18 / 23
Heart rate refers to the number of heartbeat per minute. Normally, it ranges from 60-100
bpm , which varies by age, gender, diet, emotion or other physiological factors and external
conditions. . In general, younger individuals have a higher heart rate than the elderly and
females have a heart rate than their male counterparts. The normal adult human heart rate is
60-100 bpm. Ideal heart rate is 55-70 bpm (athletes tend to have lower heart rates, usually 50
bpm).
Resting heart rate is the number of heartbeat per minute at total rest. It is found that the
changes in resting heart rate over time are related with the death rate due to heart disease. In
general, within the normal range, the resting heart rate is: the lower, the better. Ways to lower
the resting heart rate are to exercise and to lose weight.
Maximum heart rate is the highest heart rate an individual can achieve without severe
problems through exercise stress. Current prevailing calculation formula is: HRmax=220 – Age.
Target heart rate is the safe range for how fast your heart should beat while you exercise, to
improve the aerobic endurance level for cardiovascular system. Current prevailing calculation
formula is:
Target heart rate range=(HRmax-HRrest) x 0.6 + HRrest ~~ (HRmax-HRrest) x 0.8 + HRrest.
For example, a man ages 22 with HRrest of 68, his target heart rate range is:
((220-22)-68)x0.60+68=146~~((220-22)-68)x0.80+68=172, that is, 146~~172.
Normally, heart rate increases immediately after exercise and decreases at a fast rate after
exercising stopped, that is, heart rate recovery time is quite short. --------->(If occurrence of a
slow heart rate increases and decreases, please see your physician
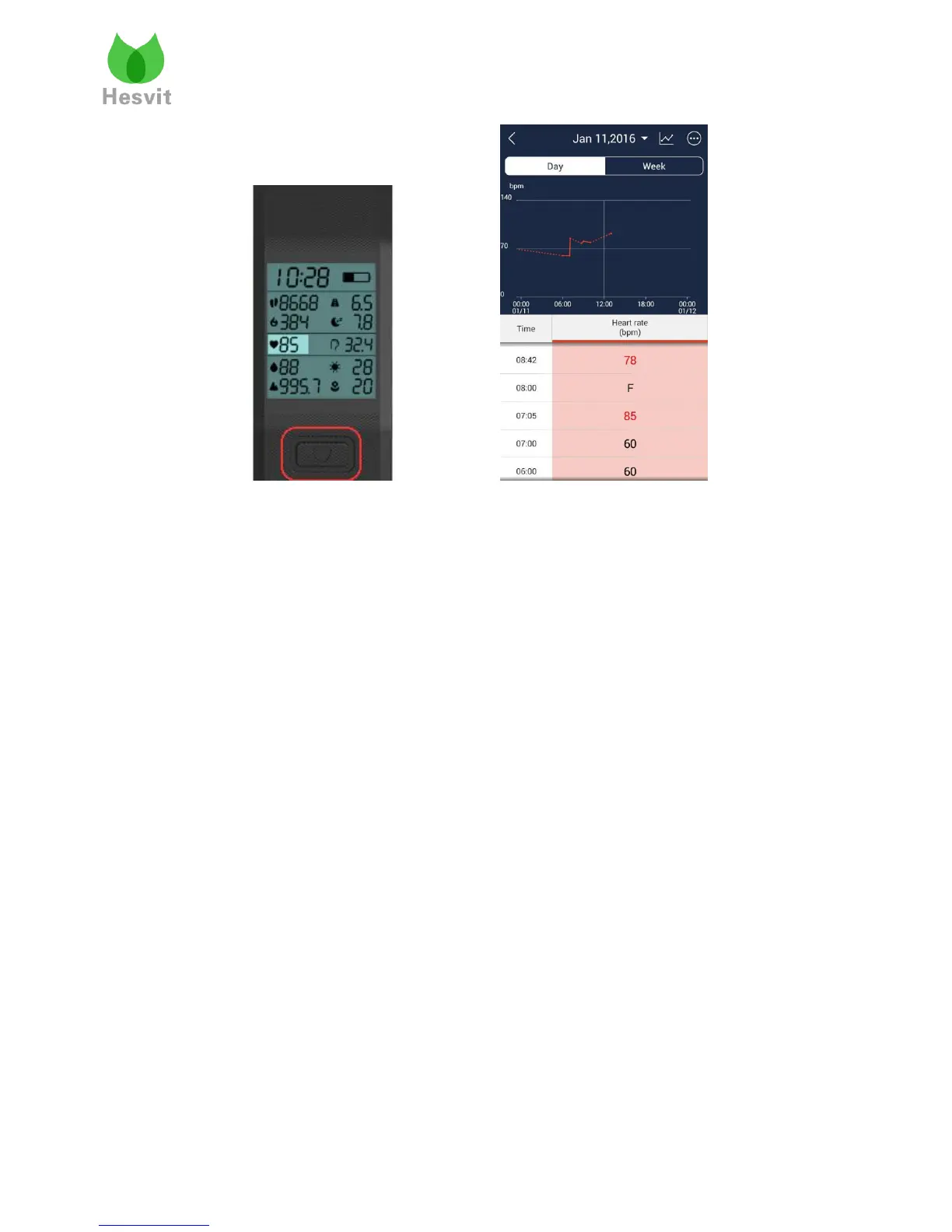
Heart rate is obtained by measuring the pulse. With the photoelectric reflection sensor, it
obtains the wrist blood pulse signal. The blood pulse is consistent with the heart rate.
To measure the heart rate accurately, wear the Hesvit S3 tightly around a bare wrist about
2cm above the wrist joint. Heart rate test may fail in the following situations: 1) Improper
wearing of the Hesvit S3; 2) Too large space between the Hesvit S3 and your wrist; 3) Too large
amplitude of the arm swings, e.g., during running or walking.
 Loading...
Loading...