Troubleshooting and fault elimination
Troubleshooting
Fault analysis with the history buffer
4
33
EDKVF93−03 EN 2.0
4.2.2 Fault analysis with the history buffer
Retracing faults
Faults can be retraced via the history buffer. Fault messages are stored in the 8 memory
locations in the order of their appearance.
The memory locations can be retrieved via codes.
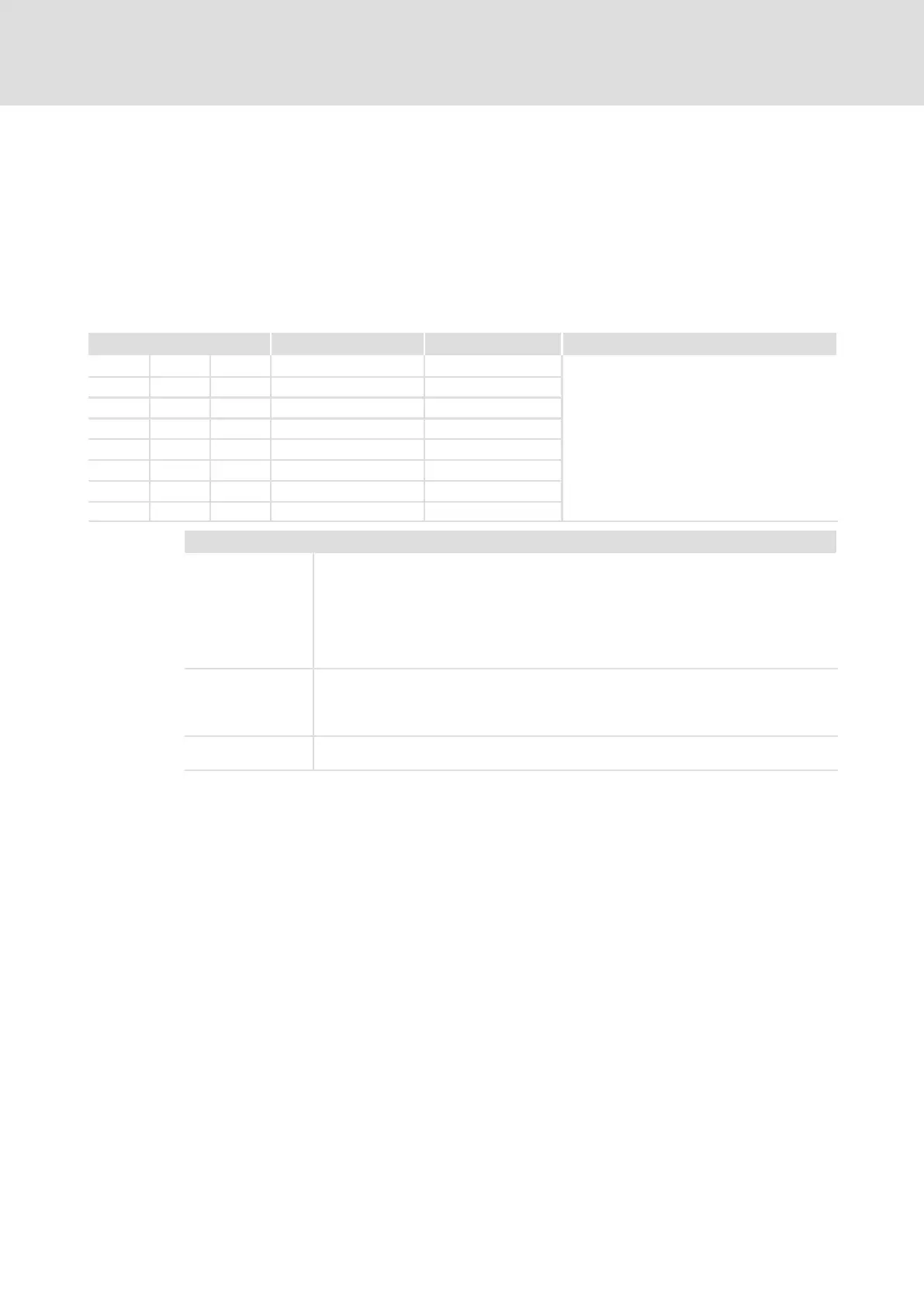
Structure of the history buffer
Code Memory location Entry Note
C0168/1 C0169/1 C0170/1 Memory location 1 Active fault
If the fault is no longer pending or has been
acknowledged:
l The contents of the memory locations
1 ... 7 are shifted "up" to the next memory
location.
l The content of memory location 8 is
deleted from the history buffer and cannot
be retrieved anymore.
l Memory location 1 is deleted (= no active
fault).
C0168/2 C0169/2 C0170/2 Memory location 2 Last fault
C0168/3 C0169/3 C0170/3 Memory location 3 Last but one fault
C0168/4 C0169/4 C0170/4 Memory location 4 Last but two fault
C0168/5 C0169/5 C0170/5 Memory location 5 Last but three fault
C0168/6 C0169/6 C0170/6 Memory location 6 Last but four fault
C0168/7 C0169/7 C0170/7 Memory location 7 Last but five fault
C0168/8 C0169/8 C0170/8 Memory location 8 Last but six fault
Explanations regarding the codes
C0168 Fault indication and response
l The entry is effected as a LECOM error number
l If several faults with different responses occur at the same time:
– Only the fault with the highest priority response is entered (1. TRIP, 2. message,
3. warning).
l If several faults with the same response (e.g. 2 messages) occur at the same time:
– Only the fault which occurred first is entered.
C0169 Time of fault occurence
l The reference time is provided by the power−on time meter (C0179).
l If the same fault occurs several times in succession, only the time of the last occurrence
is stored.
C0170 Fault frequency
l Only the time of the last occurrence is stored.
Clear history buffer
Set C0167=1 to clear the history buffer.
efesotomasyon.com - Lenze

 Loading...
Loading...



