Selecting Functions 5-35
5
PID control (I (integral time))
•
I action
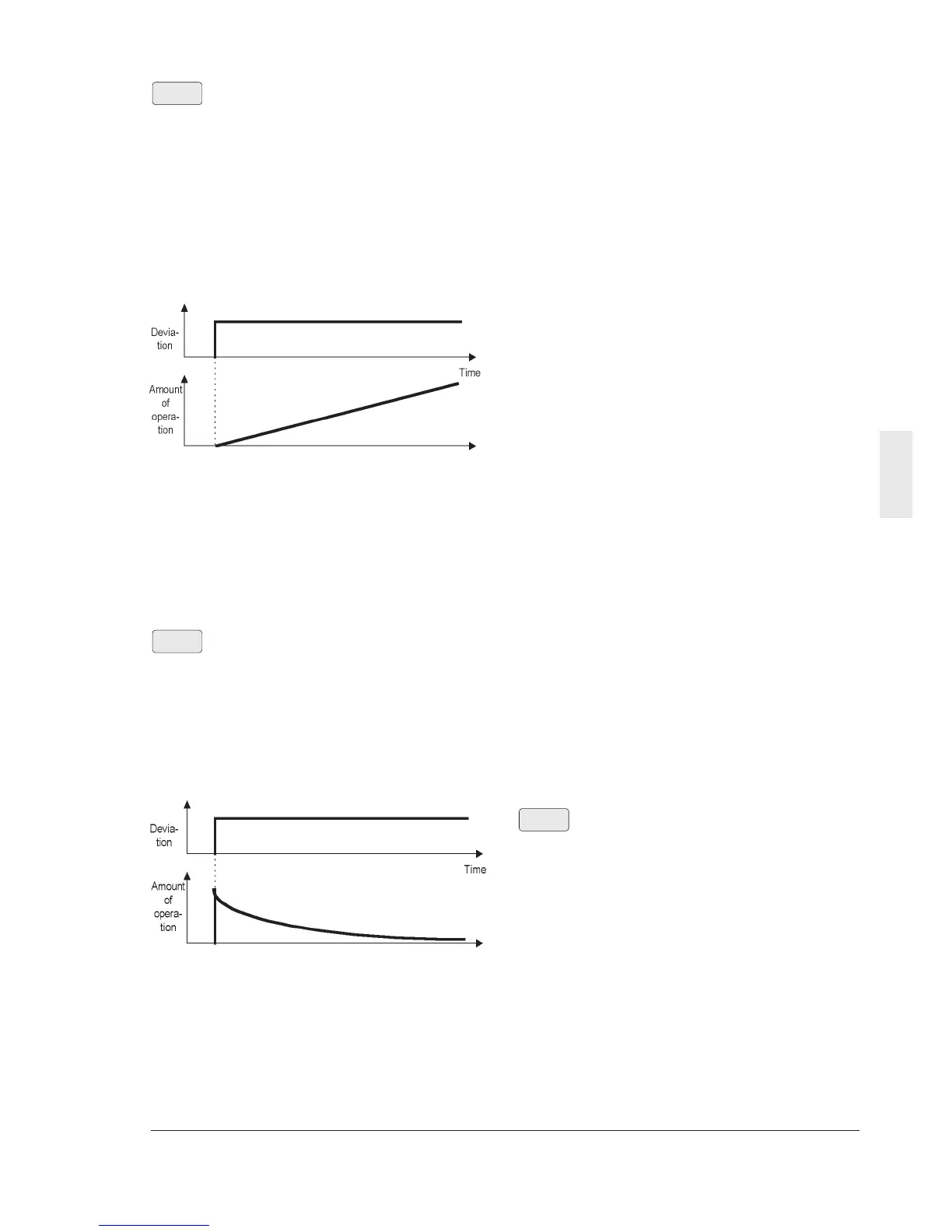
An operation where the speed of the change
in the amount of operation is proportional to
the deviation is called I action. Therefore the
I action outputs an operation amount
obtained from integration of the deviation. For
this reason, the I action is effective to
converge the control amount to the reference
value. However, response is slow to the
deviation with abrupt changes.
H23
Setting range: 0.0 Inactive, 0.1 to 3600 s
To determine the effect of the I action,
I: integral time is used as a parameter. With a
long integral time, the response is slow and
reaction to an external force is small. With a
small integral time, the response is quick.
When the integral time is too small, there is
hunting.
PID control (D (Differential time))
•
D action
An operation where the amount of operation
is proportional to the differential value of the
deviation is called D action. Therefore, the D
action outputs an operation amount obtained
from the differentiation of the deviation and the
response to abrupt changes is quick.
H24
time, vibration may become larger. With a
small differential time, decrease in the
deviation becomes smaller.
•
PI control
Deviation remains with P action only. To
eliminate the remaining deviation, I action is
added and P + I control is generally adopted.
The PI control functions to always eliminate
deviation in spite of changes in the reference
value and stationary disturbances. However,
when the I action is strong, response to the
deviation with abrupt changes is slow.
P action only can be used for loads with an
integral factor.
•
PD control
Upon deviation, the PD control generates an
operation amount larger than that obtained by
D action only, to reduce the increase of the
deviation. When deviation is reduced to
small, the function of the P action is made
smaller.
For a load including integral factors to be
controlled, the P action alone can cause
hunting in the response due to the action of
the integral factors. The PD control is used in
such cases to decrease hunting of the P
action to stabilize. That is, this control method
is applied to loads having no braking in the
process itself.
•
PID control
The function of the I action to reduce the
deviation and the function of the D action to
suppress hunting are combined with the P
action. Accurate responses without deviation
are obtained.
This control method is effective to loads
which take time from generation of deviation
to development of a response.
PID control (Feedback filter)
•
This function provides a filter for the feedback
signal input at control terminal 12 or C1. The
filter makes the operation of the PID control
system stable. However, an excessively large
setting causes a poor response.
Setting range: 0.0 to 60.0 s
H25
Setting range: 0.00 Inactive, 0.01 to 10.0 s
D: differential time is used as a parameter to
determine the effect of the D action. With a
long differential time, decrease in the
vibration caused by the P action upon
deviation is quick. With too large a differential
 Loading...
Loading...