Bevel cuts (Fig R)
Bevel cuts must always be made using the rip fence (5).
- Set the blade (4) to the desired angle.
- Proceed as for cross cutting
Caution: (Fig Q)
- Always use the push stick (19) when ripping small
workpieces (fig. Q)
- Do not cut excessively small workpieces.
Cross Cutting
- Lock the miter gauge (6) at 0 degree
- Set the bevel angle to 0 degree
- Adjust the saw blade (4) height
- Hold the workpiece flat on the table (1) and against the
fence. Keep the workpiece away from the blade.
- Keep both hands away from the path of the saw blade.
- Switch the machine on and allow the saw blade to reach
full speed.
- Hold the workpiece tightly again the fence and slowly
move the workpiece together with the fence assembly until
the workpiece comes underneath the upper blade guard.
Allow the teeth to cut, and do not force the workpiece
through the saw blade. The saw blade speed should be
kept constant.
After completing the cut, switch the machine off, allow the saw
blade to stop and remove the workpiece
- Push the and the workpiece toward the blade in order to
make the cut.
Important: Never push or hold the cut-off-side
workpiece.
Cross stop (Fig O)
- Push the miter gauge (6) into a slot (21 a/b) on the saw
table.
- Loosen the locking handle (n).
- Rotate the miter gauge (6) until the required angle is set.
The scale (p) shows the set angle.
- Re-tighten the locking handle (n)
USE
Working instructions
After each new adjustment it is advisable to carry out a trial in
order to check the set dimensions. After switching on the saw,
wait for the blade to reach its maximum speed of rotation
before commencing with the cut.
Secure long workpiece against falling off at the end of the cut
(e.g. with a roller stand etc.) Take extra care when starting the
cut! Never use the equipment without the suction function.
Regularly check and clean the suction channels.
Making longitudinal cuts (Fig P)
Longitudinal cutting (also known as slitting) is when you use
the saw to cut along the grain of the wood. Press one edge of
the workpiece against the parallel stop (5)” to be replaced to
“rip fence (5) while the flat side on the saw table (1).
The blade guard (2) must always be lowered over the
workpiece. When you make a longitudinal cut, never adopt a
working position that is in line with cutting direction.
- Set the in accordance with the workpiece height and the
desired width.
- Switch on the saw.
- Place your hands (with fingers closed) flat on the
workpiece and push the workpiece along the and into the
blade (4).
- Guide at the side with your left or right hand (depending
