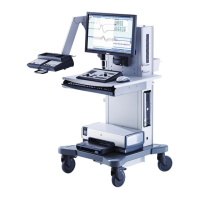
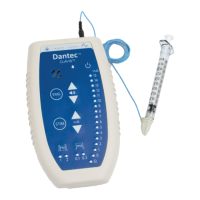
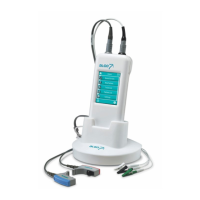
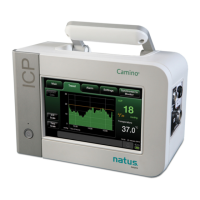
Dantec
®
Keypoint
®
G4
User and Service Guide
Part Number: 9031M1506 Rev F 23/NOV/2022
System Model Number: 9031A0701
© 2016 - 2022 Natus Medical Incorporated or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. Natus is a registered trademark of Natus Medical
Incorporated. All product names appearing on this document are trademarks or registered trademarks owned, licensed to, promoted or
distributed by Natus Medical Incorporated, its subsidiaries or affiliates. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.