PROGRAMMING NUMERIC APPLICATIONS
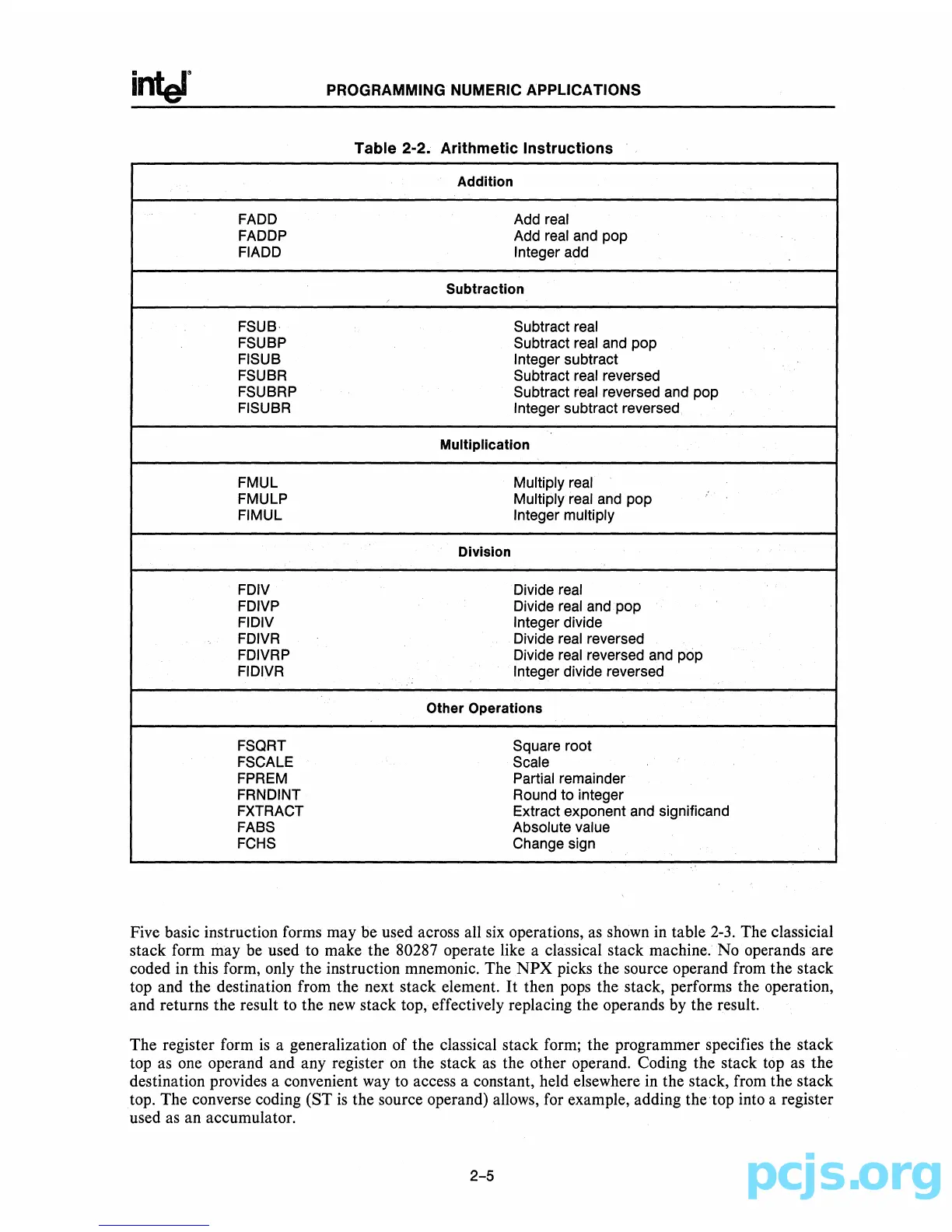
Table
2-2.
Arithmetic
Instructions
Addition
FADD Add real
FADDP Add real and pop
FIADD
Integer add
Subtraction
FSUB Subtract real
FSUBP Subtract real and pop
FISUB Integer subtract
FSUBR Subtract real reversed
FSUBRP Subtract real reversed and pop
FISUBR Integer subtract reversed
Multiplication
FMUL Multiply real
FMULP Multiply real and pop
FIMUL Integer multiply
Division
FDIV Divide real
FDIVP Divide real and pop
FIDIV Integer divide
FDIVR Divide real reversed
FDIVRP Divide real reversed and pop
FIDIVR Integer divide reversed
Other Operations
FSQRT
Square root
FSCALE Scale
FPREM Partial remainder
FRNDINT Round to integer
FXTRACT
Extract exponent and significand
FABS Absolute value
FCHS
Change sign
Five basic instruction forms may be used across all
six
operations,
as
shown
in
table
2-3.
The classicial
stack form may be used to make the 80287 operate like a classical stack machine. No operands are
coded
in
this form, only the instruction mnemonic. The
NPX
picks the source operand from the stack
top and the destination from the next stack element. It then pops the stack, performs the operation,
and returns the result to the new stack top, effectively replacing the operands by the result.
The register form
is
a generalization of the classical stack form; the programmer specifies the stack
top as one operand and any register
on
the stack
as
the other operand. Coding the stack top as the
destination provides a convenient way to access a constant, held elsewhere
in
the stack, from the stack
top. The converse coding (ST
is
the source operand) allows, for example, adding the
top
into a register
used
as
an accumulator.
2-5

 Loading...
Loading...