-
MZ-5600
15. KEYBOARD AND KEYBOARD INTERFACE
15-1
Keyboard specifications
* Intelligent keyboard containing
the
80C49 processor.
*
63
byte input buffer.
* Two key roll-over.
* Mode indicators for
CAPS',
and GRAPH.
* Two types
of
repeat functions can
be
specified by
CPU
commands.
RUN
.STOP
etc
.
.
Fl
F2 F3 F4 F5 F6
F7
I
F81
F9 I
no
I
INS
DilL
CL
/
:t
+
POLL
HOME
UP
7 8
9 -
DOWN
l
4 5 6
=
-
-
!
1
2
3
J
0
.
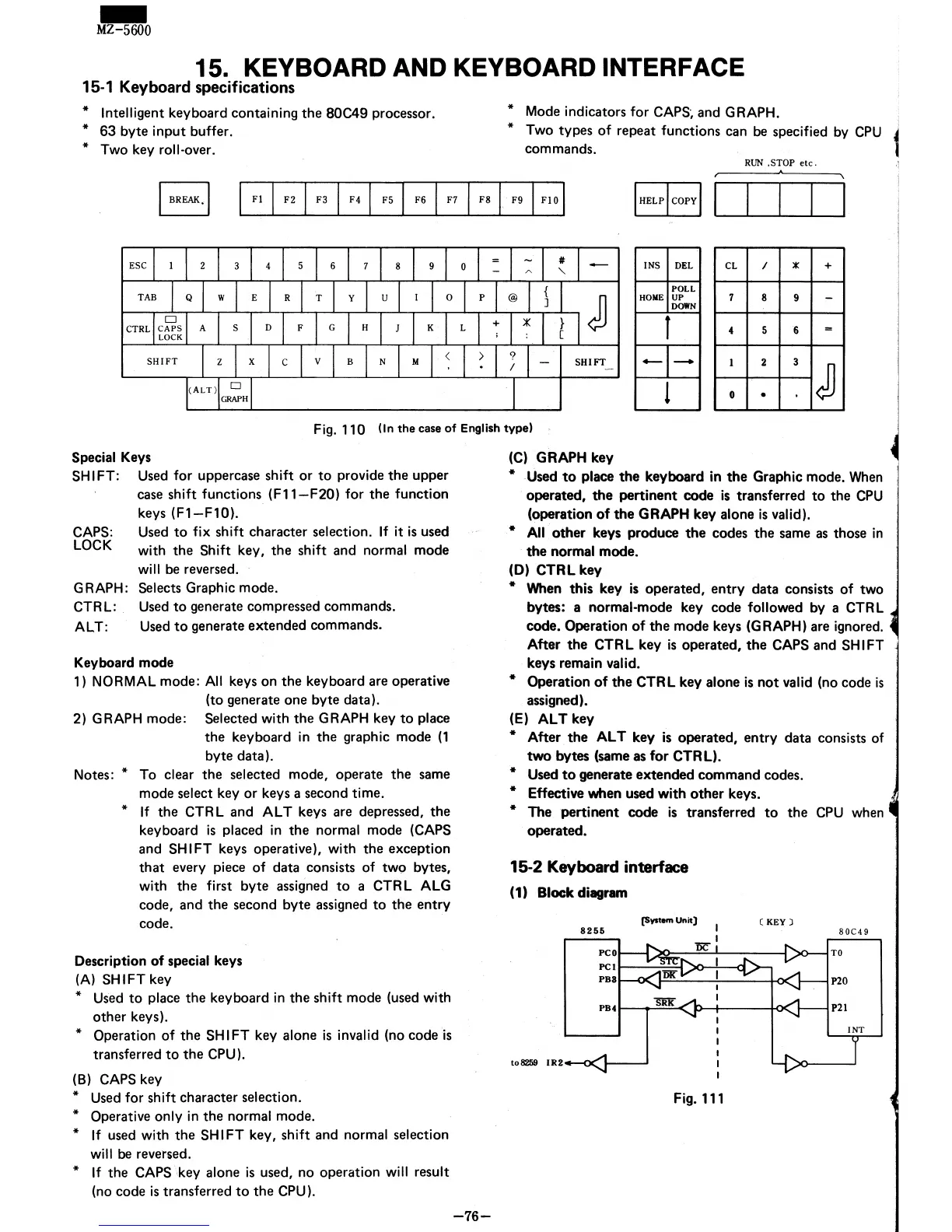
Fig. 110
(In
the
case
of
English
type)
Special Keys
SH
I FT: Used for uppercase shift
or
to
provide
the
upper
case shift functions
(F11-F20)
for
the
function
keys
(F1-F10).
CAPS:
LOCK
Used
to
fix shift character selection.
If
it
is
used
with
the
Shift key,
the
shift and normal mode
will
be
reversed.
GRAPH:
Selects Graphic mode.
CTRL:
ALT:
Used
to
generate compressed commands.
Used
to
generate extended commands.
Keyboard mode
1) NORMAL mode:
All
keys on
the
keyboard are operative
(to generate one byte data).
2) GRAPH mode:
Selected with
the
GRAPH key
to
place
the
keyboard
in
the
graphic mode
(1
byte data).
Notes:
* To clear
the
selected mode, operate
the
same
mode
select key
or
keys a second time.
*
If
the
CTRL and AL T keys are depressed,
the
keyboard
is
placed
in
the
normal mode (CAPS
and
SH
I FT keys operative
I.
with
the
exception
that
every piece of data consists of two bytes,
with
the
first byte assigned
to
a CTRL ALG
code, and
the
second byte assigned
to
the
entry
code.
Description
of
special keys
(A)
SHIFT key
* Used
to
place
the
keyboard
in
the
shift mode (used with
other keys).
* Operation
of
the
SHIFT key alone
is
invalid (no code
is
transferred
to
the
CPU).
(B)
CAPS key
* Used for shift character selection.
* Operative only
in
the
normal mode.
*
If
used with
the
SH
I FT key, shift and normal selection
will
be
reversed.
*
If
the
CAPS key alone
is
used, no operation will result
(no code
is
transferred
to
the
CPU).
-76-
(C)
GRAPH key
* Used
to
place
the
keyboard in
the
Graphic mode.
When
operated,
the
pertinent
code
is
transferred
to
the
CPU
(operation
of
the
GRAPH key alone
is
valid).
*
All
other
keys produce
the
codes
the
same
as
those
in
the
normal mode.
(D) CTRL key
* When this key
is
operated,
entry
data consists
of
two
bytes: a normal-mode key code followed by a CTR L
code. Operation
of
the
mode keys (GRAPH) are ignored.
After
the
CTR L key
is
operated,
the
CAPS and
SH
I FT
keys remain valid.
* Operation
of
the
CTR L key alone
is
not
valid (no code
is
assigned).
(E) ALT key
* After
the
AL T key
is
operated, entry data consists of
two
bytes (same as for CTRL).
* Used
to
generate extended command codes.
* Effective when used with
other
keys.
* The pertinent code
is
transferred
to
the
CPU
when
operated.
15-2 Keyboard interface
(1) Block diagram
[System Unit)
8255
peo
PC
I
t----::::::-t
X>"-:-----<l
PB3
(KEY)
PB4
r-""T"='-<
P--t-----t<x:..
to8259
IR2
Fig. 111

 Loading...
Loading...