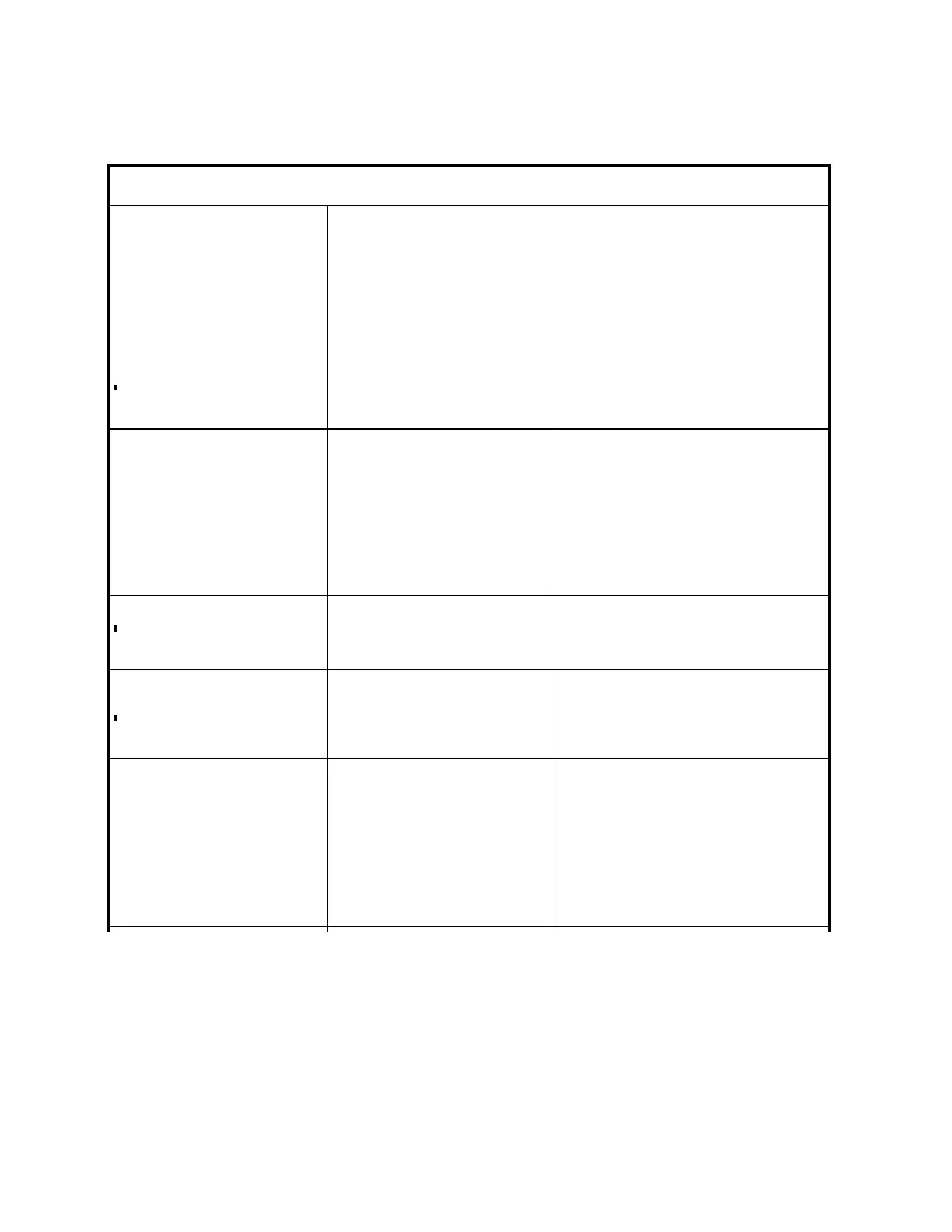
14
I
DIFFICULTY
I
PROBABLE CAUSE
I
REMEDY
1. Pump not primed.
2. Suction and/or discharge valve
closed.
3. Wrong direction or rotation.
4. Suction plugged.
5. Air leak in suction.
6. Suction lift too high.
7. Motor incorrectly wired.
8.
Magnetic coupling decoupled.
1. Prime pump.
2. Open valves.
3. Reverse rotation
4. Eliminate plug.
5. Locate and repair leak.
6. Do not exceed vapor pressure of
liquid.
7. Check wiring diagram.
8. Stop motor, eliminate discharge
blockage or foreign matter jamming
gears and restart. If no blockage
exists verify motor supply voltage is
correct and restart.
1. Discharge pressure higher than
expected.
2. Air leak in suction.
3.
Rotational speed incorrect.
4. Inlet obstructed or clogged.
5.
Liquid viscosity higher than
expected.
6. Leaky relief valve.
7. Insufficient suction pressure.
8.
Worn or damaged internal parts.
1. Reduce pressure.
2. Locate and repair leak.
3.
Check speed and wiring
4. Remove restriction
5. Thin liquid or accept lower flow.
6. Correctly set or repair relief valve.
7. Increase suction pressure.
8.
Inspect and repair as required.
PUMP GRADUALLY
LOSES PRIME
1. Air leak in suction
2. Suction lift too high.
3.
Air or gas in liquid.
4.
Pump worn or damaged.
1. Locate and repair leak.
2. Increase suction pressure.
3. Eliminate air or gas.
4.
Inspect and repair as required.
1. Pump cavitating.
2.
Pump worn or damaged.
3.
Air or gas in liquid.
4.
Foreign particles in liquid.
1. Increase suction pressure to provide
sufficient NPSH
2. Inspect and repair as required.
3.
Eliminate air or gas.
4.
Install (or clean) strainer in inlet pipe.
MOTOR RUNS HOT OR
OVERLOADS
1. It is normal for motors to feel hot
even when not overloading.
2.
Discharge pressure too high.
3. Liquid viscosity higher than
expected.
4. Rotational speed too high.
5.
Binding internal pump parts.
6. Motor wired incorrectly.
1. Check motor amp draw to be sure.
2. Lower pressure. Check pressure relief
valve setting and for defective
discharge pressure gauge.
3. Thin liquid or install larger motor.
4. Reduce speed.
5. Inspect and correct condition.
6. Check wiring diagram.
TROUBLESHOOTING
I

 Loading...
Loading...