AQ-00073-000, Rev. 7 24
where S' represents the contribution of the specular component of the test sample to
the apparent hemispherical reflectance factor of the sample. This quantity is analo-
gous to the value M' given in Eq. 7 and its relation to the actual specular component
of hemispherical reflectance (S) is described in Eq. 10:
5. On this analysis, the best estimate for the 8°/hemispherical reflectance factor of the
test sample (R
T
), is given as follows:
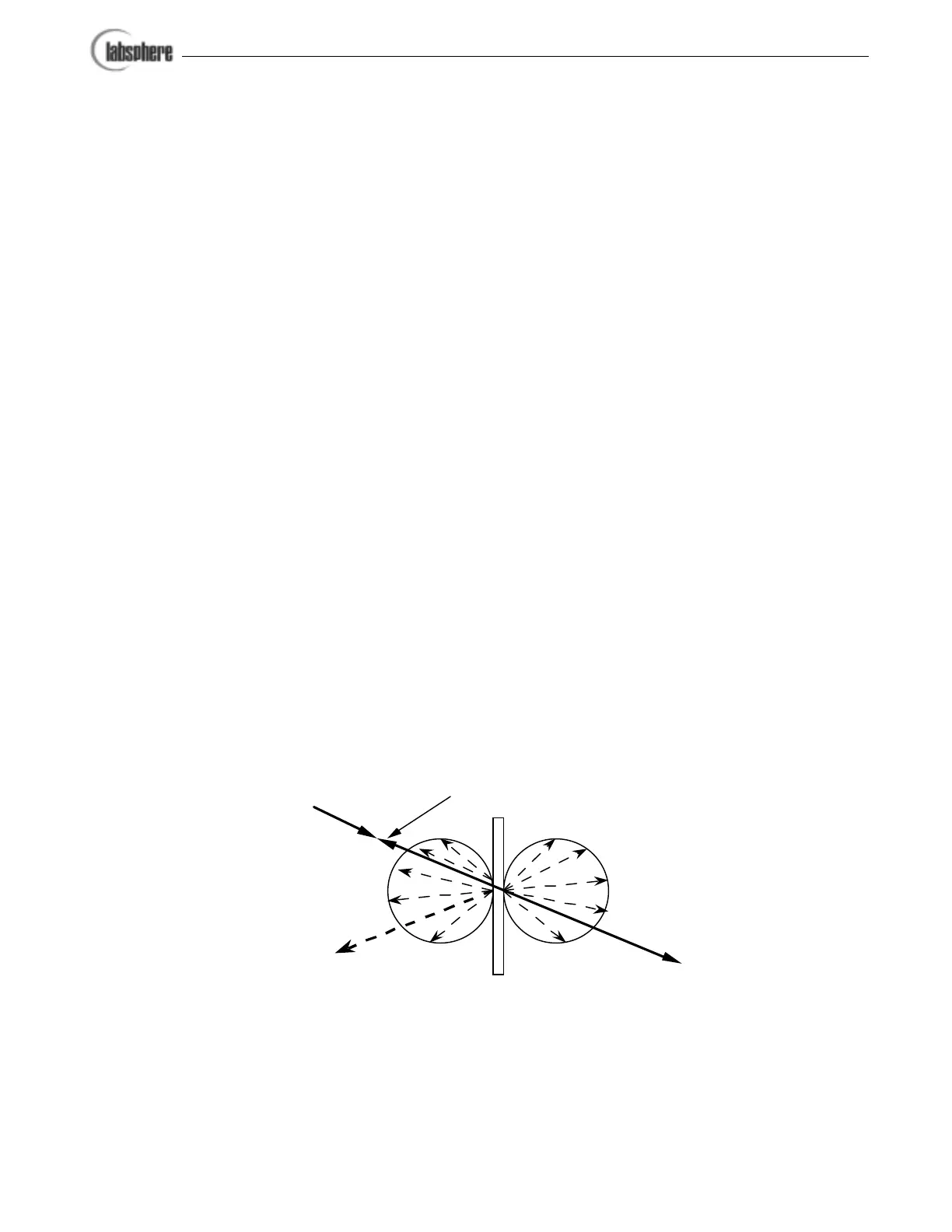
Transmittance Measurements
ASTM E 179-91a describes three categories of transmittance measurement: regular transmit-
tance, diffuse transmittance, and total transmittance. These three terms relate to each other in the
same fashion as regular or specular, diffuse and total reflectance. Regular transmittance is the
ratio of the undiffused transmitted flux to the incident flux. Diffuse transmittance is the ratio of
transmitted flux measured at all forward angles except the regular transmittance angle, to the
incident flux. Total transmittance is the ratio of flux transmittance at all forward angles to the
incident flux. An illustrative description from ASTM E 179-91a is shown in Figure 10.
DR
SEX
ρ
0
=
S' R
SIN
R
SEX
–
()ρ
0
⁄
=
and
Eq. 9
S
γ
S'
γ
R
SIN
R
SEX
–
()ρ
0
==
Eq. 10
R
T
SD+
γ
R
SIN
1
γ
–
()
R
SEX
+
()ρ
0
==
Eq. 11
Regular Transmittance
Impinging Light Beam
Retroreflection
Specular Reflection
Diffuse
Reflectance
Diffuse
Transmittance
Figure 10. Components of reflectance and transmittance phenomena.

 Loading...
Loading...