on the position) only as far as the front edge of the saw
blade guard (2).
- Always push the workpiece through to the end of the riving
knife (3)
- The offcut piece remains on the saw table (4) until the
blade (4) is back in its position of rest.
- Secure long workpiece against falling off at the end of the
cut ) with a roller stand etc.
6 21an
p
O
P
5 2 4
3
1
19
Q
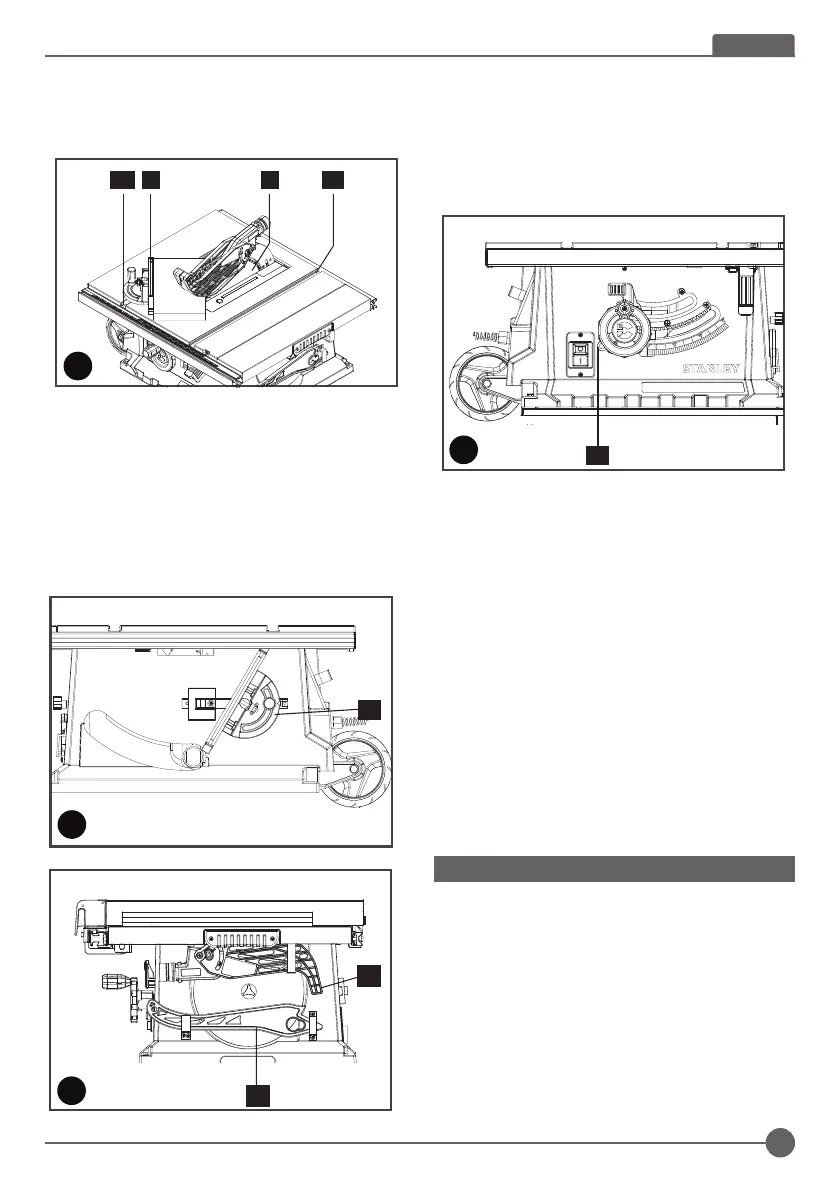
Blade jamming handling (Fig U)
- Ensure the machine is disconnected from the power
source.
- Remove the wookpiece at first. Warning: Be careful of
your hands not toughing the saw blade.
- Press the overloaded protector (22) and connect the plug
again, the machine can be resumed to work. (Fig. U)
Applications
1. Make sure the kerf is made on the scrap side of the
measuring line.
2. Cut the wood with the finished side up.
3. Always have a proper support for the wood as it comes
out of the blade.
4. Make a test cut for important cuts.
5. Always use the correct blade depth setting. The top of the
blade teeth should clear the top of the material being cut
by 1⁄8” (3 mm) to 1⁄4” (6 mm).
6. Inspect the work-piece for knots or nails before beginning
a cut. Remove any loose knots with a hammer.
7. Always use clean, sharp, properly-set blades. Never make
a cut with a dull blade.
8. When making a cut, use steady, even pressure. Never
force a cut.
9. DO NOT cut wet or warped lumber.
10. Always hold your work-piece firmly with both hands or use
a push stick.
MAINTENANCE
Remove the plug from the socket before carrying out any
adjustment, servicing or maintenance. Keep tools sharp and
clean for better and safer performane. Inspect tool cords
periodically and if damaged, have repaired by an authorized
service facility. Your power tool requires no additional
lubrication or maintenance. There are no user serviceable
parts in your power tool. Never use water or chemical cleaners
to clean your power tool. Wipe clean with a dry cloth. Always
store your power tool in a dry place. Keep the motor ventilation
slots clean. Keep all working controls free of dust. If you see
some sparks flashing in the ventilation slots, this is normal and
will not damage your power tool. If the supply cord is damaged,
it must be replaced by the manufacturer, its service agent or
similarly qualified persons in order to avoid a hazard.
Bevel cuts (Fig R)
Bevel cuts must always be made using the rip fence (5).
- Set the blade (4) to the desired angle.
- Proceed as for cross cutting
Cutting particle boards
To prevent the cutting edges from cracking when working with
particle boards, the saw blade must be higher than the
workpiece height.
