5 Troubleshooting
48
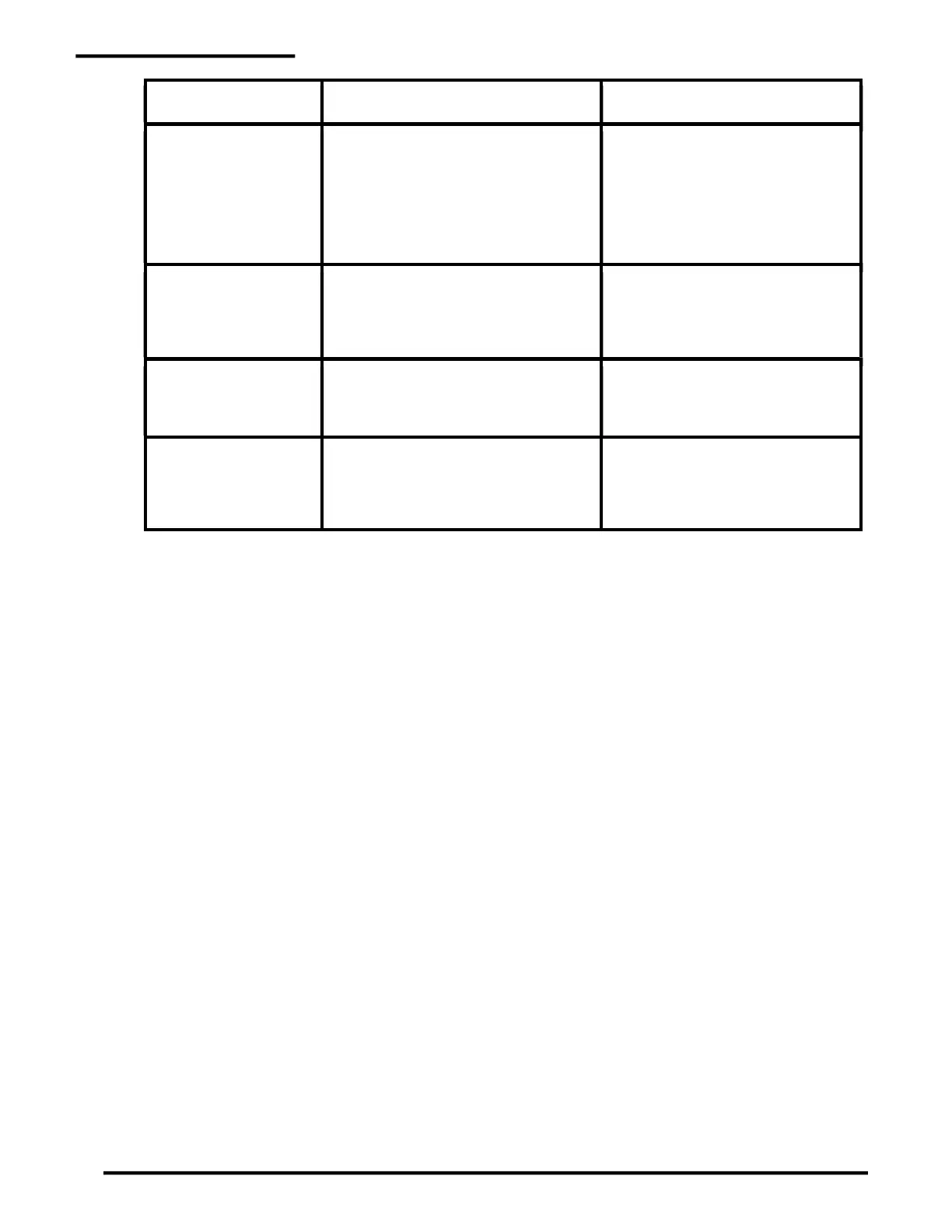
SYMPTOM POSSIBLE PROBLEM ACTION
No communication using
RS-232 or RS-485
Jumpers incorrect at J1 and J2 for
selecting RS-232/RS-485
Wiring incorrect or loose at terminal strip
T1
Port data type incorrect – Modbus RTU
or ASCII (for Palcom)
Baud rate of PAL-AT not correct
PAL-AT address not correct
Refer to PAL-AT Installation Manual,
section 2.61
Refer to section 2.9.4 in this manual
Refer to section 2.9.5 in this manual
Ethernet has link lights but
no communication
Ethernet client using wrong port to talk to
PAL-AT
PAL-AT address not correct
PAL-AT Ethernet addresses incorrect
Modbus TCP > port 502
Modbus RTU over TCP > port 1050
ASCII (Palcom) > port 1024
Refer to section 2.9.5 in this manual
No Ethernet link lights
Wrong speed / duplex setting
Port not active at connected switch
Bad cable
Change jumper to Auto Negotiate per
section 2.10.3.3
Verify connection at switch
Test / re-terminate structured cable
AT-ORC communications
problems
Wrong firmware in AT-ORC (AT-ORC
was originally used with older generation
PAL-AT)
Wrong firmware in PAL-AT (versions
1.10 & 1.12 must be upgraded to 1.14)
Send AT-ORC in to PermAlert for
firmware upgrade.
Upgrade PAL-AT firmware to 1.14
5.7 Restrictions & Limitations
For proper operation of the PAL-AT Leak Detection and Location system, the following restrictions and
limitations apply.
5.7.1 Sensor Cables
1. Sensor cables and jumper cables should not be installed in locations subject to frequent moisture
intrusion or wetness. The only exceptions are JMP-U and JPP jumper cable and TFH/TFH-Gold
sensor cables.
2. Electrical conduit for jumper cables must be sealed against moisture intrusion.
3. Cable connectors should be located in accessible areas. They must be electrically tested for
integrity and then encapsulated with shrink tubing and sealant.
The ability of PAL-AT to sense and locate leaks can be affected by the following occurrences:
1. An improperly installed connector can limit the ability of the system to see beyond it. Pinching or
cutting the cable can have the same effect.
2. Contamination such as dirt or mud filling a portion of the cable may make it insensitive to leaks in the
contaminated portion.
3. A large amount of wet cable will decrease the sensitivity and accuracy of the system beyond the wet
area. Several probes activated simultaneously have the same effect.
4. While the cables are made of durable and corrosion resistant materials, caution must be exercised in
cable handling to avoid excessive abrasion or damage. The damage may have a detrimental effect
on the operation of the system. Pulling the cable around sharp edges, or pulling cable through
secondary contained piping not properly designed to accept leak detection cables may cause abrasion
to the cable.
5. The sensor cables are corrosion resistant but if they are exposed to corrosive liquids, the contaminants
should be neutralized and the cables flushed. Untreated contamination may shorten the life of the
cable.
The following precautions must be observed for TFH and TFH-Gold hydrocarbon sensor cables.
1. The maximum burial depth is 20 ft [6 m].
 Loading...
Loading...