NEVER exceed the rated wattage capacity of your generator.
OVERLOADING may cause SERIOUS DAMAGE to the generator and
attached electrical devices, and may result in fire.
Your generator MUST BE SIZED PROPERLY to provide both the running and starting
wattage of the devices you will be powering. Before using your generator, determine the
running and starting wattage requirements of all the electrical devices you will be powering
simultaneously.
The sum of the running and starting wattages of the devices being powered must not exceed the
continuous output rating of your generator. (The continuous output rating of your generator is
listed in the “Specifications” section of this manual.) Note that:
• Devices without electric motors such as light bulbs, radios, and televisions have the
same running and starting wattage.
• Devices with electric motors such as refrigerators, compressors, and hand tools
typically require a starting wattage that is 3 to 5 times greater than the running
wattage.
The running and starting wattage requirements are often listed on a device’s nameplate. If
wattage is not given on the device’s nameplate, the wattage may be calculated by multiplying
the nameplate voltage by nameplate amperage, Watts = Volts X Amps.
Example conversion to watts:
240VoltsX5Amps=1200Watts
If only the running voltage is given on the nameplate for a device with an electric motor, the
starting wattage can be approximated to be three to five times the running wattage.
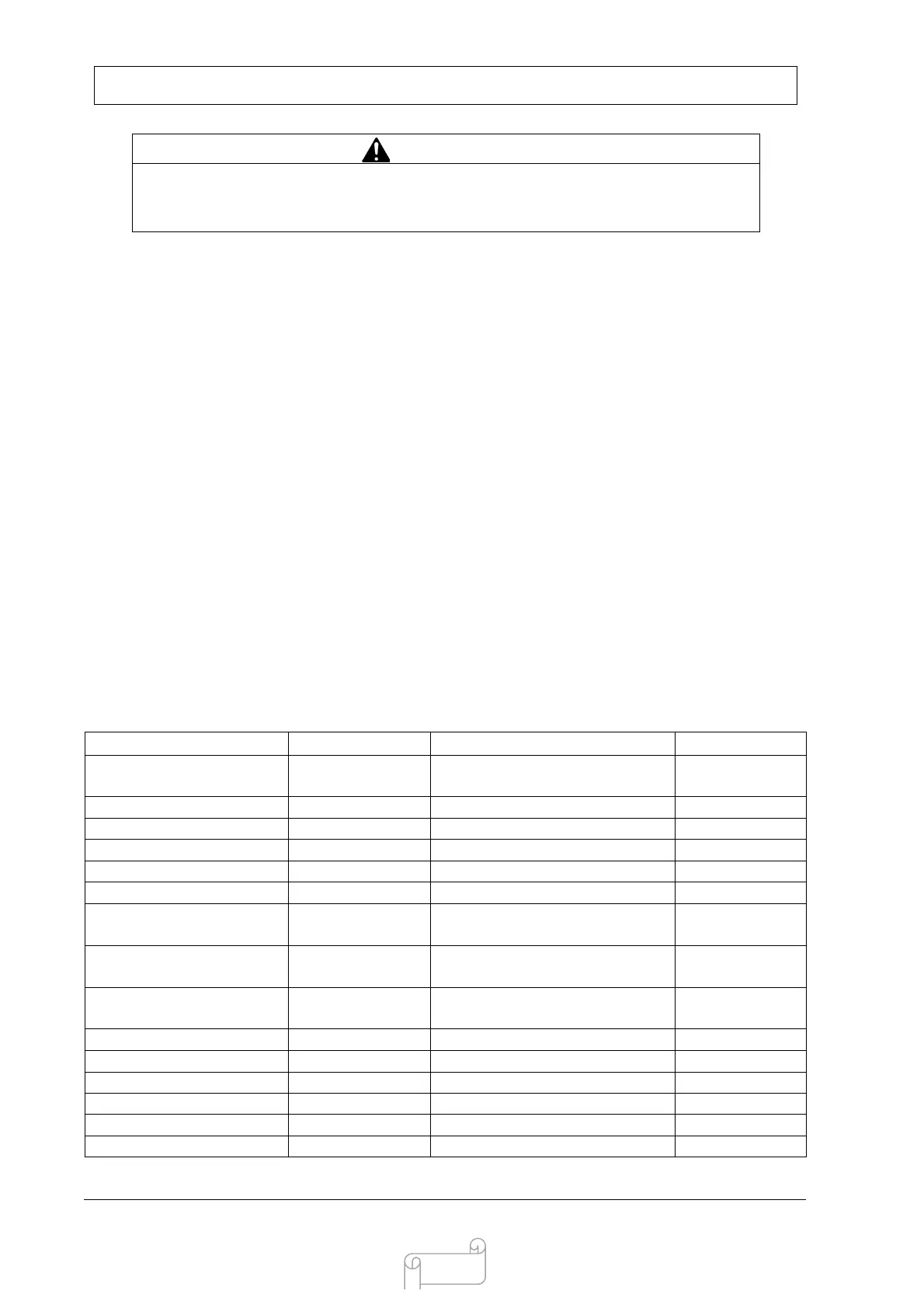
Estimates for the running wattage requirements for common devices are listed in Table 1
below.
Guidance for starting wattages is provided in the table’s footnotes.
Table 1 Typical Device Power Requirements( Guide Only)
 Loading...
Loading...