MEMORY MANAGEMENT AND VIRTUAL ADDRESSING
Thus,
so
long
as
a particular selector value
is
valid (i.e., it points
to
a valid segment descriptor within
the bounds of the d()scriptor table), it can
be
readily associated with an 8-byte descriptor. When a
selector value
is
loaded
into.
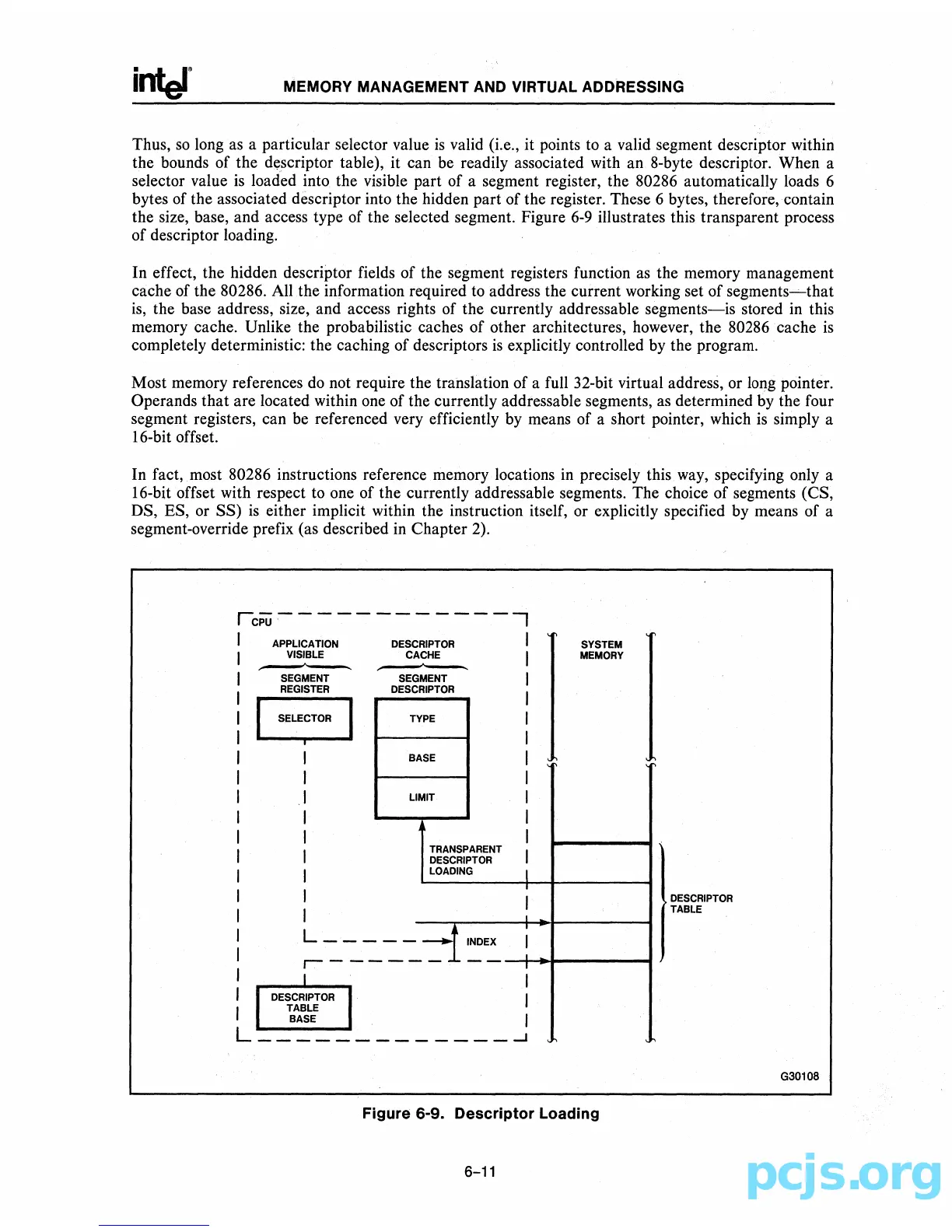
the visible part of a segment register, the 80286 automatically loads 6
bytes of the associated descriptor into the hidden part of the register. These 6 bytes, therefore, contain
the size, base, and access type of the selected segment. Figure
6-9
illustrates this transparent process
of descriptor loading.
In effect, the hidden descriptor fields of the segment registers function
as
the memory management
cache of the 80286. All the information required to address the current working set of
is,
the base address, size, and access rights of the currently addressable
segments-is
stored
in
this
memory cache. Unlike the probabilistic caches of other architectures, however, the 80286 cache
is
completely deterministic: the caching of descriptors
is
explicitly controlled by the program.
Most memory references
do
not require the translation of a full 32-bit virtual address, or
long
pointer.
Operands that are located within one of the currently addressable segments,
as
determined by the four
segment registers, can be referenced very efficiently
by
means of a short pointer, which
is
simply a
16-bit offset.
In fact, .most 80286 instructions reference memory locations
in
precisely this
way,
specifying only a
16-bit offset with respect
to
one of the currently addressable segments. The choice of segments (CS,
DS, ES, or SS)
is
either implicit within the instruction itself, or explicitly specified by means of a
segment-override prefix (as described in Chapter
2).
ICPii:-----
---
-----,
APPLICATION
VISIBLE
--
SEGMENT
REGISTER
-
I I
1
1
.1
I
1
I
1
1
I
L
__
_
r----
DESCRIPTOR
CACHE
SEGMENT
DESCRIPTOR
TYPE
BASE
LIMIT
TRANSPARENT
DESCRIPTOR
LOADING
I
I
I
I
I
I
_______
--1
SYSTEM
MEMORY
Figure 6-9. Descriptor Loading
6-11
DESCRIPTOR
TABLE
G30108
 Loading...
Loading...