3.2.1 Motor Status
Run LED shows the motor status. Upon power on the
relay, if there is no tripping, Relay 1 turns on.
If motor current is more than 1.1 x I
B
, motor is
considered starting, Run LED blinks. If motor current is
less than 1.05 x IB, motor is running, Run LED on. Motor
is stopping when motor current drops below 0.1 x I
B
.
If motor starts abnormally for longer than 60s, Run LED
stops blinking and turns off, Relay 1 also turns off. This
condition reset when motor current drops below 0.1 x I
B
.
3.2.2 Thermal Overload
The protection is based on mathematical model of motor
thermal image. The thermal capacity is calculated
continuously when motor is starting, overloading or even
after tripping. Tripping takes place when the thermal
capacity of the motor reaches 100%. This could happen
when the motor current is higher than 1.05 x I
B
. After
tripping a new start is not allowed until the motor cools
down to less than 40% of thermal capacity. Thermal
capacity can be cleared to 0% by pressing "UP" and
"DOWN" simultaneously for longer than 1.5 seconds
during thermal capacity display.
Warning: Clearing thermal capacity effectively reset
to cold start condition, user is not encouraged to
clear thermal capacity until motor is cool enough to
start/run within its thermal limit.
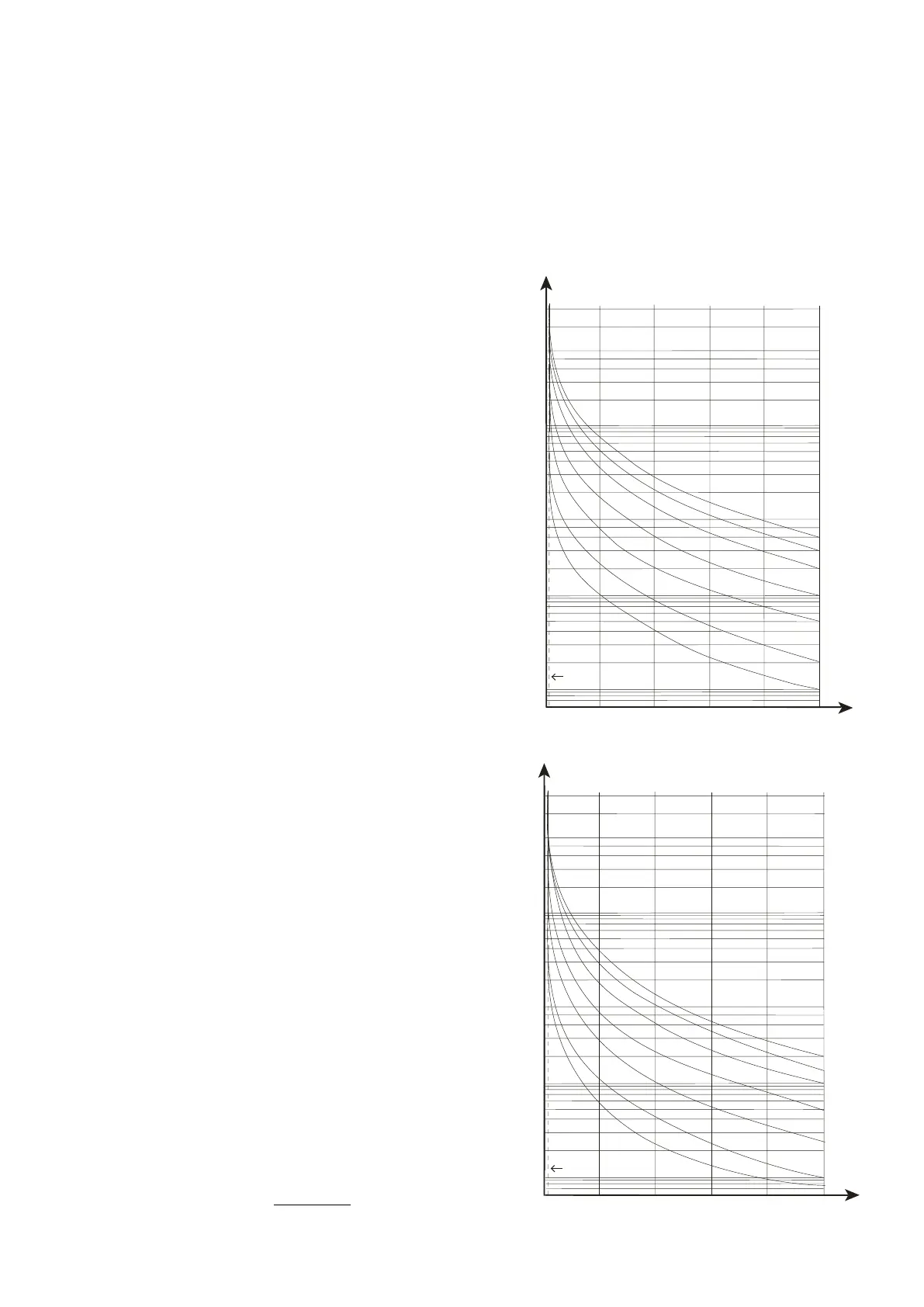
3.2.3 t
6X
Thermal overload Time Constant
t
6X
sets the themal overload time constant (heating
constant), which is the maximum period of time when
motor current is allowed to reach a 6 x I
B
. Cooling
constant time is defined as 4 times of heating constant
time and is applicable when motor current is less than
0.2 x I
B
. Refer to the thermal tripping curve on Figure 4.
3.2.4 Short Circuit
This protection is to trip the relay quickly when high
current is detected due to short circuit. I>> is normally
set higher than motor starting current to avoid false
tripping during motor starting and t>> is set to very short
duration.
Tripping takes place when any phase of motor current is
larger than I>> for longer than t>>. It can be disabled by
setting t>> to 'off'.
3.2.5 Undercurrent
Undercurrent protection is activated when average motor
current is larger than 0.1 x I
B
. Tripping takes place when
average motor current is smaller than I<< for longer than
t<<. It can be disabled by setting t<< to 'off'.
4
(a) With 0% thermal capacity (cold start)
time
t6x
I/I
B
10s
1s
2s
3s
5s
21
3 4
5
6
20s
30s
40s
1min
2min
3min
5min
10min
20min
30min
1hour
2hour
2s
5s
10s
20s
30s
40s
1s
where:
I
max
is the maximum phase current among the 3 phases.
I
min
is the minimum phase current among the 3 phases.
Tripping takes place when unbalance value is more than
unbalance setting % for longer than unbalance delay. It
can be disabled by setting unbalance delay to 'off'.
time
t6x
I/I
B
10s
1s
2s
3s
5s
20s
30s
40s
1min
2min
3min
5min
10min
20min
30min
1hour
2hour
2s
5s
10s
20s
30s
40s
1s
Figure 4: Thermal tripping curve
(b) With prior 50% thermal capacity
3.2.6 Unbalance
Unbalance is calculated as:
I
max
- I
min
I
min
X 100 %
21
3 4
5
6
1.05
1.05

 Loading...
Loading...