2. Faults
2-1. Power
2-2. Compressor
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
-67-
Problems Causes Checks Measures Remarks
No power on - Power cord cut. - Check the voltage with tester. -Replace the components.
outlet. - Faulty connector insertion. - Check visually. -Reconnect the connecting parts.
- Faulty connection between plug - Check visually. -Reconnect the connecting parts.
and adapter.
Fuse blows out. - Short circuit by wrong connection. - Check the fuse with tester - Find and remove the cause of - Replace with rated
- Low voltage products are or visually. problem (ex. short, high voltage, fuse after confirming
connected to high voltage. - Check the input volt are with tester low voltage). its specification.
- Short caused by vermin. (between power cord and products). - Replace with rated fuse.
- Electricity leakage. - Check the resistance of power cord ■ If fuse blowns out
- High voltage. with tester (if it is 0Ω, it is shorted). frequently, confirm
- Short circuit of components the cause and repair.
(tracking due to moisture and dust
penetration).
Problems Causes Checks Measures Remarks
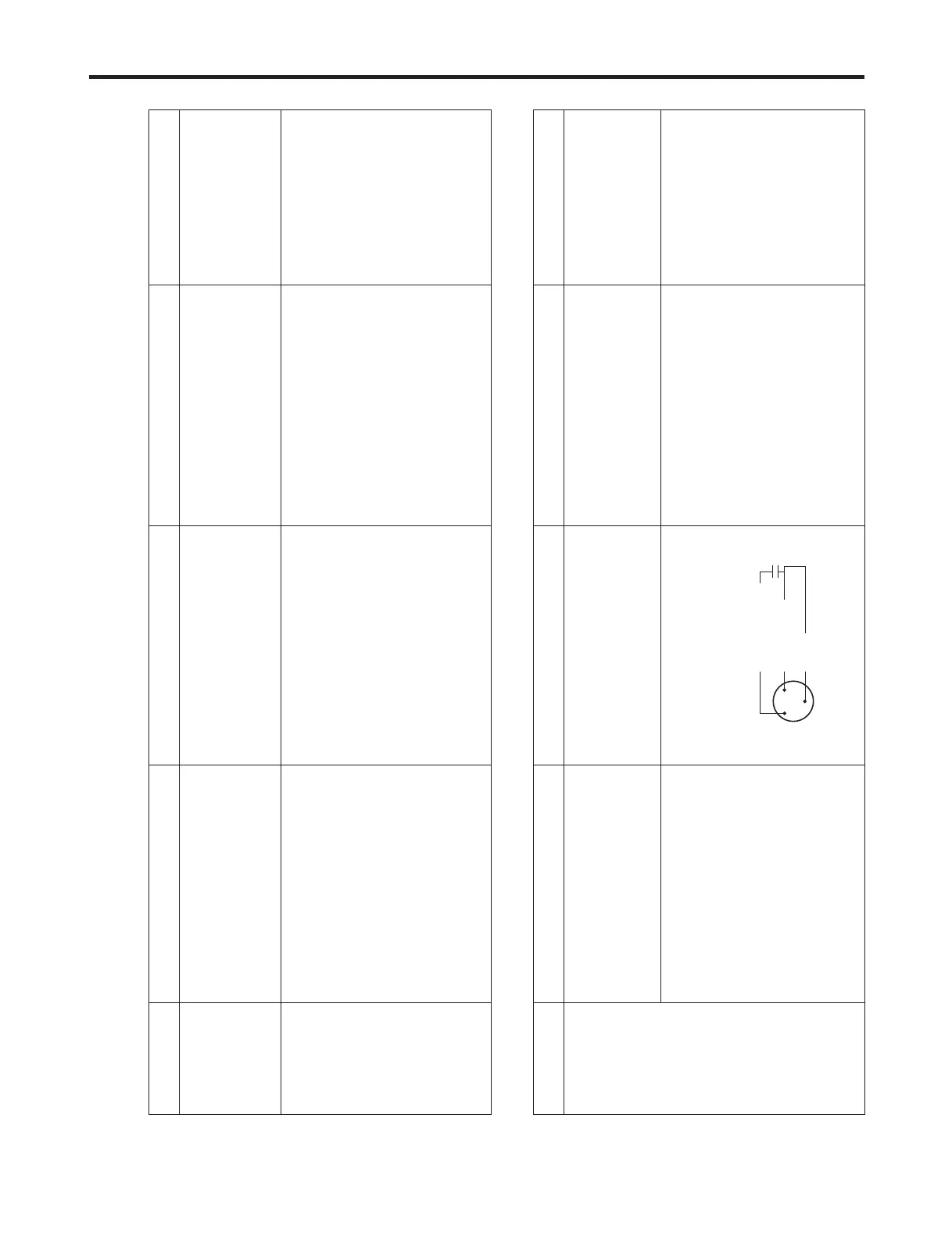
Compressor - Faulty PTC. - Check the resistance. - If resistance is infinite, replace it
does not Vlaue:∞ is defective. with new one.
operate. - If it is not infinite, it is normal.
- Check other parts.
- Compressor is locked up. - If compressor assembly parts are - During forced operation:
normal (capacitor, PTC, OLP), - Operates: Check other parts.
apply power directly to the - Does not operate operate:
compressor to force operation. Replace the frozen compressor
with new one, weld, evacuate,
and recharge refrigerant.
OLP It starts as soon as it is • Refer to weld repair procedures.
contacted.
Auxiliary winding
Main winding
Power

 Loading...
Loading...