Fault tolerance
Drive failure, although rare, is potentially catastrophic. For example, using simple striping as shown
in Figure 17, failure of any hard drive leads to failure of all logical drives in the same array, and
hence to data loss.
To protect against data loss from hard drive failure, storage servers should be configured with fault
tolerance. HP recommends adhering to RAID 5 configurations.
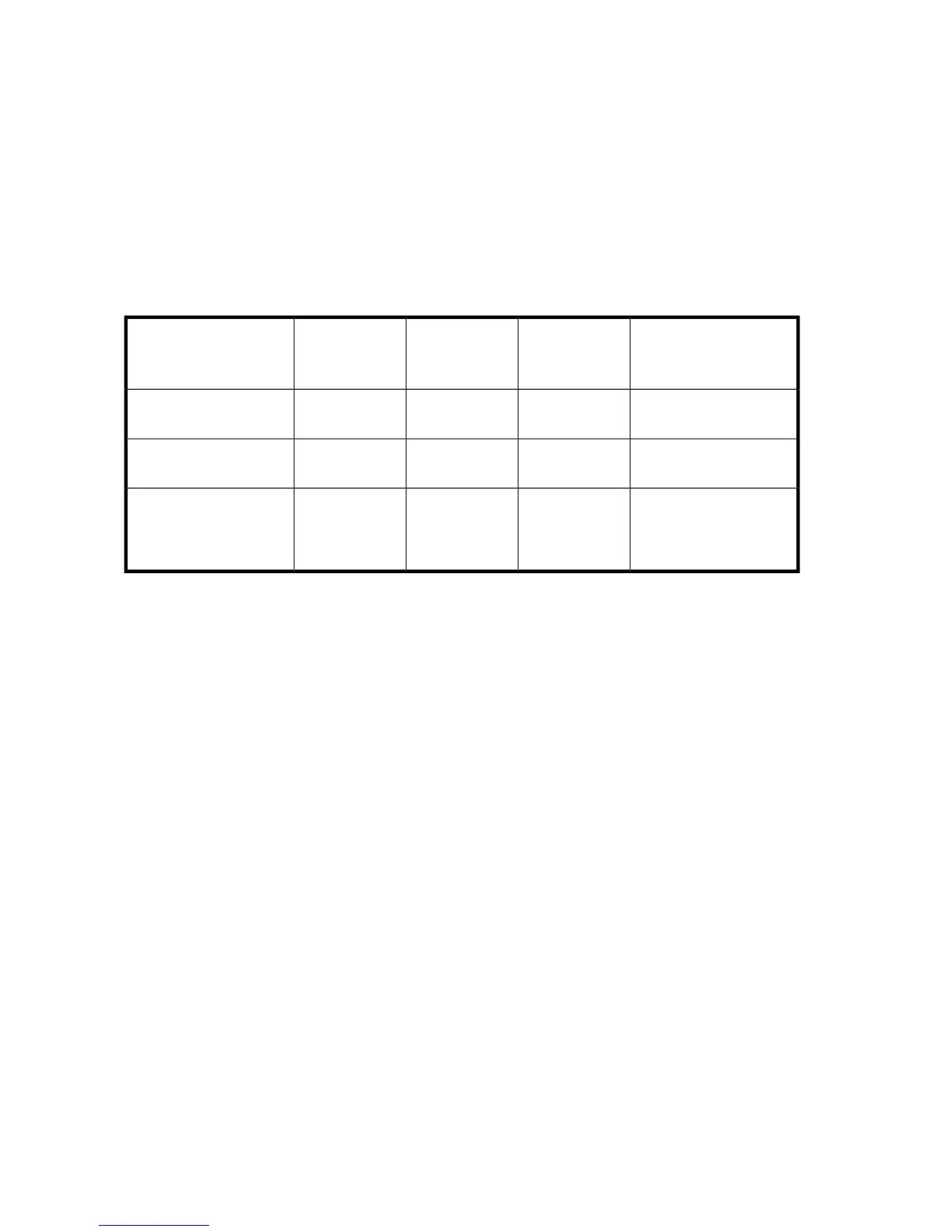
The table below summarizes the important features of the different kinds of RAID supported by the
Smart Array controllers. The decision chart in the following table can help determine which option is
best for different situations.
Table 19 Summary of RAID methods
RAID 6 (ADG)
RAID 5
Distributed
Data Guarding
RAID 1+0
Mirroring
RAID 0
Striping (no
fault tolerance)
Storage system dependent14N/AN/A
Maximum number of hard
drives
YesYesYesNo
Tolerant of single hard
drive failure?
Yes (two drives can fail)No
If the failed
drives are not
mirrored to
each other
No
Tolerant of multiple
simultaneous hard drive
failures?
Online spares
Further protection against data loss can be achieved by assigning an online spare (or hot spare) to
any configuration except RAID 0. This hard drive contains no data and is contained within the same
storage subsystem as the other drives in the array. When a hard drive in the array fails, the controller
can then automatically rebuild information that was originally on the failed drive onto the online spare.
This quickly restores the system to full RAID level fault tolerance protection. However, unless RAID
Advanced Data Guarding (ADG) is being used, which can support two drive failures in an array, in
the unlikely event that a third drive in the array should fail while data is being rewritten to the spare,
the logical drive still fails.
Logical storage elements
Logical storage elements consist of those components that translate the physical storage elements to
file system elements. The storage server uses the Window Disk Management utility to manage the
various types of disks presented to the file system. There are two types of LUN presentation: basic
disk and dynamic disk. Each of these types of disk has special features that enable different types of
management.
Logical drives (LUNs)
While an array is a physical grouping of hard drives, a logical drive consists of components that
translate physical storage elements into file system elements.
Storage management overview56

 Loading...
Loading...











