4-6 Troubleshooting
Analog circuits
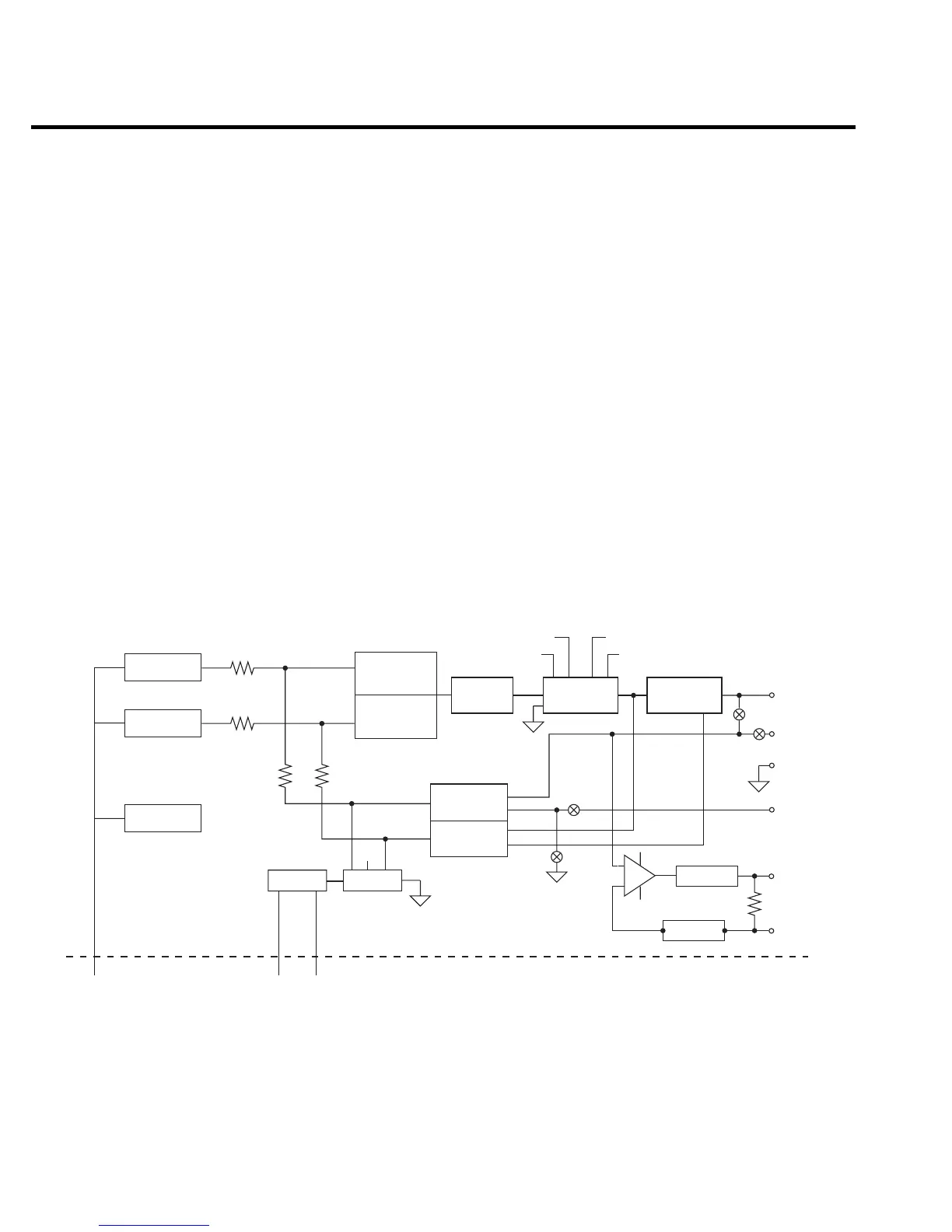
Figure 4-2 shows a block diagram of the analog circuits.
D/A converters control the programmed voltage and current, or voltage compliance and current
compliance. Each DAC has two ranges, a 10V full-scale output or a 1V full-scale output. The
DAC outputs are fed to the summing node, FB. Either the V DAC or the I DAC has the ability to
control the main loop. If the unit is set for SV (source voltage), it will source voltage until the com
-
pliance current is reached (as determined by the I DAC setting), and the current loop will override
the voltage loop. If, however, the unit is set for SI (source current), it will source current until the
compliance voltage is reached (as determined by the V DAC setting), and the voltage loop will
override the current loop. A priority bit in the Vclamp/I clamp circuit controls these functions.
The error amplifier adds open-loop gain and slew-rate control to the system to assure accu-
racy and provide a controllable signal for the output stage, which provides the necessary voltage
and current gain to drive the output. Sense resistors in the HI output lead provide output current
sensing, and a separate sense resistor is used for each current range. The 1A and 3A ranges use
0.2V full-scale for a full-range output, while all other ranges use 2V output for full-scale current.
Voltage feedback is routed either internally or externally.
V DAC
I DAC
Control
O
+
-
V Clamp
I Clamp
Error
Amp
Output
Stage
Sense
Resistors
FB
VFB
IFB
VFB
IFB
MUX
+7
S
A/D
-150
-42
+42
+150
Output
HI
S+
O
Output
LO
S-
O
Remote
Protection
Protection
Guard
Out
Guard
Sense
Figure 4-2
Analog circuitry block diagram
There are four voltage ranges: 0.2V, 2V, 20V, and 100V. The feedback gain changes only for
the 20V and 100V ranges, resulting in three unique feedback gain values. A multiplexer directs
the voltage feedback, current feedback, reference, or ground signal to the A/D converter. An
opto-isolated interface provides control signals for both DACs, analog circuit control, and A/D
converter communication to the digital section.
 Loading...
Loading...