Auxiliary tools stored (Fig S,T)
Auxiliary tools can be stored on the machine Miter gauge (6)
could be put on hook as Fig S showed. Blade guard (2) and
push stick (19) could be put on hook as Fig T showed.
R
621a 21b4
Cutting particle boards
To prevent the cutting edges from cracking when working with
particle boards, the saw blade must be higher than the
workpiece height.
Auxiliary tools stored (Fig S,T)
Auxiliary tools can be stored on the machine Miter gauge (6)
could be put on hook as Fig S showed. Blade guard (2) and
push stick (19) could be put on hook as Fig T showed.
Caution: (Fig Q)
- Always use the push stick (19) when ripping small
workpieces (fig. Q)
- Do not cut excessively small workpieces.
Cross Cutting
- Lock the miter gauge (6) at 0 degree
- Set the bevel angle to 0 degree
- Adjust the saw blade (4) height
- Hold the workpiece flat on the table (1) and against the
fence. Keep the workpiece away from the blade.
- Keep both hands away from the path of the saw blade.
- Switch the machine on and allow the saw blade to reach
full speed.
- Hold the workpiece tightly again the fence and slowly
move the workpiece together with the fence assembly until
the workpiece comes underneath the upper blade guard.
Allow the teeth to cut, and do not force the workpiece
through the saw blade. The saw blade speed should be
kept constant.
After completing the cut, switch the machine off, allow the saw
blade to stop and remove the workpiece
- Push the and the workpiece toward the blade in order to
make the cut.
Important: Never push or hold the cut-off-side
workpiece.
Cross stop (Fig O)
- Push the miter gauge (6) into a slot (21 a/b) on the saw
table.
- Loosen the locking handle (n).
- Rotate the miter gauge (6) until the required angle is set.
The scale (p) shows the set angle.
- Re-tighten the locking handle (n)
USE
Working instructions
After each new adjustment it is advisable to carry out a trial in
order to check the set dimensions. After switching on the saw,
wait for the blade to reach its maximum speed of rotation
before commencing with the cut.
Secure long workpiece against falling off at the end of the cut
(e.g. with a roller stand etc.) Take extra care when starting the
cut! Never use the equipment without the suction function.
Regularly check and clean the suction channels.
Making longitudinal cuts (Fig P)
Longitudinal cutting (also known as slitting) is when you use
the saw to cut along the grain of the wood. Press one edge of
the workpiece against the parallel stop (5)” to be replaced to
“rip fence (5) while the flat side on the saw table (1).
The blade guard (2) must always be lowered over the
workpiece. When you make a longitudinal cut, never adopt a
working position that is in line with cutting direction.
- Set the in accordance with the workpiece height and the
desired width.
- Switch on the saw.
- Place your hands (with fingers closed) flat on the
workpiece and push the workpiece along the and into the
blade (4).
- Guide at the side with your left or right hand (depending
on the position) only as far as the front edge of the saw
blade guard (2).
- Always push the workpiece through to the end of the riving
knife (3)
- The offcut piece remains on the saw table (4) until the
blade (4) is back in its position of rest.
- Secure long workpiece against falling off at the end of the
cut ) with a roller stand etc.
6 21an
p
O
P
5 2 4
3
1
19
Q
Blade jamming handling (Fig U)
- Ensure the machine is disconnected from the power
source.
- Remove the wookpiece at first. Warning: Be careful of
your hands not toughing the saw blade.
- Press the overloaded protector (22) and connect the plug
again, the machine can be resumed to work. (Fig. U)
Applications
1. Make sure the kerf is made on the scrap side of the
measuring line.
2. Cut the wood with the finished side up.
3. Always have a proper support for the wood as it comes
out of the blade.
4. Make a test cut for important cuts.
5. Always use the correct blade depth setting. The top of the
blade teeth should clear the top of the material being cut
by 1⁄8” (3 mm) to 1⁄4” (6 mm).
6. Inspect the work-piece for knots or nails before beginning
a cut. Remove any loose knots with a hammer.
7. Always use clean, sharp, properly-set blades. Never make
a cut with a dull blade.
8. When making a cut, use steady, even pressure. Never
force a cut.
