21
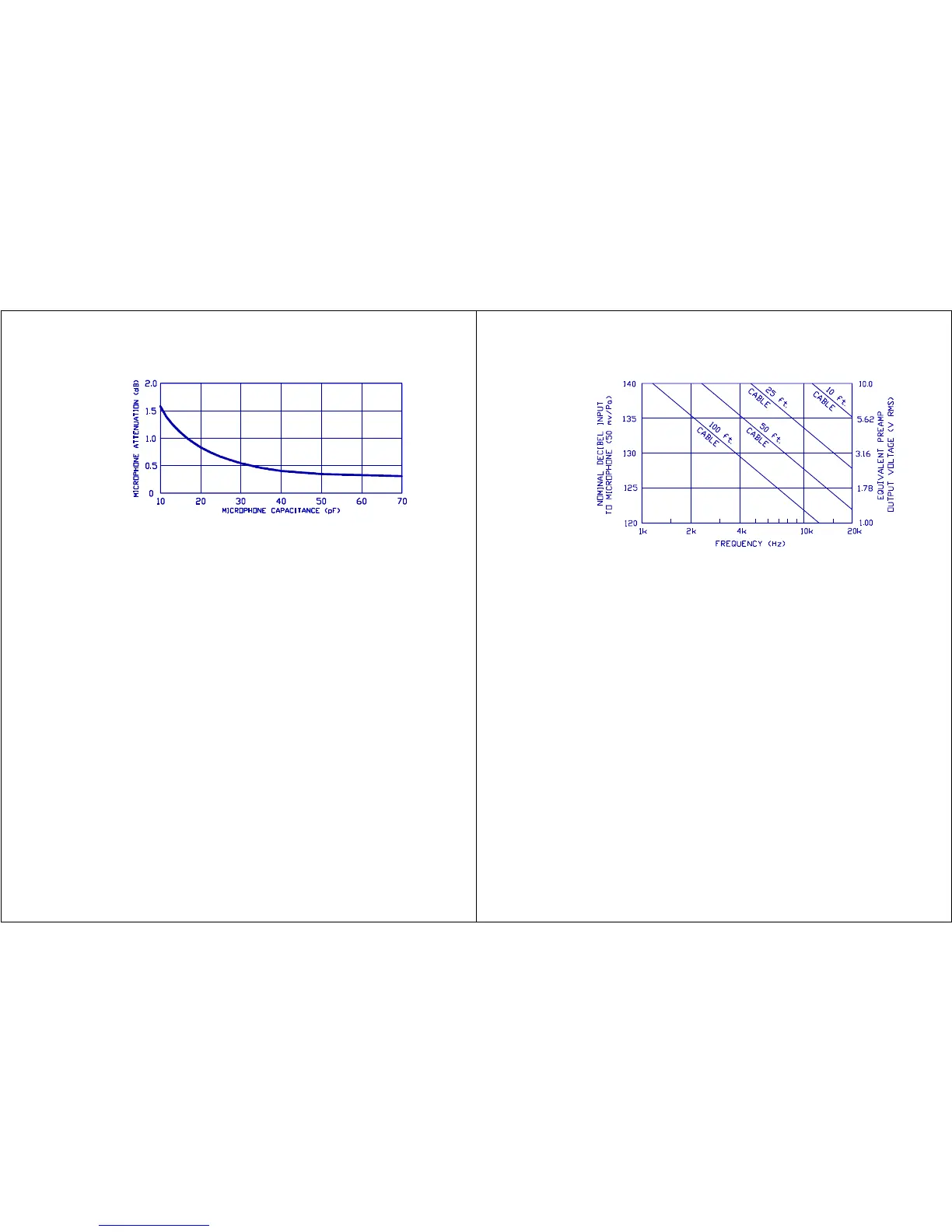
Figure 13. Microphone Output Attenuation Caused by Input
Capacitance of Preamp
D.
Microphone
Preamp
Extension
Cables
The
microphone
preamp
converts
the high
output
impedance
of the
microphone
to a low
output
impedance.
An extension cable of up to 100 feet in length can be connected between the
preamp and meter. Quest Electronics offers the following lengths of remote
cables:
# 59-733 ICM-10 10 Ft. Remote Cable.
# 59-734 ICM-50 50 Ft. Remote Cable.
The calibration level at 1kHz and below is affected by less than 0.1 dB with
the insertion of a cable. Therefore, there is no need to recalibrate when
the cable is added. Maximum output at high frequencies is affected by long
cable lengths. This effect is shown in Figure 14.
22
Figure 14. Frequency/Amplitude Limitations with Extension
Cables
E. Input
Buffer
Circuitry
The high
impedance
input
circuitry
(1 Megohm
in series
with 0.1
MFD) will
accept up
to a 10
volt RMS
signal.
With the
microphone
and preamp
removed,
other
transducer
devices
(such as the Quest Model VI-90 Vibration Integrator) can be interfaced to
give a dB readout on the meter.
Note that when interfacing other input devices to the Model 1800, the 200
volt microphone polarization switch located inside of the battery compartment
should be turned OFF for safety. Only use pins 1 and 3 for the AC signal
input. NEVER connect to pins 2 and 4.
To remove the preamp, keep the preamp housing steady while unscrewing the
black plastic collar below the preamp housing. Turn in a counter-clockwise
direction when viewed from the meter top.
To input an AC voltage electrically requires a special connector - Quest part
number 14-739. Figure 15 describes the function of each of the pins within
the meter input connector.
 Loading...
Loading...