15
In the following example, the program segments perform the
same function.
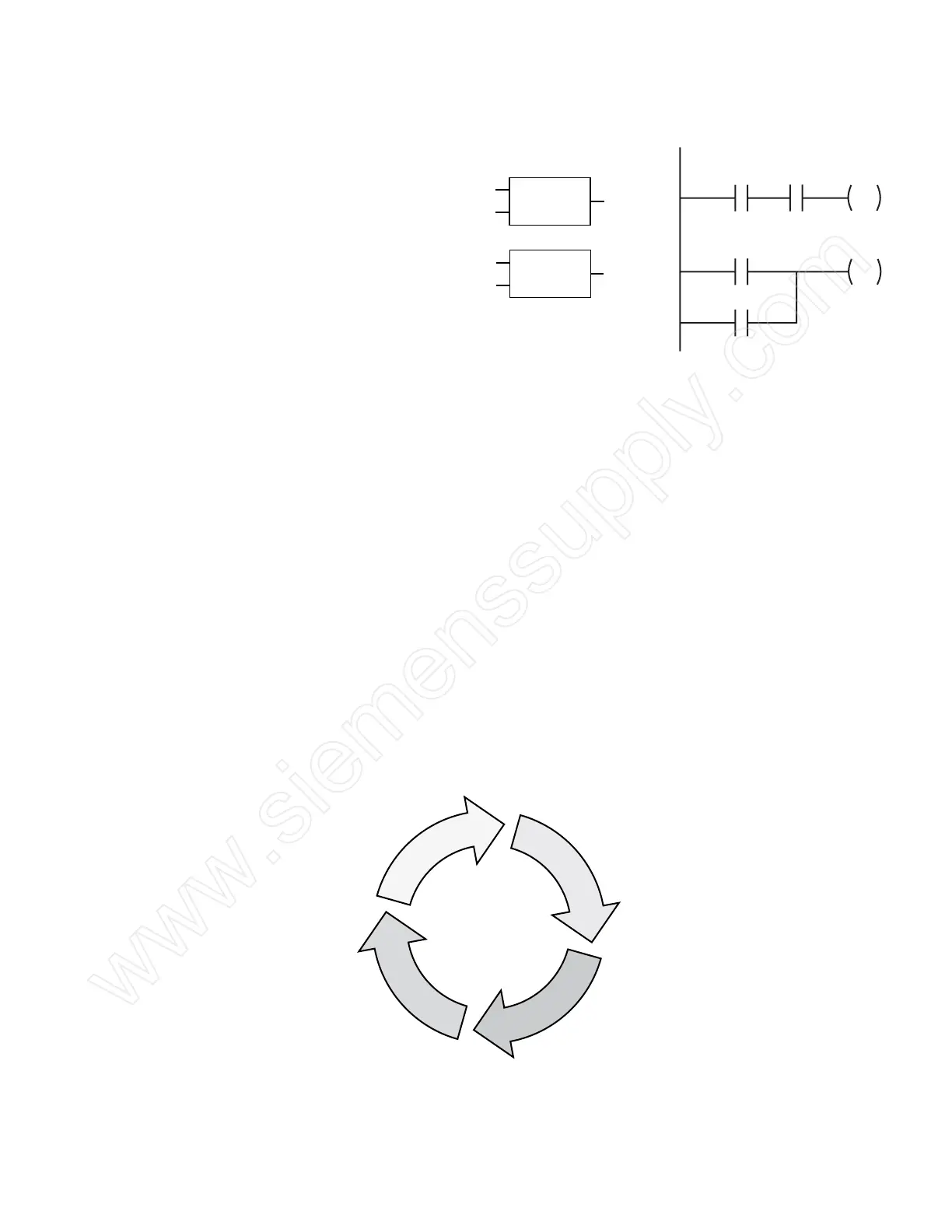
Network 1
Network 2
I0.0 I0.1 Q0.0
I0.4
I0.5
Q0.0
Network 1
LD
A
=
I0.0
I0.1
Q0.0
LD
O
=
I0.4
I0.5
Q0.1
Network 2
AND
I0.0
I0.1
Q0.0
OR
Q0.1
I0.4
I0.5
Network 1
Network 2
Statement List (STL) Function Block Diagram (FBD) Ladder Logic (LAD)
In addition to LAD, STL, and FBD, multiple other types of
programming languages are used for PLCs. Each type of
programming has its advantages and disadvantages. Factors
such as application complexity, types of programming available
for a specific PLC model, and user standards and preferences
determine which type of programming is used for an
application.
PLC Scan The PLC program is executed as part of a repetitive process
referred to as a scan. A PLC scan starts with the CPU
reading the status of inputs. Next, the application program is
executed. Then, the CPU performs internal diagnostics and
communication tasks. Finally, the CPU updates the status of
outputs. This process repeats as long as the CPU in the run
mode. The time required to complete a scan depends on the
size of the program, the number of I/Os, and the amount of
communication required.
PLC Scan
R
e
a
d
I
n
p
u
t
s
E
x
e
c
u
t
e
P
r
o
g
r
a
m
D
i
a
g
n
o
s
t
i
c
s
&
C
o
m
m
u
n
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
U
p
d
a
t
e
O
u
t
p
u
t
s
 Loading...
Loading...