9. DO NOT cut wet or warped lumber.
10. Always hold your work-piece firmly with both hands or use
a push stick.
MAINTENANCE
Remove the plug from the socket before carrying out any
adjustment, servicing or maintenance. Keep tools sharp and
clean for better and safer performane. Inspect tool cords
periodically and if damaged, have repaired by an authorized
service facility. Your power tool requires no additional
lubrication or maintenance. There are no user serviceable
parts in your power tool. Never use water or chemical cleaners
to clean your power tool. Wipe clean with a dry cloth. Always
store your power tool in a dry place. Keep the motor ventilation
slots clean. Keep all working controls free of dust. If you see
some sparks flashing in the ventilation slots, this is normal and
will not damage your power tool. If the supply cord is damaged,
it must be replaced by the manufacturer, its service agent or
similarly qualified persons in order to avoid a hazard.
Bevel cuts (Fig R)
Bevel cuts must always be made using the rip fence (5).
- Set the blade (4) to the desired angle.
- Proceed as for cross cutting
Cutting particle boards
To prevent the cutting edges from cracking when working with
particle boards, the saw blade must be higher than the
workpiece height.
Auxiliary tools stored (Fig S,T)
Auxiliary tools can be stored on the machine Miter gauge (6)
could be put on hook as Fig S showed. Blade guard (2) and
push stick (19) could be put on hook as Fig T showed.
R
621a 21b4
6
S
2
19
T
Blade jamming handling (Fig U)
- Ensure the machine is disconnected from the power
source.
- Remove the wookpiece at first. Warning: Be careful of
your hands not toughing the saw blade.
- Press the overloaded protector (22) and connect the plug
again, the machine can be resumed to work. (Fig. U)
Caution: (Fig Q)
- Always use the push stick (19) when ripping small
workpieces (fig. Q)
- Do not cut excessively small workpieces.
Cross Cutting
- Lock the miter gauge (6) at 0 degree
- Set the bevel angle to 0 degree
- Adjust the saw blade (4) height
- Hold the workpiece flat on the table (1) and against the
fence. Keep the workpiece away from the blade.
- Keep both hands away from the path of the saw blade.
- Switch the machine on and allow the saw blade to reach
full speed.
- Hold the workpiece tightly again the fence and slowly
move the workpiece together with the fence assembly until
the workpiece comes underneath the upper blade guard.
Allow the teeth to cut, and do not force the workpiece
through the saw blade. The saw blade speed should be
kept constant.
After completing the cut, switch the machine off, allow the saw
blade to stop and remove the workpiece
- Push the and the workpiece toward the blade in order to
make the cut.
Important: Never push or hold the cut-off-side
workpiece.
Cross stop (Fig O)
- Push the miter gauge (6) into a slot (21 a/b) on the saw
table.
- Loosen the locking handle (n).
- Rotate the miter gauge (6) until the required angle is set.
The scale (p) shows the set angle.
- Re-tighten the locking handle (n)
USE
Working instructions
After each new adjustment it is advisable to carry out a trial in
order to check the set dimensions. After switching on the saw,
wait for the blade to reach its maximum speed of rotation
before commencing with the cut.
Secure long workpiece against falling off at the end of the cut
(e.g. with a roller stand etc.) Take extra care when starting the
cut! Never use the equipment without the suction function.
Regularly check and clean the suction channels.
Making longitudinal cuts (Fig P)
Longitudinal cutting (also known as slitting) is when you use
the saw to cut along the grain of the wood. Press one edge of
the workpiece against the parallel stop (5)” to be replaced to
“rip fence (5) while the flat side on the saw table (1).
The blade guard (2) must always be lowered over the
workpiece. When you make a longitudinal cut, never adopt a
working position that is in line with cutting direction.
- Set the in accordance with the workpiece height and the
desired width.
- Switch on the saw.
- Place your hands (with fingers closed) flat on the
workpiece and push the workpiece along the and into the
blade (4).
- Guide at the side with your left or right hand (depending
on the position) only as far as the front edge of the saw
blade guard (2).
- Always push the workpiece through to the end of the riving
knife (3)
- The offcut piece remains on the saw table (4) until the
blade (4) is back in its position of rest.
