10 Description of the Osmometer K-7400
Fig. 5 Putting down the measuring head without vial
Measurement Principle and Process
The osmotic pressure in a solution is proportional the freezing point
depression of that solution. An aqueous solution, with an osmotic
pressure corresponding to an ideal 1-molal solution, freezes at -1.858 °C.
An aqueous solution with this freezing point has a concentration of
1 Osm/kg.
To perform a measurement first the sample solution is cooled down
without stirring. Even pure water can be super-cooled down to about -5
through -8°C without freezing. The freezing is initiated by an
automatically start of the vibrator at a set temperature. The temperature
reaches the freezing point, 0°C in case of pure water.
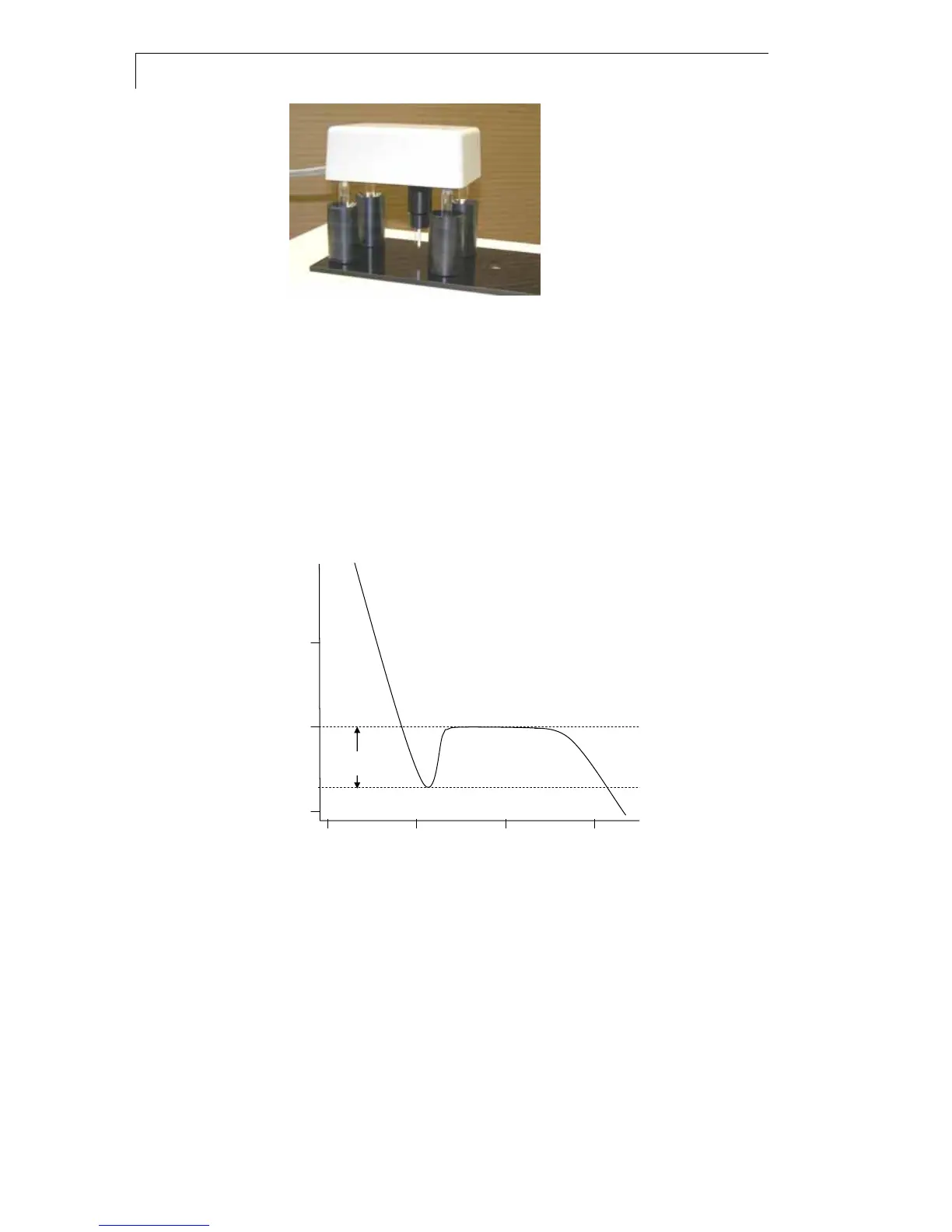
°C
10
0
-10
0 1 2 3 min
Freezing point
Super-cooling
Fig. 6 Temperature-time-curve for pure water
The freezing point of a solution is below 0°C. The freezing point
depression T is a measure for the osmolality of a solution, which can be
red directly from the display given in mOsm/kg.
 Loading...
Loading...