3 Piping work and refrigerant charge
Copper refrigerant pipe
SMGB0099 rev.0 - 12/2016
100
3.4 Copper refrigerant pipe
3.4.1 Three principles on work with refrigerant pipes
The basic refrigerant pipe installation work must be carried out paying particular attention to avoid the inltration of
humidity or dust while working with the refrigerant piping. Otherwise, rust may appear inside the system or the units and
cause serious faults.
Therefore, all work carried out on the copper pipes for refrigerant must follow the three principles described below.
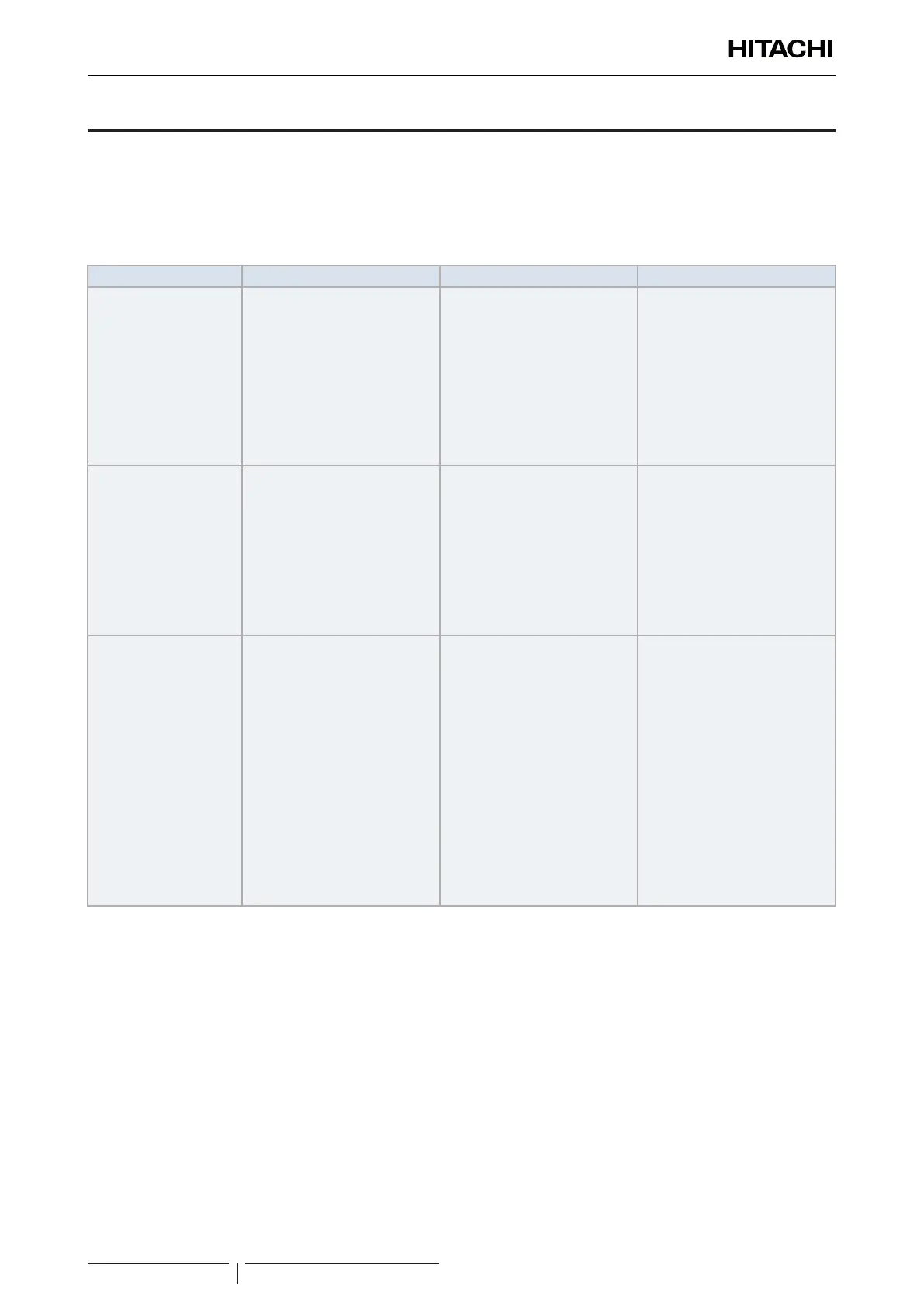
Principle Cause of the fault Possible fault Preventive measure
1. Absence of humidity
Ensure the atmosphere
remains totally dry
Water inltration due to
insufcient protection on the ends
of the pipes.
Condensation on the inside of the
pipes.
Insufcient vacuum.
Ice on the inside of the pipe,
on the expansion valve (water
obstruction)
+
Absorption of oil humidity and
oxidation
↓
Filter clogging, insulation and
compressor fault
Pipe protection:
1. Seal the ends of the pipes.
2. Protect and insulate the ends
of the pipes.
↓
Wash
↓
Vacuum dry
(*)
2. Cleaning
Absence of dust on the
inside of the piping
Dust or other elements entering
the ends of the pipes.
Film of rust formed during
brazing without nitrogen
injection.
Insufcient nitrogen wash after
brazing.
Expansion valve, capillary tube
and lter clogging.
Oil oxidation.
Compressor fault
↓
Compressor fault, insufcient
cooling or heating
Pipe protection:
1. Fit caps to the ends of the
pipes.
2. Protect and insulate the ends
of the pipes.
↓
Wash
3. Absence of leaks
There must be no leaks
Brazing fault.
Flaring fault and insufcient
torque.
Insufcient torque on
compressor connectors.
Lack of refrigerant
Drop in performance
Compressor fault
Oil oxidation.
↓
Compressor overheating
Carry out basic brazing work
carefully
↓
Carry out basic aring work
carefully
↓
Carry out basic connection work
carefully
↓
Airtight test
↓
Preserving of vacuum in the
installation
(*) One gram of water becomes approximately 1000 l of steam at 1 Torr. (1 Torr = 1 mmHg = 133.32 Pa). Therefore, a
long time must be spent on vacuum work using a small pump.

 Loading...
Loading...











