28
3-3 APPLICATION AND SELECTION
Selection of thermal overload relays must be determined by taking into consideration the type of motor, required
function, type of load and starting method, etc.
3-3-1 General Selection
Table 21 gives the general selection in case running and stopping do not include inching and plugging and the starting
time is not so long.
If the probability of phase failure and negative phase trouble is considered to be extremely low, selection of
standard type (1E) thermal overload relay makes it possible to protect the motor almost completely.
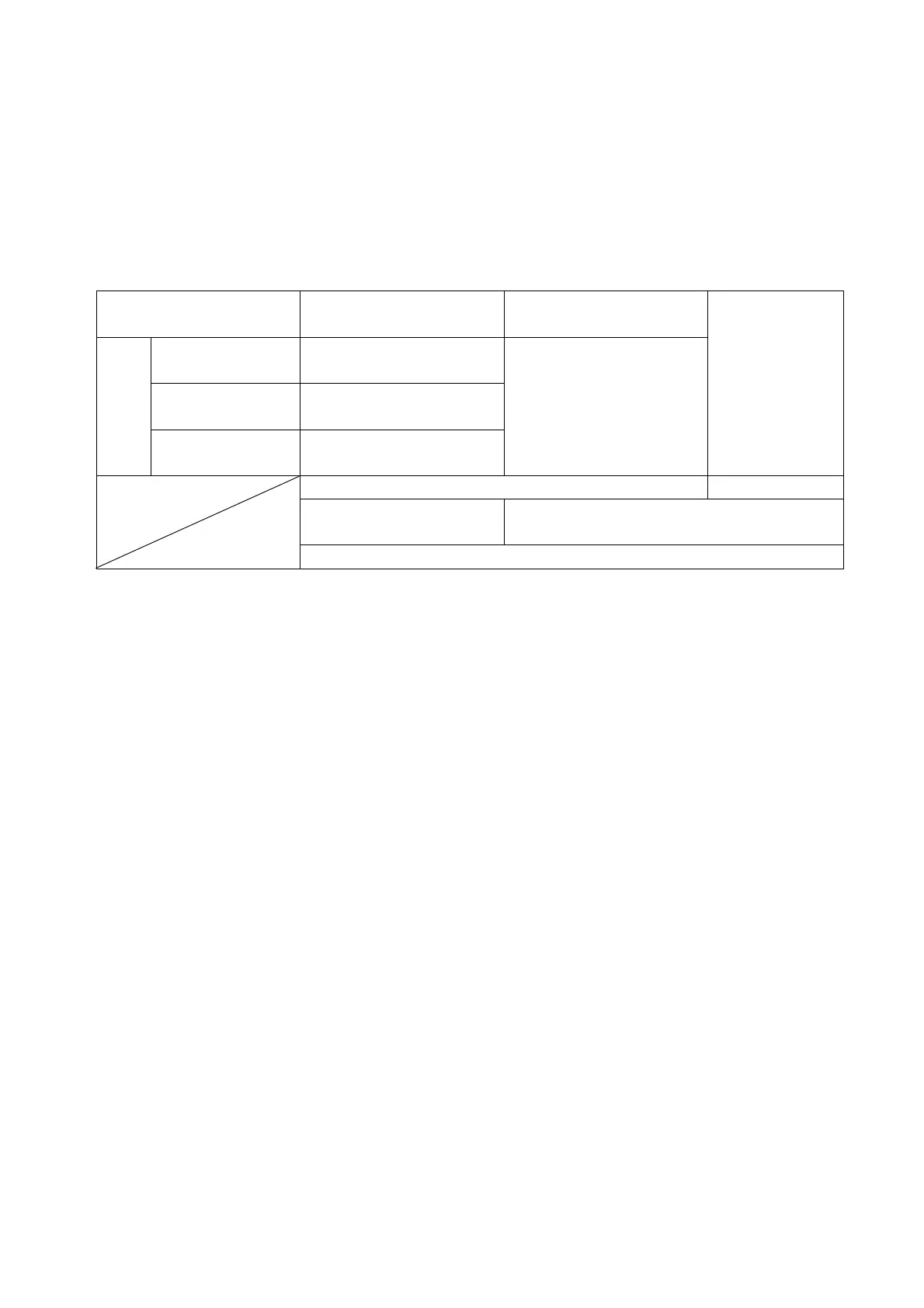
Table 21. General selection
Submerged pump
and motor
Quick response type
1E thermal overload relay
Quick response type
2E thermal overload relay
Motor up to
200kW
3 -element
1E thermal overload relay
Motor of less than
3.7 kW
2-element
1E thermal overload relay
General-purpose
motor
Very small capacity
motor
3-lement
1E thermal overload relay
2E thermal overload relay
Static 3E relay
-
Rough protection to
Phase failure
More stringent phase-failure protection
Object
Required
function
Overload/restriction protection
3-3-2 Selection for Small Capacity Motor
The reasons why a 2-element 1E thermal overload relay is selected for a small capacity motor of less than 3.7kW
in Table 21 are as follows :
・ Even in the case of 2-element thermal overload relay, the phase-failure operating performance is extremely high.
The 2-elernent thermal overload relay has the same phase-failure operating performance (conform to IEC standard)
as the 3-element type.
・ The small capacity motor has a characteristic that the winding temperature rise is lower at phase-failure running
compared with medium- or large capacity motors due to structural reasons, such as star-connect ion of motor
winding.
Fig. 25 indicates the experimental values of the temperature rise ratio at phase-failure. Fig. 26 indicates conversion
of the experimental values in Fig. 25 into temperature rise ratio at operation of thermal overload relay. When using
the 2-element type with high performance, it is possible judging from the figure to make protection at phase-failure.

 Loading...
Loading...