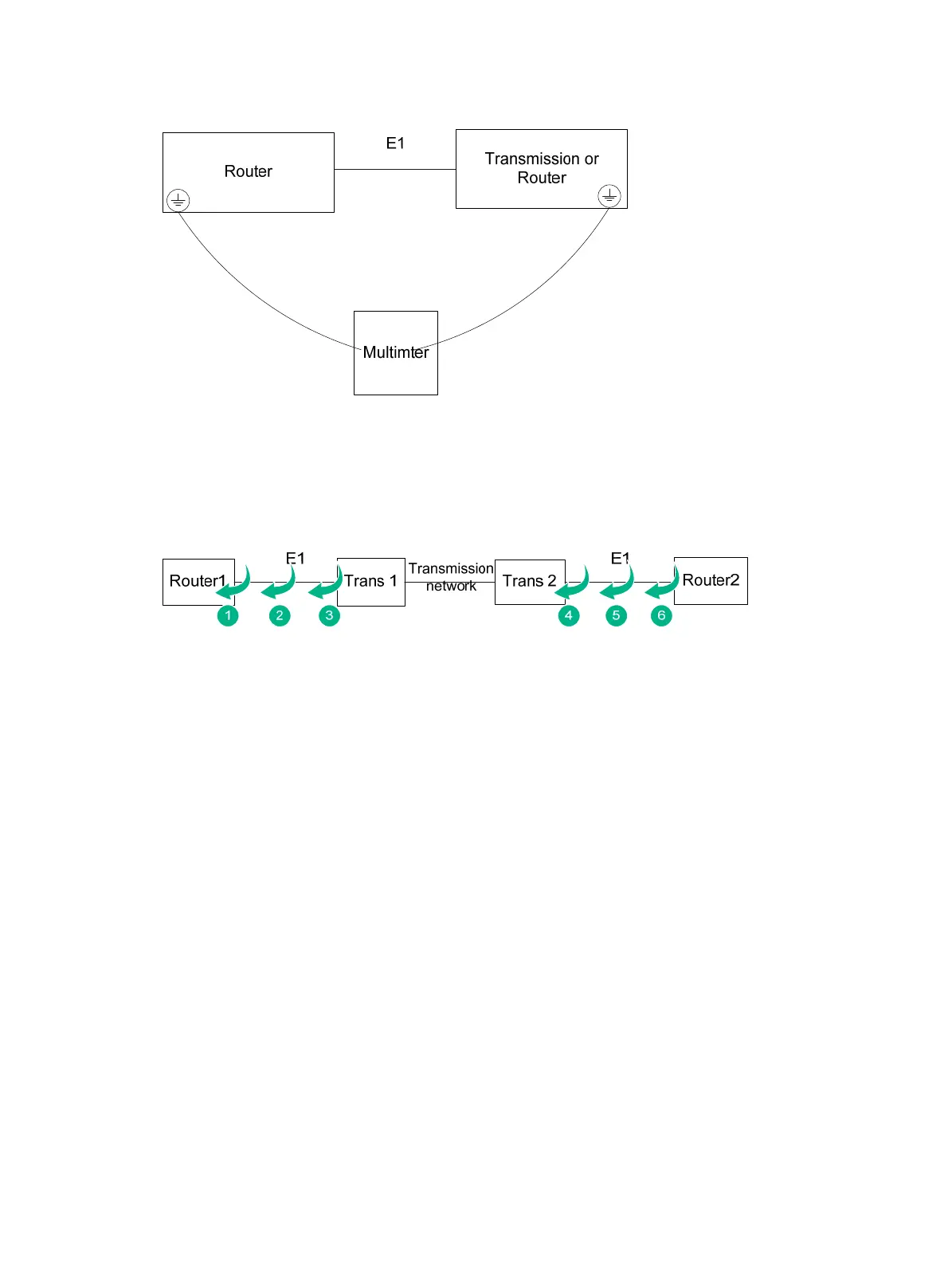
Common looping points
Figure 9 Common looping points (vice versa)
Looping point 1
Method: Execute the loopback local command on the E1 interface of the router, and execute the
fe1 loopback local command on the FE1 interface.
Purpose: Verify that the router interface can properly send and receive packets.
Looping points 2 and 3
Method: Short connect the Rx and Tx cables between Router1 and transmission device 1 or form a
leftwards loop on the transmission device.
Purpose: Verify that the line between Router1 and transmission device 1 is normal.
Looping point 4
Method: Form a leftwards loop on transmission device 2.
Purpose: Verify that the transmission network is normal.
Looping point 5
Method: Short connect the E1 Rx and Tx cables between Router1 and transmission device 1.
Purpose: Verify that the line whole physical link between Router1 and Router 2 is normal.
Looping point 6
Method: Execute the loopback remote/payload command on the E1 interface of Router 2, and
execute the fe1 loopback remote/payload command on the FE1 interface of Router 2.
Purpose: Verify that the whole link including Router 2 is normal.
Troubleshooting lines after looping
Use the self-loopback test function of the router to troubleshoot lines

 Loading...
Loading...