- Secure long workpiece against falling off at the end of the
cut ) with a roller stand etc.
6 21an
p
O
P
5 2 4
3
1
19
Q
Blade jamming handling (Fig U)
- Ensure the machine is disconnected from the power
source.
- Remove the wookpiece at first. Warning: Be careful of
your hands not toughing the saw blade.
- Press the overloaded protector (22) and connect the plug
again, the machine can be resumed to work. (Fig. U)
Applications
1. Make sure the kerf is made on the scrap side of the
measuring line.
2. Cut the wood with the finished side up.
3. Always have a proper support for the wood as it comes
out of the blade.
4. Make a test cut for important cuts.
5. Always use the correct blade depth setting. The top of the
blade teeth should clear the top of the material being cut
by 1⁄8” (3 mm) to 1⁄4” (6 mm).
6. Inspect the work-piece for knots or nails before beginning
a cut. Remove any loose knots with a hammer.
7. Always use clean, sharp, properly-set blades. Never make
a cut with a dull blade.
8. When making a cut, use steady, even pressure. Never
force a cut.
9. DO NOT cut wet or warped lumber.
10. Always hold your work-piece firmly with both hands or use
a push stick.
MAINTENANCE
Remove the plug from the socket before carrying out any
adjustment, servicing or maintenance. Keep tools sharp and
clean for better and safer performane. Inspect tool cords
periodically and if damaged, have repaired by an authorized
service facility. Your power tool requires no additional
lubrication or maintenance. There are no user serviceable
parts in your power tool. Never use water or chemical cleaners
to clean your power tool. Wipe clean with a dry cloth. Always
store your power tool in a dry place. Keep the motor ventilation
slots clean. Keep all working controls free of dust. If you see
some sparks flashing in the ventilation slots, this is normal and
will not damage your power tool. If the supply cord is damaged,
it must be replaced by the manufacturer, its service agent or
similarly qualified persons in order to avoid a hazard.
Bevel cuts (Fig R)
Bevel cuts must always be made using the rip fence (5).
- Set the blade (4) to the desired angle.
- Proceed as for cross cutting
Cutting particle boards
To prevent the cutting edges from cracking when working with
particle boards, the saw blade must be higher than the
workpiece height.
Auxiliary tools stored (Fig S,T)
Auxiliary tools can be stored on the machine Miter gauge (6)
could be put on hook as Fig S showed. Blade guard (2) and
push stick (19) could be put on hook as Fig T showed.
R
621a 21b4
6
S
2
19
T
22
U
Applications
1. Make sure the kerf is made on the scrap side of the
measuring line.
2. Cut the wood with the finished side up.
3. Always have a proper support for the wood as it comes
out of the blade.
4. Make a test cut for important cuts.
5. Always use the correct blade depth setting. The top of the
blade teeth should clear the top of the material being cut
by 1⁄8” (3 mm) to 1⁄4” (6 mm).
6. Inspect the work-piece for knots or nails before beginning
a cut. Remove any loose knots with a hammer.
7. Always use clean, sharp, properly-set blades. Never
make a cut with a dull blade.
8. When making a cut, use steady, even pressure. Never
force a cut.
9. DO NOT cut wet or warped lumber.
10. Always hold your work-piece firmly with both hands or
use a push stick.
MAINTENANCE
Remove the plug from the socket before carrying out any
adjustment, servicing or maintenance. Keep tools sharp and
clean for better and safer performane. Inspect tool cords
periodically and if damaged, have repaired by an authorized
service facility. Your power tool requires no additional lubrication
or maintenance. There are no user serviceable parts in your
power tool. Never use water or chemical cleaners to clean your
power tool. Wipe clean with a dry cloth. Always store your power
tool in a dry place. Keep the motor ventilation slots clean. Keep
all working controls free of dust. If you see some sparks flashing
in the ventilation slots, this is normal and will not damage your
power tool. If the supply cord is damaged, it must be replaced by
the manufacturer, its service agent or similarly qualified persons
in order to avoid a hazard.
13
ENGLISH
 Loading...
Loading...