Grove Published 3-25-2020, Control # 595-10 3-71
GRT8100 OPERATOR MANUAL OPERATING CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
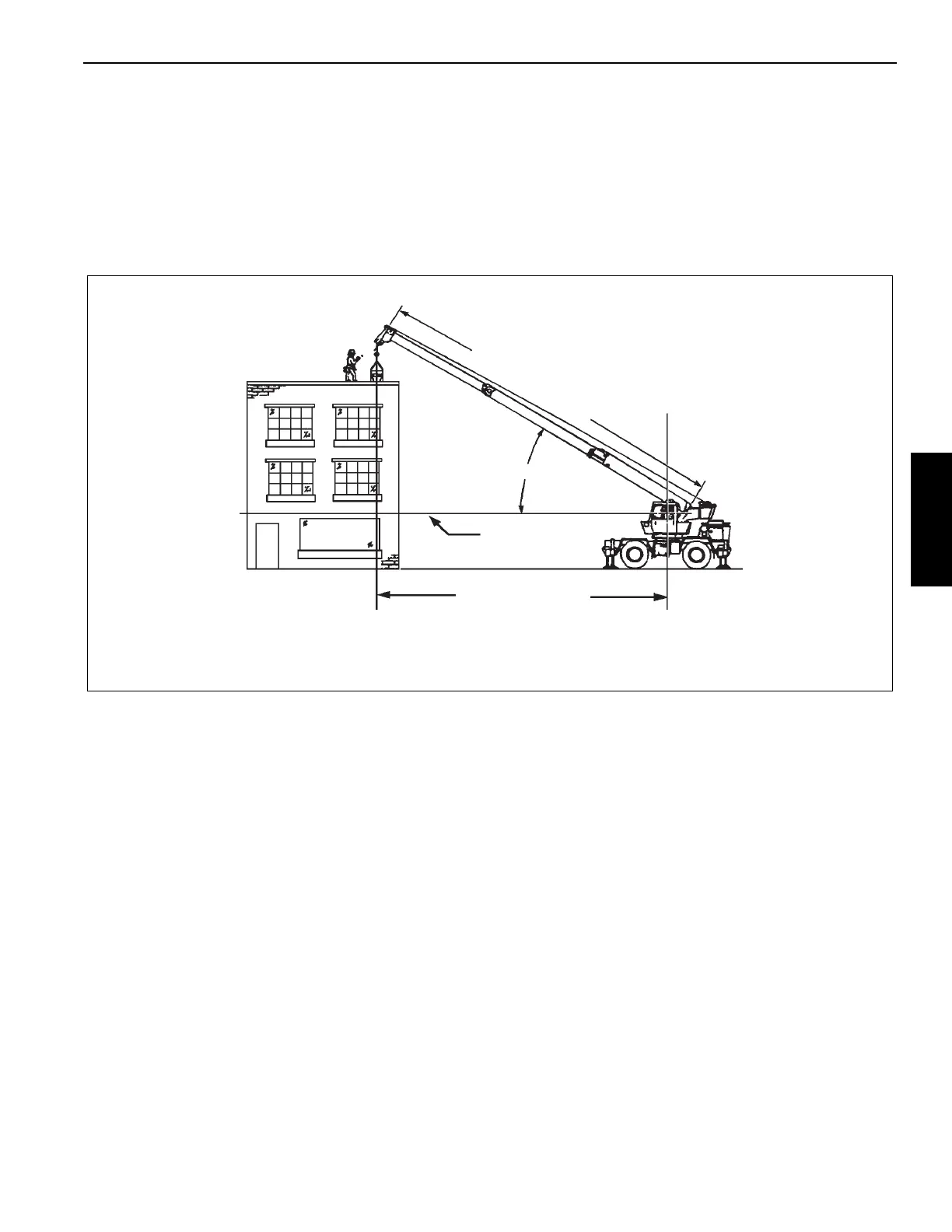
The left column is the load radius, which is the distance from
axis of crane rotation to load center of gravity. The top row
lists various boom lengths from fully retracted to fully
extended (with swingaway extension). The number at the
intersection of the left column and top row is the total load
limit for that load radius and boom length. The number in
parentheses below the total load limit is required boom angle
(in degrees) for that load. Use lower weight limit for the 2
boom lengths.
Another important section is the range diagram. The range
diagram shows operating radius and tip height that can be
achieved at a given boom length and angle. If the operator
knows radius and tip height required for a specific lift, the
angle and boom length can quickly be determined from the
range diagram. Or, if an operator knows boom length and
angle, they can quickly determine tip height and operating
radius.
A lifting diagram is included for over-side, over-rear, and
over-front lifting areas. The lifting area diagram shows
locations of the outrigger jack cylinders in full extended
position are used to mark lifting area boundaries.
Another section contains notes for lifting capacities. Be sure
to read and understand all notes concerning lifting
capacities.
The load chart also gives weight reductions for Grove Crane
load handling devices such as hook blocks, overhaul balls,
boom extension sections, etc., which must be considered as
part of the load. Weight of any other load handling devices
such as chains, slings, or spreader bars must also be added
to the weight of the load.
NOTE: Information in the following paragraph is an
example only of how to compute a lift. Numbers
may not match load chart in the crane cab.
Example: A concrete beam weighing 2268 kg (5000 lb)
needs to be lifted to a height of 9.1 m (30 ft) at a radius of
15.2 m (50 ft) (maximum). The range diagram indicates the
boom must be extended to 18.9 m (62 ft) to reach a height of
9.1 m (30 ft) at a radius of 15.2 m (50 ft).
First check the crane for load handling devices. In our
example, the crane is equipped with a auxiliary boom nose
(rooster sheave) and a five ton overhaul ball. The rooster
sheave is 50 kg (110 lb), and the overhaul ball is 78 kg
(172 lb) for a total of 128 kg (282 lb). The lift requires slings
and spreader bars weighing 159 kg (350 lb) which makes
the total weight for the load handling devices 286 kg (632 lb).
A check of the load chart for a 15.2 m (50 ft) radius and
19.5 m (64 ft) of boom length shows a capacity of 3601 kg
(7940 lb) on outriggers over-front and 4970 lb on outriggers
360 degrees.
Subtract load handling weight of 632 lb from load capacity of
3601 kg (7940 lb) and 2254 kg (4970 lb). The result is a
weight capacity of 3315 kg (7308 lb) over-the-front and
1968 kg (4338 lb) for 360 degrees.
We are restricted in making the lift over-front only, with a
boom angle of about 29 degrees.
Proper Crane Leveling
ASME B30.5 specifies if a crane is not level within 1% of
grade, allowable capacities must be reduced. Therefore,
FIGURE 3-31
OPERATING RADIUS
HORIZONTAL
BOOM ANGLE
M
A
I
N
B
O
O
M
L
E
N
G
T
H
AXIS OF ROTATION
4605
TERMS TO KNOW

 Loading...
Loading...











