3-10 Overcurrent, Voltage, Synchronism Check, and Frequency Elements Date Code 20010307
SEL-351A Instruction Manual
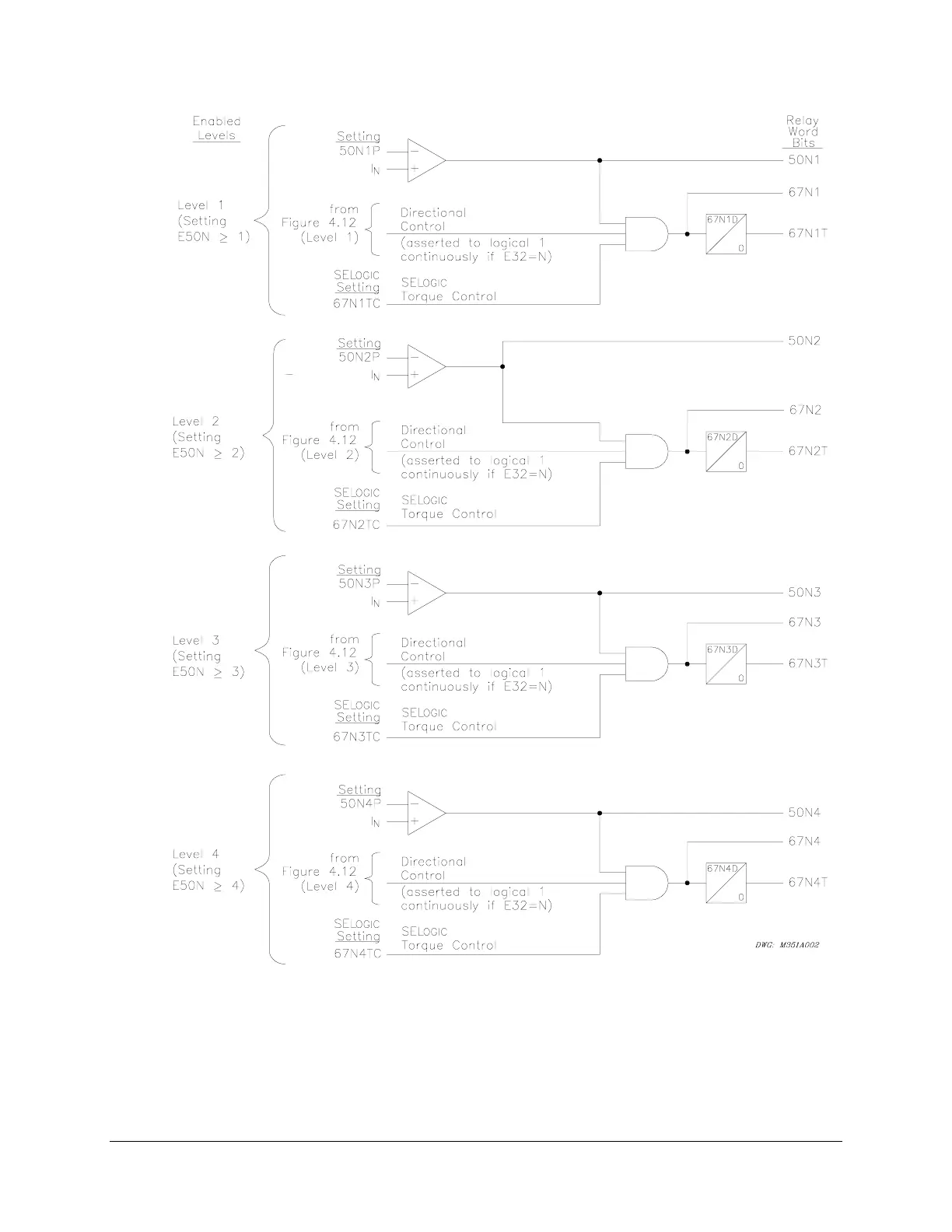
)LJXUH/HYHOV7KURXJK1HXWUDO*URXQG,QVWDQWDQHRXV'HILQLWH7LPH2YHUFXUUHQW
(OHPHQWV:LWK'LUHFWLRQDO&RQWURO2SWLRQ
 Loading...
Loading...