Functional Safety KCD2-UT2-(Ex)1, HiC2081
Operation
2018-02
25
5.3.2 Resistance Thermometer Input (RTD)
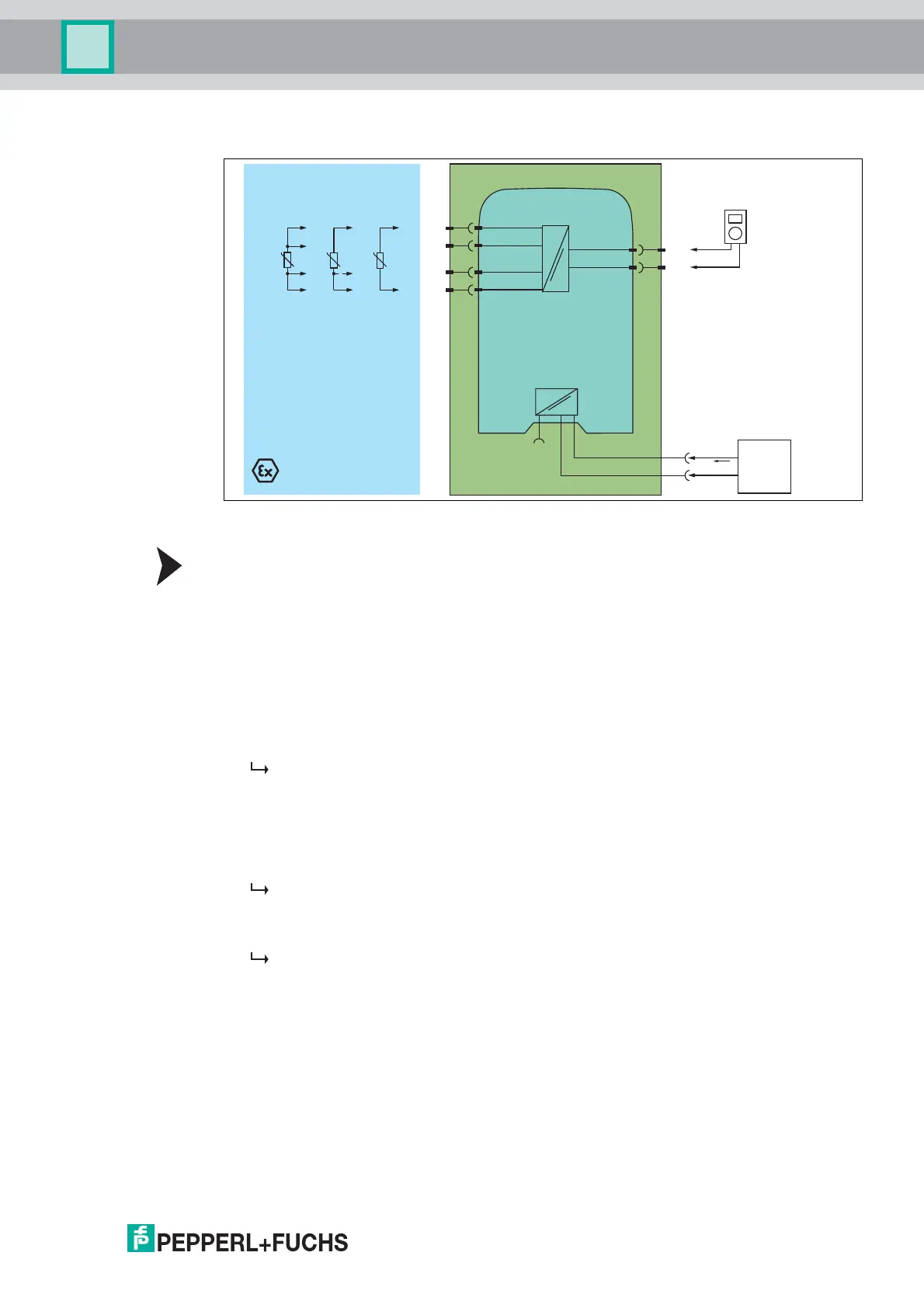
Figure 5.6 Proof test set-up for HiC2081 with resistance thermometer input (RTD)
Proof Test Procedure for Resistance Thermometer Input
1. Connect a RTD simulator, depending on the application.
• for 4-wire connection: terminals 1, 2, 5 and 4
• for 3-wire connection: terminals 1, 5 and 4
• for 2-wire connections: terminals 1 and 4
2. Connect the digital multimeter to the terminals 11 and 14.
3. Set the RTD simulator sequentially to the temperature values
representing 4 mA, 12 mA, 20 mA at the output.
4. Measure the output current.
The proof test is passed if the following values are measured at the output
1
:
– for the 4 mA application: 3,7 mA to 4,3 mA
– for the 12 mA application: 11,7 mA to 12,3 mA
– for the 20 mA application: 19.7 mA to 20.3 mA
5. Apply a short circuit between terminal 1 and 4. Do not remove the RTD simulator. Check if
a short circuit of the cold junction compensation is detected.
The red LED is flashing. The output behavior in the event of a fault depends on the
device configuration.
6. Remove the RTD simulator. Check if a lead breakage is detected.
The red LED is flashing. The output behavior in the event of a fault depends on the
device configuration.
7. Set the device back to the original settings after the test.
11
14
1
2
5
4
HiC2081
Termination Board
Zone 0, 1, 2
Fault
+
-
+
SL2
5a
1a
-
1b
5b
SL1
8a
7a
Multimeter
(mA)
T
T
T
Supply +
Supply -
24 V DC
Power
supply
I supply
Supply
Bus
1
Additionally the loop diagnosis shall be tested to prove that the fault signalling via the current output is working
correctly. The output current in the event of a failure depends on the device configuration. Please record this
configuration and the resulting expected fault signalling current in the test report. Example: if downscale is
configured, 2.0 mA ±1 % must be measured in the event of a failure. The red LED must be flashing.
 Loading...
Loading...