53
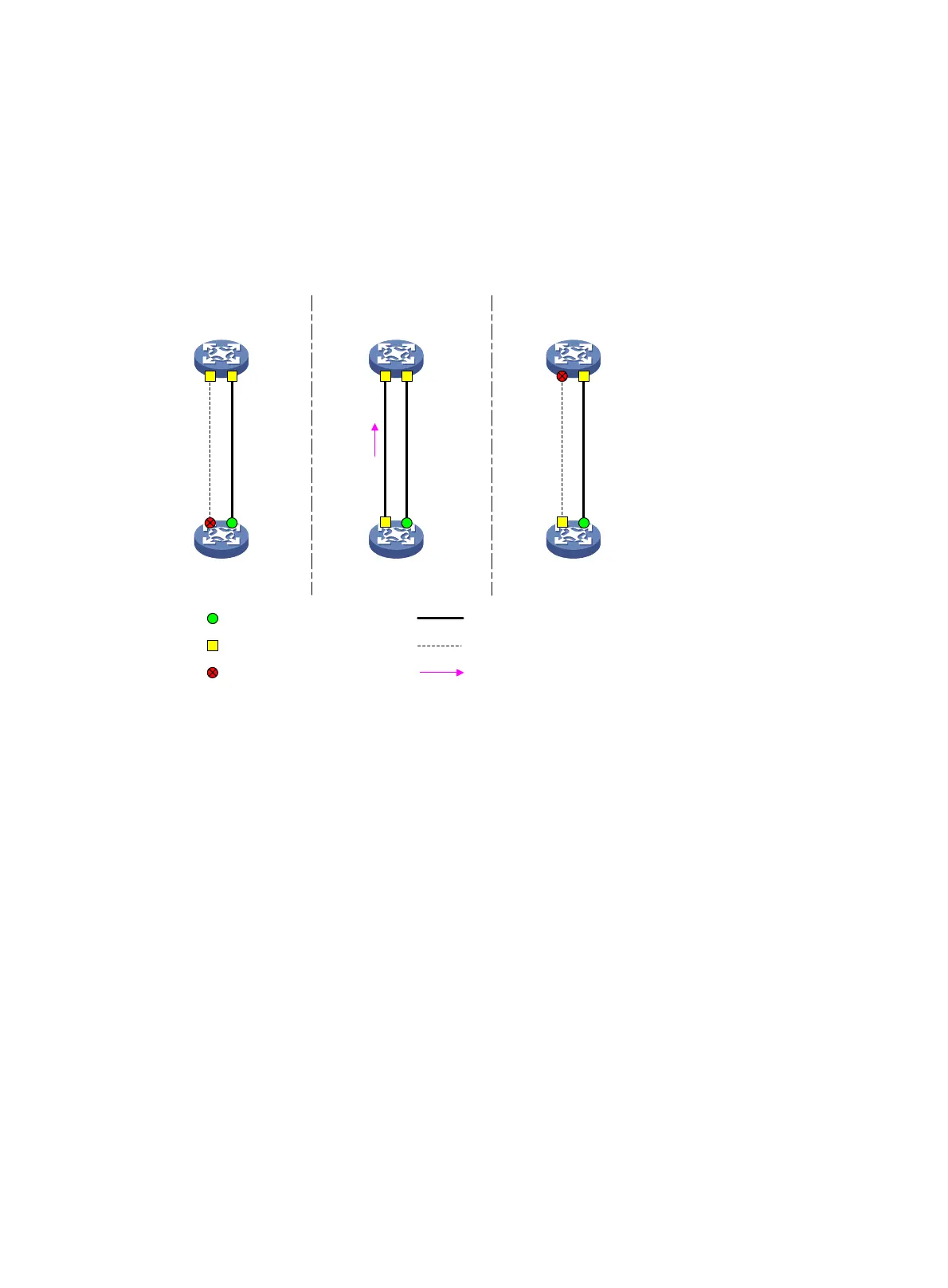
1. Port A1 can only receive BPDUs and cannot send BPDUs to Port B1.
2. Port B1 does not receive BPDUs from Port A1 for a certain period of time.
3. Device B determines itself as the root bridge.
4. Port B1 sends its BPDUs to Port A1.
5. Port A1 determines the received BPDUs are inferior to its own BPDUs. A dispute is detected.
6. Dispute guard is triggered and blocks Port A1 to prevent a loop.
Figure 19 Dispute guard triggering scenario (on a designated port)
As shown in Figure 20, in normal conditions, Device A is the root bridge, and Port B1 and Port C1 are
root ports. When the links between Device A and Device B become unidirectional (the links fail in the
direction of Port A1 to Port B1), the following events occur:
1. Device B cannot receive BPDUs from Device A.
2. Device B determines itself as the root bridge.
3. Port B1 sends BPDUs in which the root bridge is Device B to Port C1.
4. Port C1 receives BPDUs from two root bridges, Device A and Device B. A dispute is detected.
5. Dispute guard is triggered and blocks Port C1 to avoid a loop.
Device A
Device B
Root
Root port
Designated port
Normal link
Blocked link
Blocked port
Port A1 Port A2
Port B1 Port B2
Device A
Device B
Root
Port A1 Port A2
Port B1 Port B2
Normal condition
Unidirectional link
occurs
Device A
Device B
Root
Port A1
Port B1 Port B2
Dispute guard is
triggered
Port A2
Unidirectional link

 Loading...
Loading...











